High-throughput deep sequencing reveals that microRNAs play important roles in salt tolerance of euhalophyte Salicornia europaea
- PMID: 25848810
- PMCID: PMC4349674
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-015-0451-3
High-throughput deep sequencing reveals that microRNAs play important roles in salt tolerance of euhalophyte Salicornia europaea
Abstract
Background: microRNAs (miRNAs) are implicated in plant development processes and play pivotal roles in plant adaptation to environmental stresses. Salicornia europaea, a salt mash euhalophyte, is a suitable model plant to study salt adaptation mechanisms. S. europaea is also a vegetable, forage, and oilseed that can be used for saline land reclamation and biofuel precursor production on marginal lands. Despite its importance, no miRNA has been identified from S. europaea thus far.
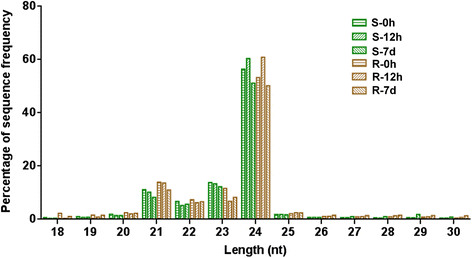
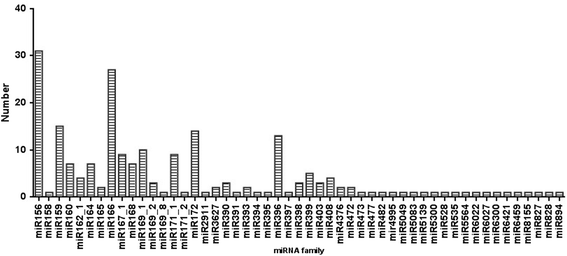
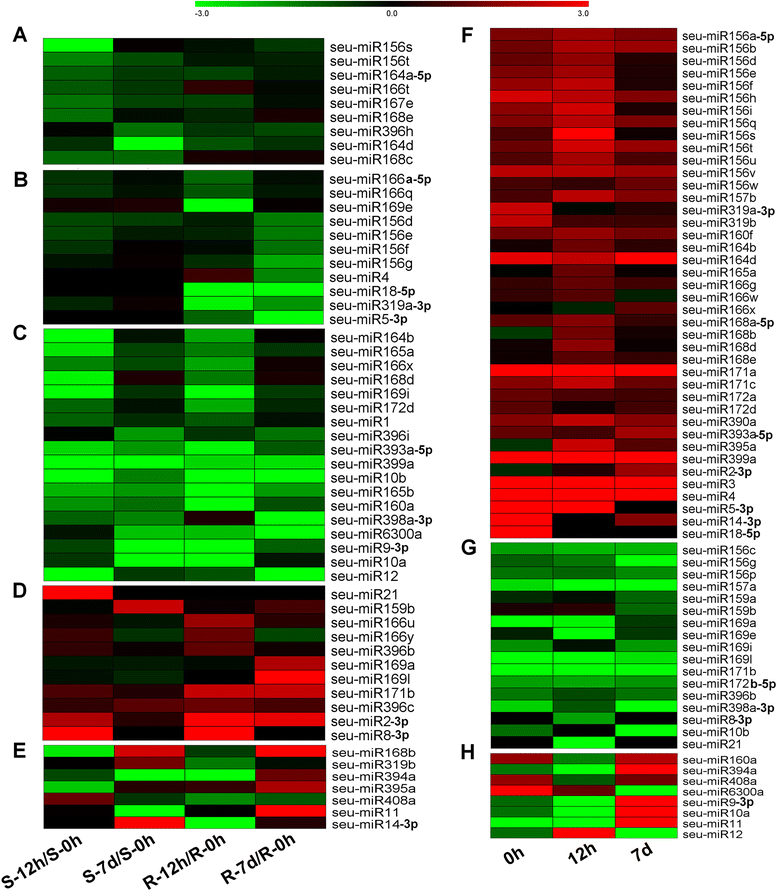
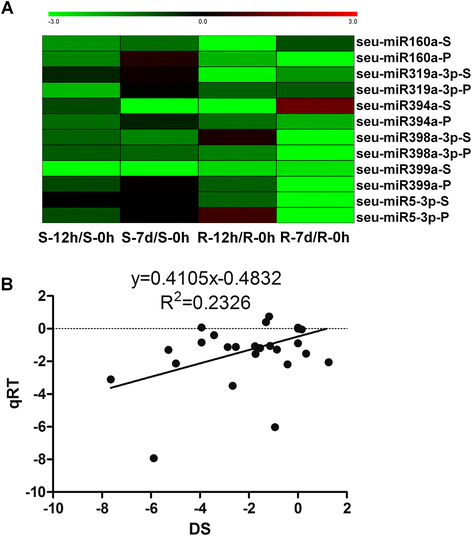
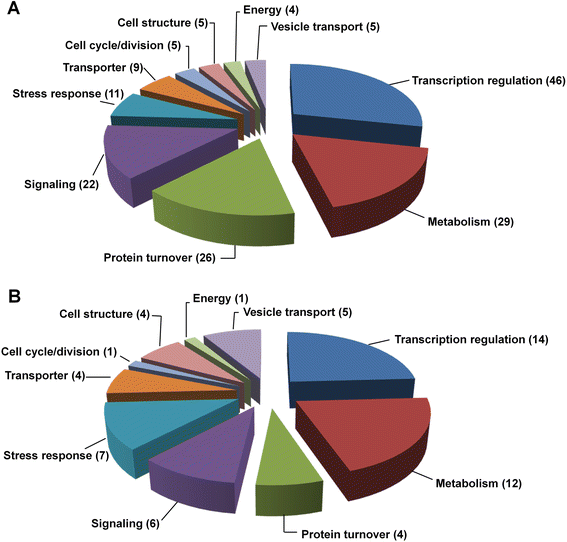
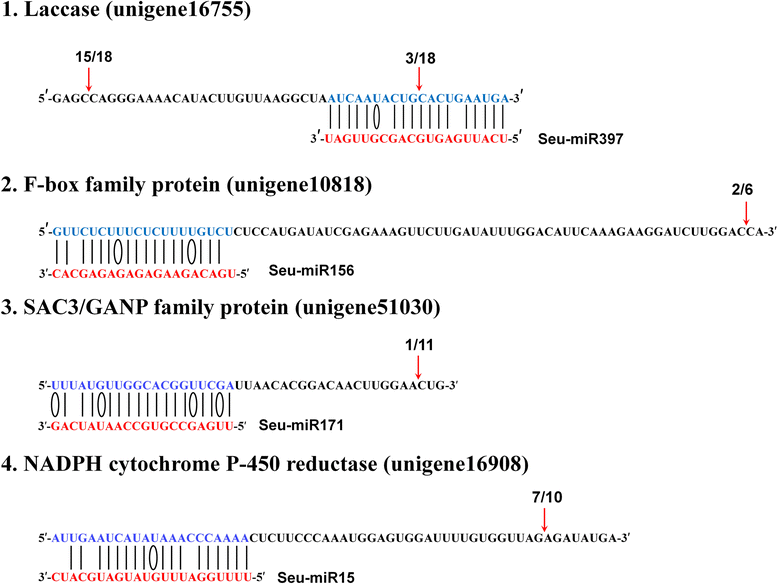
Results: Deep sequencing was performed to investigate small RNA transcriptome of S. europaea. Two hundred and ten conserved miRNAs comprising 51 families and 31 novel miRNAs (including seven miRNA star sequences) belonging to 30 families were identified. About half (13 out of 31) of the novel miRNAs were only detected in salt-treated samples. The expression of 43 conserved and 13 novel miRNAs significantly changed in response to salinity. In addition, 53 conserved and 13 novel miRNAs were differentially expressed between the shoots and roots. Furthermore, 306 and 195 S. europaea unigenes were predicted to be targets of 41 conserved and 29 novel miRNA families, respectively. These targets encoded a wide range of proteins, and genes involved in transcription regulation constituted the largest category. Four of these genes encoding laccase, F-box family protein, SAC3/GANP family protein, and NADPH cytochrome P-450 reductase were validated using 5'-RACE.
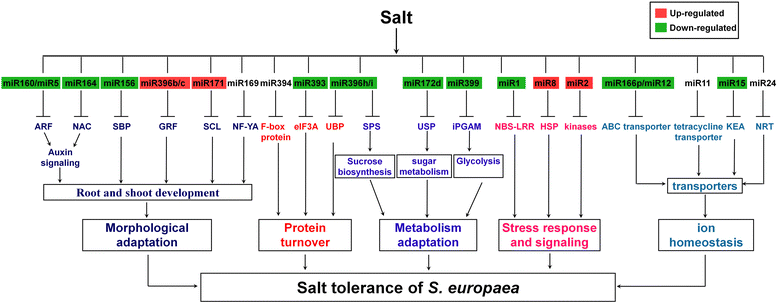
Conclusions: Our results indicate that specific miRNAs are tightly regulated by salinity in the shoots and/or roots of S. europaea, which may play important roles in salt tolerance of this euhalophyte. The S. europaea salt-responsive miRNAs and miRNAs that target transcription factors, nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat proteins and enzymes involved in lignin biosynthesis as well as carbon and nitrogen metabolism may be applied in genetic engineering of crops with high stress tolerance, and genetic modification of biofuel crops with high biomass and regulatable lignin biosynthesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High-throughput sequencing of small RNA transcriptome reveals salt stress regulated microRNAs in sugarcane.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59423. