Biallelic mutations in SNX14 cause a syndromic form of cerebellar atrophy and lysosome-autophagosome dysfunction
- PMID: 25848753
- PMCID: PMC4414867
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3256
Biallelic mutations in SNX14 cause a syndromic form of cerebellar atrophy and lysosome-autophagosome dysfunction
Abstract
Pediatric-onset ataxias often present clinically as developmental delay and intellectual disability, with prominent cerebellar atrophy as a key neuroradiographic finding. Here we describe a new clinically distinguishable recessive syndrome in 12 families with cerebellar atrophy together with ataxia, coarsened facial features and intellectual disability, due to truncating mutations in the sorting nexin gene SNX14, encoding a ubiquitously expressed modular PX domain-containing sorting factor. We found SNX14 localized to lysosomes and associated with phosphatidylinositol (3,5)-bisphosphate, a key component of late endosomes/lysosomes. Patient-derived cells showed engorged lysosomes and a slower autophagosome clearance rate upon autophagy induction by starvation. Zebrafish morphants for snx14 showed dramatic loss of cerebellar parenchyma, accumulation of autophagosomes and activation of apoptosis. Our results characterize a unique ataxia syndrome due to biallelic SNX14 mutations leading to lysosome-autophagosome dysfunction.
Figures

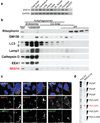
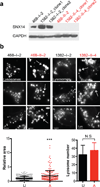
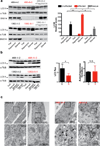
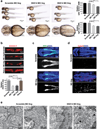
References
METHODS-ONLY REFERENCES
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U54 HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 NS089859/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS048453/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K99NS089859-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS048453/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG006504/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG006504/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS052455/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD070494/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P01HD070494/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

