Rapid linkage of innate immunological signals to adaptive immunity by the brain-fat axis
- PMID: 25848866
- PMCID: PMC4564120
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.3133
Rapid linkage of innate immunological signals to adaptive immunity by the brain-fat axis
Abstract
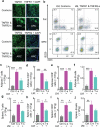
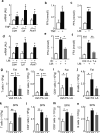
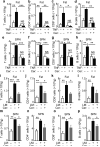
Innate immunological signals induced by pathogen- and/or damage-associated molecular patterns are essential for adaptive immune responses, but it is unclear if the brain has a role in this process. Here we found that while the abundance of tumor-necrosis factor (TNF) quickly increased in the brain of mice following bacterial infection, intra-brain delivery of TNF mimicked bacterial infection to rapidly increase the number of peripheral lymphocytes, especially in the spleen and fat. Studies of various mouse models revealed that hypothalamic responses to TNF were accountable for this increase in peripheral lymphocytes in response to bacterial infection. Finally, we found that hypothalamic induction of lipolysis mediated the brain's action in promoting this increase in the peripheral adaptive immune response. Thus, the brain-fat axis is important for rapid linkage of innate immunity to adaptive immunity.
Figures





Comment in
-
Brainless immunity no more.Nat Immunol. 2015 May;16(5):440-1. doi: 10.1038/ni.3145. Nat Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25898188 No abstract available.
-
Immune regulation: Brain-fat axis in adaptive immunity.Nat Rev Immunol. 2015 May;15(5):267. doi: 10.1038/nri3853. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25907457 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Immune regulation: Brain-fat axis in adaptive immunity.Nat Rev Immunol. 2015 May;15(5):267. doi: 10.1038/nri3853. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25907457 No abstract available.
-
Brainless immunity no more.Nat Immunol. 2015 May;16(5):440-1. doi: 10.1038/ni.3145. Nat Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25898188 No abstract available.
-
Amplifying IFN-γ Signaling in Dendritic Cells by CD11c-Specific Loss of SOCS1 Increases Innate Immunity to Infection while Decreasing Adaptive Immunity.J Immunol. 2018 Jan 1;200(1):177-185. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700909. Epub 2017 Nov 17. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29150567 Free PMC article.
-
A knockout approach to understanding CD8+ cell effector mechanisms in adaptive immunity to Listeria monocytogenes.Immunobiology. 1999 Dec;201(2):196-204. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(99)80059-X. Immunobiology. 1999. PMID: 10631568 Review.
-
The Regulation of Inflammation by Innate and Adaptive Lymphocytes.J Immunol Res. 2018 Jun 11;2018:1467538. doi: 10.1155/2018/1467538. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 29992170 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune regulation: Brain-fat axis in adaptive immunity.Nat Rev Immunol. 2015 May;15(5):267. doi: 10.1038/nri3853. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25907457 No abstract available.
-
Hypothalamic Menin regulates systemic aging and cognitive decline.PLoS Biol. 2023 Mar 16;21(3):e3002033. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002033. eCollection 2023 Mar. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 36928253 Free PMC article.
-
An in vivo brain-bacteria interface: the developing brain as a key regulator of innate immunity.NPJ Regen Med. 2020 Feb 4;5:2. doi: 10.1038/s41536-020-0087-2. eCollection 2020. NPJ Regen Med. 2020. PMID: 32047653 Free PMC article.
-
Reversal of prolonged obesity-associated cerebrovascular dysfunction by inhibiting microglial Tak1.Nat Neurosci. 2020 Jul;23(7):832-841. doi: 10.1038/s41593-020-0642-6. Epub 2020 May 25. Nat Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32451485
-
Ketogenic diet uncovers differential metabolic plasticity of brain cells.Sci Adv. 2022 Sep 16;8(37):eabo7639. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abo7639. Epub 2022 Sep 16. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36112685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beutler B. Innate immunity: an overview. Mol. Immunol. 2004;40:845–859. - PubMed
-
- Janeway CA, Jr., Medzhitov R. Innate immune recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002;20:197–216. - PubMed
-
- Rubartelli A, Lotze MT. Inside, outside, upside down: damage-associated molecular-pattern molecules (DAMPs) and redox. Trends. Immunol. 2007;28:429–436. - PubMed
-
- Hoebe K, Janssen E, Beutler B. The interface between innate and adaptive immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2004;5:971–974. - PubMed
-
- Kabelitz D, Medzhitov R. Innate immunity--cross-talk with adaptive immunity through pattern recognition receptors and cytokines. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2007;19:1–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

