Creating a connected community: lessons learned from the Western new york beacon community
- PMID: 25848618
- PMCID: PMC4371445
Creating a connected community: lessons learned from the Western new york beacon community
Abstract
Introduction: Secure exchange of clinical data among providers has the potential to improve quality, safety, efficiency, and reduce duplication. Many communities are experiencing challenges in building effective health information exchanges (HIEs). Previous studies have focused on financial and technical issues regarding HIE development. This paper describes the Western New York (WNY) HIE growth and lessons learned about accelerating progress to become a highly connected community.
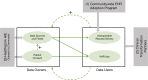
Methods: HEALTHeLINK, with funding from the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) under the Beacon Community Program, expanded HIE usage in eight counties. The communitywide transformation process used three main drivers: (1) a communitywide Electronic Health Record (EHR) adoption program; (2) clinical transformation partners; and (3) HIE outreach and infrastructure development.
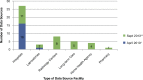
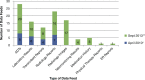
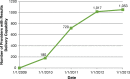
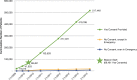
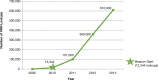
Results: ONC Beacon Community funding allowed WNY to achieve a new level in the use of interoperable HIE. Electronic delivery of results into the EHR expanded from 23 practices in 2010 to 222 practices in 2013, a tenfold increase. There were more than 12.5 million results delivered electronically (HL7 messages) to 222 practices' EHRs via the HIE in 2013. Use of a secure portal and Virtual Health Record (VHR) to access reports (those not delivered directly to the EHR) also increased significantly, from 13,344 report views in 2010 to over 600,000 in 2013.
Discussion and conclusion: The WNY Beacon successfully expanded the sharing of clinical information among different sources of data and providers, creating a highly connected community to improve the quality and continuity of care. Technical, organizational, and community lessons described in this paper should prove beneficial to others as they pursue efforts to create connected communities.
Figures
References
-
- Gold MR, McLaughlin CG, Berenson RA, Bovbjerg RR. Obtaining providers “buy-in” and establishing effective means of information exchange will be critical to HITECH’s success. Health Aff (Millwood) 2012 Mar;31(3):514–26. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
