Florbetapir PET, FDG PET, and MRI in Down syndrome individuals with and without Alzheimer's dementia
- PMID: 25849033
- PMCID: PMC4543530
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2015.01.006
Florbetapir PET, FDG PET, and MRI in Down syndrome individuals with and without Alzheimer's dementia
Abstract
Introduction: Down syndrome (DS) is associated with amyloid b (Ab) deposition.
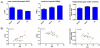
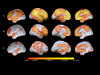
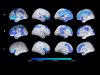
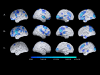
Methods: We characterized imaging measurements of regional fibrillar Ab burden, cerebral metabolic rate for glucose (rCMRgl), gray matter volumes (rGMVs), and age associations in 5 DS with dementia (DS/AD1), 12 DS without dementia (DS/AD2), and 9 normal controls (NCs).
Results: There were significant group differences in mean standard uptake value ratios (SUVRs) for florbetapir with DS/AD1 having the highest, followed by DS/AD2, followed by NC. For [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography, posterior cingulate rCMRgl in DS/AD1 was significantly reduced compared with DS/AD2 and NC. For volumetric magnetic resonance imaging (vMRI), hippocampal volumes were significantly reduced for the DS/AD1 compared with DS/AD2 and NC. Age-related SUVR increases and rCMRgl reductions were greater in DS participants than in NCs.
Discussion: DS is associated with fibrillar Ab, rCMRgl, and rGMV alterations in the dementia stage and before the presence of clinical decline. This study provides a foundation for the studies needed to inform treatment and prevention in DS.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Dementia; Down syndrome; FDG-PET; Florbetapir; Imaging; PET.
Copyright © 2015 The Alzheimer's Association. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Davidson MA. Primary care for children and adolescents with down syndrome. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2008;55:1099–1111. - PubMed
-
- Mann DM, Esiri MM. The pattern of acquisition of plaques and tangles in the brains of participants under 50 years of age with down's syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 1989;89:169–179. - PubMed
-
- Wisniewski KE, Dalton AJ, McLachlan C, Wen GY, Wisniewski HM. Alzheimer's disease in down's syndrome: Clinicopathologic studies. Neurology. 1985;35:957–61. - PubMed
-
- Zigman WB, Lott IT. Alzheimer's disease in Down syndrome: neurobiology and risk. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2007;13(3):237–46. - PubMed
-
- Bittles AH, Bower C, Hussain R, Glasson EJ. The four ages of Down syndrome. Eur J Public Health. 2007 Apr;17(2):221–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