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059423. Epub 2013 Mar 27. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23544066 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of Salicornia europaea under saline conditions revealed the adaptive primary metabolic pathways as early events to facilitate salt adaptation.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 12;8(11):e80595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080595. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24265831 Free PMC article.
-
Novel and conserved miRNAs in the halophyte Suaeda maritima identified by deep sequencing and computational predictions using the ESTs of two mangrove plants.BMC Plant Biol. 2015 Dec 29;15:301. doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0682-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2015. PMID: 26714456 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the regulation of plant salt-stress tolerance by miRNA.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jun;49(6):5041-5055. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07179-6. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35381964 Review.
-
Regulatory role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in the recent development of abiotic stress tolerance of plants.Gene. 2022 May 5;821:146283. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146283. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Gene. 2022. PMID: 35143944 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of microRNA-target modules of African rice (Oryza glaberrima) under salinity stress.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 12;8(1):570. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18206-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29330361 Free PMC article.
-
Redox Balance-DDR-miRNA Triangle: Relevance in Genome Stability and Stress Responses in Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Aug 2;10:989. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00989. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31428113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment of a gene function analysis system for the euhalophyte Salicornia europaea L.Plant Cell Rep. 2017 Aug;36(8):1251-1261. doi: 10.1007/s00299-017-2150-z. Epub 2017 May 2. Plant Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28466186
-
Learning from Salicornia: Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Mechanisms of Salinity Tolerance.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 20;26(13):5936. doi: 10.3390/ijms26135936. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomics analysis unveils important changes involved in the salt tolerance of Salicornia europaea.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jan 20;13:1097076. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1097076. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36743536 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

