Gut-liver axis in liver cirrhosis: How to manage leaky gut and endotoxemia
- PMID: 25848468
- PMCID: PMC4381167
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i3.425
Gut-liver axis in liver cirrhosis: How to manage leaky gut and endotoxemia
Abstract
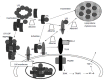
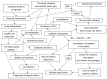
A "leaky gut" may be the cutting edge for the passage of toxins, antigens or bacteria into the body, and may play a pathogenic role in advanced liver cirrhosis and its complications. Plasma endotoxin levels have been admitted as a surrogate marker of bacterial translocation and close relations of endotoxemia to hyperdynamic circulation, portal hypertension, renal, cardiac, pulmonary and coagulation disturbances have been reported. Bacterial overgrowth, increased intestinal permeability, failure to inactivate endotoxin, activated innate immunity are all likely to play a role in the pathological states of bacterial translocation. Therapeutic approach by management of the gut-liver axis by antibiotics, probiotics, synbiotics, prebiotics and their combinations may improve the clinical course of cirrhotic patients. Special concern should be paid on anti-endotoxin treatment. Adequate management of the gut-liver axis may be effective for prevention of liver cirrhosis itself by inhibiting the progression of fibrosis.
Keywords: Bacterial translocation; Complications; Endotoxemia; Gut-liver axis; Leaky gut; Liver cirrhosis; Pathogenesis; Probiotics; Selective intestinal decontamination; Toll-like receptors.
Figures
References
-
- Tandon P, Garcia-Tsao G. Bacterial infections, sepsis, and multiorgan failure in cirrhosis. Semin Liver Dis. 2008;28:26–42. - PubMed
-
- Arvaniti V, D’Amico G, Fede G, Manousou P, Tsochatzis E, Pleguezuelo M, Burroughs AK. Infections in patients with cirrhosis increase mortality four-fold and should be used in determining prognosis. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:1246–1256, 1256e1-e5. - PubMed
-
- Campillo B, Richardet JP, Kheo T, Dupeyron C. Nosocomial spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and bacteremia in cirrhotic patients: impact of isolate type on prognosis and characteristics of infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;35:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Bellot P, Francés R, Such J. Pathological bacterial translocation in cirrhosis: pathophysiology, diagnosis and clinical implications. Liver Int. 2013;33:31–39. - PubMed
-
- Prytz H, Holst-Christensen J, Korner B, Liehr H. Portal venous and systemic endotoxaemia in patients without liver disease and systemic endotoxaemia in patients with cirrhosis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1976;11:857–863. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

