Lobular breast cancer: incidence and genetic and non-genetic risk factors
- PMID: 25848941
- PMCID: PMC4357148
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-015-0546-7
Lobular breast cancer: incidence and genetic and non-genetic risk factors
Abstract
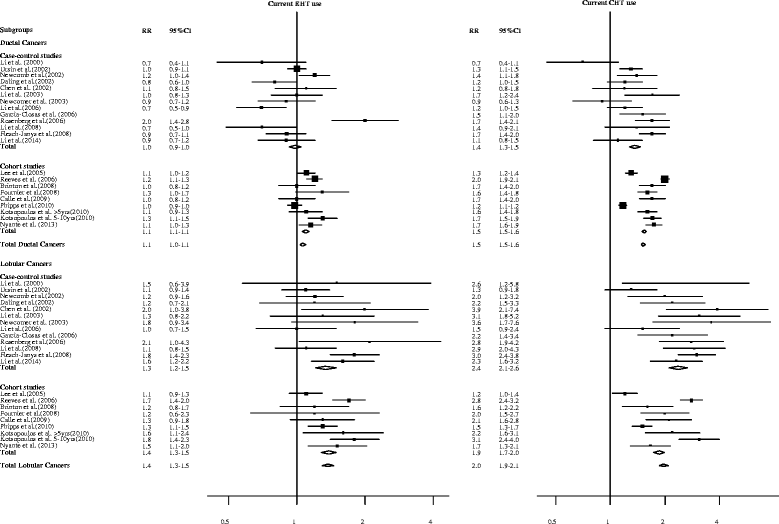
While most invasive breast cancers consist of carcinomas of the ductal type, about 10% are invasive lobular carcinomas. Invasive lobular and ductal carcinomas differ with respect to risk factors. Invasive lobular carcinoma is more strongly associated with exposure to female hormones, and therefore its incidence is more subject to variation. This is illustrated by US figures during the 1987 to 2004 period: after 12 years of increases, breast cancer incidence declined steadily from 1999 to 2004, reflecting among other causes the decreasing use of menopausal hormone therapy, and these variations were stronger for invasive lobular than for invasive ductal carcinoma. Similarly, invasive lobular carcinoma is more strongly associated with early menarche, late menopause and late age at first birth. As for genetic risk factors, four high-penetrance genes are tested in clinical practice when genetic susceptibility to breast cancer is suspected, BRCA1, BRCA2, TP53 and CDH1. Germline mutations in BRCA1 and TP53 are predominantly associated with invasive ductal carcinoma, while BRCA2 mutations are associated with both ductal and lobular cancers. CDH1, the gene coding for the E-cadherin adhesion protein, is of special interest as mutations are associated with invasive lobular carcinoma, but never with ductal carcinoma. It was initially known as the main susceptibility gene for gastric cancer of the diffuse type, but the excess of breast cancers of the lobular type in CDH1 families led researchers to identify it also as a susceptibility gene for invasive lobular carcinoma. The risk of invasive lobular carcinoma is high in female mutation carriers, as about 50% are expected to develop the disease. Carriers must therefore undergo intensive breast cancer screening, with, for example, yearly magnetic resonance imaging and mammogram starting at age 30 years.
Figures
References
-
- Rossouw JE, Anderson GL, Prentice RL, LaCroix AZ, Kooperberg C, Stefanick ML, et al. Risks and benefits of estrogen plus progestin in healthy postmenopausal women: principal results from the Women's Health Initiative randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2002;288:321–33. doi: 10.1001/jama.288.3.321. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous