Cigarette smoke inhibits BAFF expression and mucosal immunoglobulin A responses in the lung during influenza virus infection
- PMID: 25849069
- PMCID: PMC4364338
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-015-0201-y
Cigarette smoke inhibits BAFF expression and mucosal immunoglobulin A responses in the lung during influenza virus infection
Abstract
Background: It is incompletely understood how cigarette smoke (CS) exposure affects lung mucosal immune responses during viral respiratory infections. B cell activating factor belonging to the tumor necrosis factor family (BAFF) plays an important role in the induction of secretory immunoglobulin A (S-IgA) which is the main effector of the mucosal immune system. We therefore investigated the effects of CS exposure on BAFF expression and S-IgA responses in the lung during influenza virus infection.
Methods: Mice were exposed to CS and/or infected with influenza virus. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and lung compartments were analyzed for BAFF expression, influenza-specific S-IgA level and histological changes. Lung B cells were isolated and the activation-induced cytidine deaminase (Aicda) expression was determined. BEAS-2B cells were treated with CS extract (CSE), influenza virus, interferon beta or N-acetylcysteine and BAFF expression was measured.
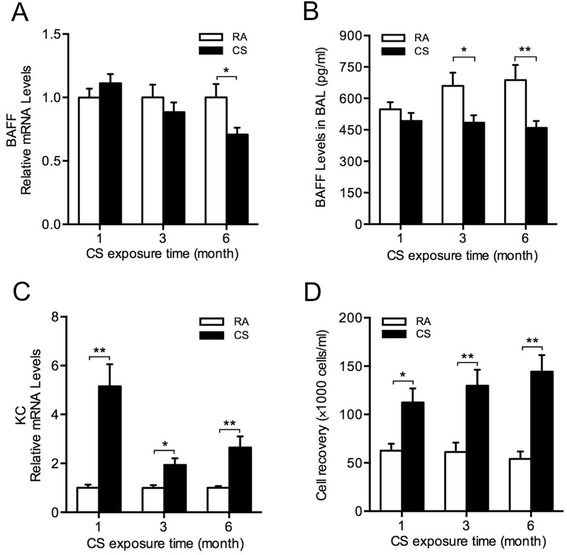
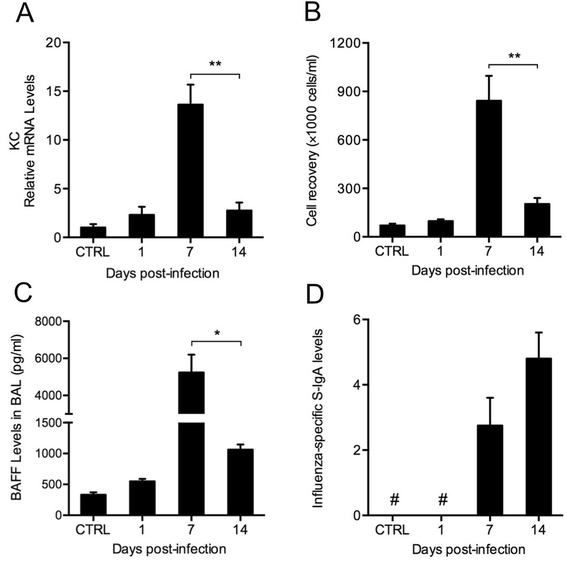
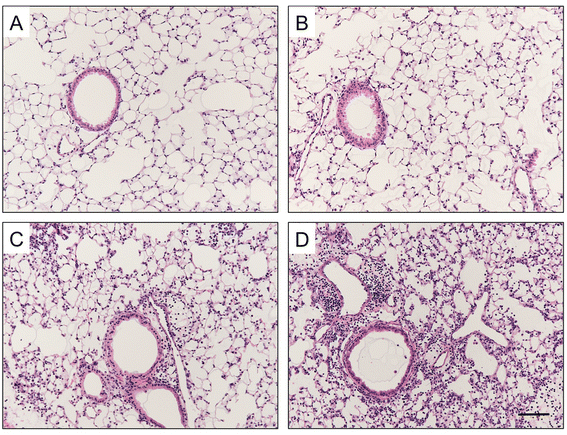
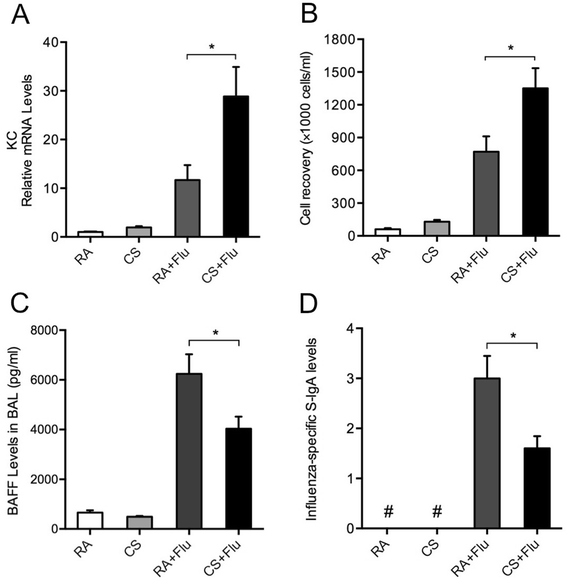
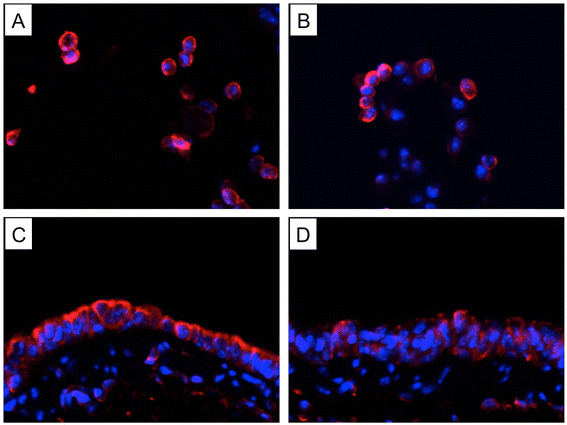
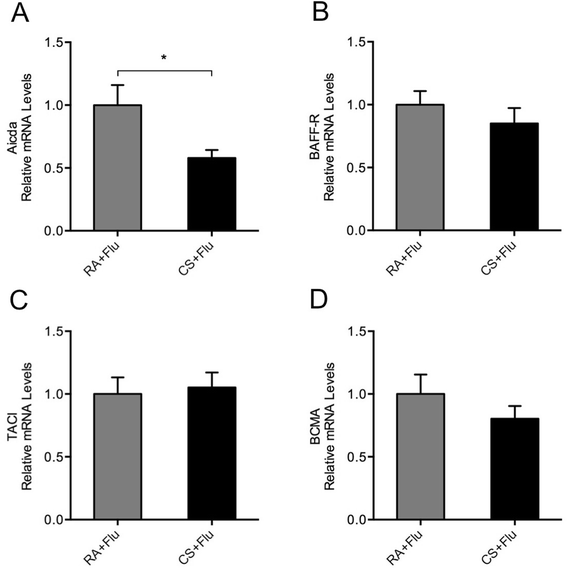
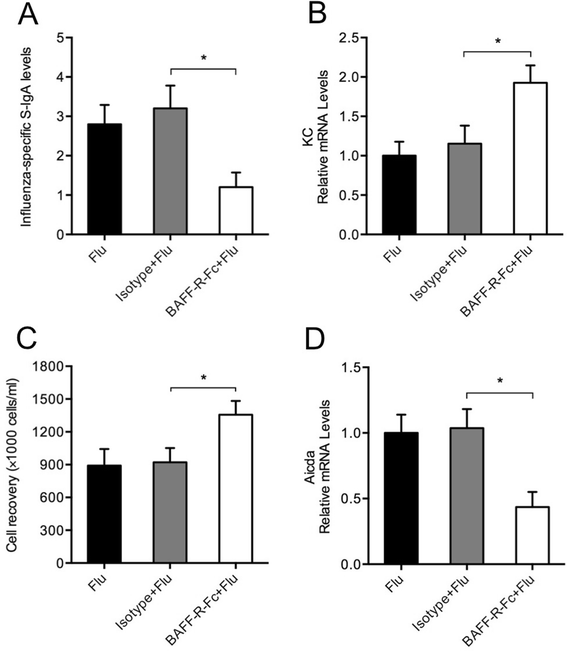
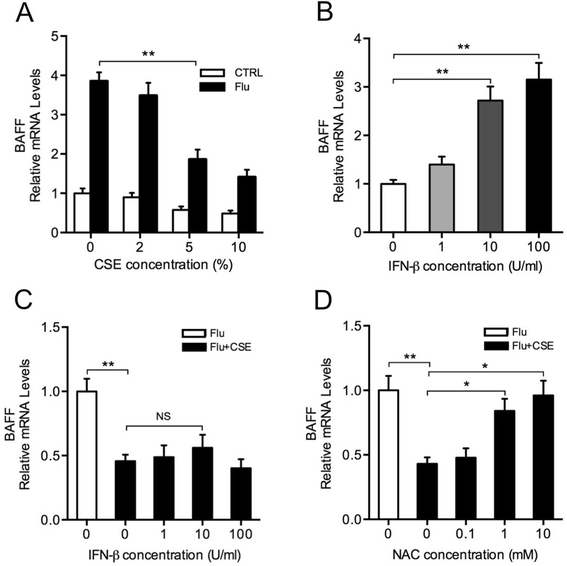
Results: CS inhibited BAFF expression in the lung, particularly after long-term exposure. BAFF and S-IgA levels were increased during influenza virus infection. Three-month CS exposure prior to influenza virus infection resulted in reduced BAFF and S-IgA levels in the lung as well as augmented pulmonary inflammation on day 7 after infection. Prior CS exposure also caused decreased Aicda expression in lung B cells during infection. Neutralization of BAFF in the lung resulted in reduced S-IgA levels during influenza virus infection. CSE inhibited virus-mediated BAFF induction in a dose-dependent manner in BEAS-2B cells, while this inhibition of BAFF by CSE was prevented by pretreatment with the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that CS may hinder early mucosal IgA responses in the lung during influenza virus infection through oxidative inhibition of BAFF, which might contribute to the increased incidence and severity of viral infections in smokers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
B-Cell Activating Factor Secreted by Neutrophils Is a Critical Player in Lung Inflammation to Cigarette Smoke Exposure.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 29;11:1622. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01622. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32849550 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term cigarette smoke exposure dysregulates pulmonary T cell response and IFN-γ protection to influenza virus in mouse.Respir Res. 2021 Apr 20;22(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12931-021-01713-z. Respir Res. 2021. PMID: 33879121 Free PMC article.
-
Oral clarithromycin enhances airway immunoglobulin A (IgA) immunity through induction of IgA class switching recombination and B-cell-activating factor of the tumor necrosis factor family molecule on mucosal dendritic cells in mice infected with influenza A virus.J Virol. 2012 Oct;86(20):10924-34. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01207-12. Epub 2012 Aug 15. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22896605 Free PMC article.
-
Defense mechanisms against influenza virus infection in the respiratory tract mucosa.Jpn J Infect Dis. 2004 Dec;57(6):236-47. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 15623947 Review.
-
Recognition of Viral RNA by Pattern Recognition Receptors in the Induction of Innate Immunity and Excessive Inflammation During Respiratory Viral Infections.Viral Immunol. 2017 Jul/Aug;30(6):408-420. doi: 10.1089/vim.2016.0178. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Viral Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28609250 Review.
Cited by
-
Teleost swim bladder, an ancient air-filled organ that elicits mucosal immune responses.Cell Discov. 2022 Apr 5;8(1):31. doi: 10.1038/s41421-022-00393-3. Cell Discov. 2022. PMID: 35379790 Free PMC article.
-
Differential serum interferon-β levels in autoimmune thyroid diseases.Arch Med Sci. 2021 Jan 31;18(5):1231-1240. doi: 10.5114/aoms/110164. eCollection 2022. Arch Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 36160354 Free PMC article.
-
Circ-RBMS1 Knockdown Alleviates CSE-Induced Apoptosis, Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via Up-Regulating FBXO11 Through miR-197-3p in 16HBE Cells.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021 Jul 16;16:2105-2118. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S311222. eCollection 2021. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021. PMID: 34295155 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 versus Influenza A Virus: Characteristics and Co-Treatments.Microorganisms. 2023 Feb 24;11(3):580. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11030580. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36985154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Sequencing of H3N2 Influenza Virus-Infected Human Nasal Epithelial Cells from Multiple Subjects Reveals Molecular Pathways Associated with Tissue Injury and Complications.Cells. 2019 Aug 27;8(9):986. doi: 10.3390/cells8090986. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31461941 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

