Association of type and location of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations with risk of breast and ovarian cancer
- PMID: 25849179
- PMCID: PMC4537700
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2014.5985
Association of type and location of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations with risk of breast and ovarian cancer
Erratum in
-
Incorrect Element in Figure.JAMA. 2015 Aug 11;314(6):628. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.7352. JAMA. 2015. PMID: 26262809 No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: Limited information about the relationship between specific mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2 (BRCA1/2) and cancer risk exists.
Objective: To identify mutation-specific cancer risks for carriers of BRCA1/2.
Design, setting, and participants: Observational study of women who were ascertained between 1937 and 2011 (median, 1999) and found to carry disease-associated BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations. The international sample comprised 19,581 carriers of BRCA1 mutations and 11,900 carriers of BRCA2 mutations from 55 centers in 33 countries on 6 continents. We estimated hazard ratios for breast and ovarian cancer based on mutation type, function, and nucleotide position. We also estimated RHR, the ratio of breast vs ovarian cancer hazard ratios. A value of RHR greater than 1 indicated elevated breast cancer risk; a value of RHR less than 1 indicated elevated ovarian cancer risk.
Exposures: Mutations of BRCA1 or BRCA2.
Main outcomes and measures: Breast and ovarian cancer risks.
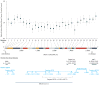
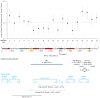
Results: Among BRCA1 mutation carriers, 9052 women (46%) were diagnosed with breast cancer, 2317 (12%) with ovarian cancer, 1041 (5%) with breast and ovarian cancer, and 7171 (37%) without cancer. Among BRCA2 mutation carriers, 6180 women (52%) were diagnosed with breast cancer, 682 (6%) with ovarian cancer, 272 (2%) with breast and ovarian cancer, and 4766 (40%) without cancer. In BRCA1, we identified 3 breast cancer cluster regions (BCCRs) located at c.179 to c.505 (BCCR1; RHR = 1.46; 95% CI, 1.22-1.74; P = 2 × 10(-6)), c.4328 to c.4945 (BCCR2; RHR = 1.34; 95% CI, 1.01-1.78; P = .04), and c. 5261 to c.5563 (BCCR2', RHR = 1.38; 95% CI, 1.22-1.55; P = 6 × 10(-9)). We also identified an ovarian cancer cluster region (OCCR) from c.1380 to c.4062 (approximately exon 11) with RHR = 0.62 (95% CI, 0.56-0.70; P = 9 × 10(-17)). In BRCA2, we observed multiple BCCRs spanning c.1 to c.596 (BCCR1; RHR = 1.71; 95% CI, 1.06-2.78; P = .03), c.772 to c.1806 (BCCR1'; RHR = 1.63; 95% CI, 1.10-2.40; P = .01), and c.7394 to c.8904 (BCCR2; RHR = 2.31; 95% CI, 1.69-3.16; P = .00002). We also identified 3 OCCRs: the first (OCCR1) spanned c.3249 to c.5681 that was adjacent to c.5946delT (6174delT; RHR = 0.51; 95% CI, 0.44-0.60; P = 6 × 10(-17)). The second OCCR spanned c.6645 to c.7471 (OCCR2; RHR = 0.57; 95% CI, 0.41-0.80; P = .001). Mutations conferring nonsense-mediated decay were associated with differential breast or ovarian cancer risks and an earlier age of breast cancer diagnosis for both BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers.
Conclusions and relevance: Breast and ovarian cancer risks varied by type and location of BRCA1/2 mutations. With appropriate validation, these data may have implications for risk assessment and cancer prevention decision making for carriers of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations.
Figures

References
-
- Miki Y, Swensen J, Shattuck-Eidens D, et al. A strong candidate for the breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1. Science. 1994;266(5182):66–71. - PubMed
-
- Wooster R, Neuhausen SL, Mangion J, et al. Localization of a breast cancer susceptibility gene, BRCA2, to chromosome 13q12-13. Science. 1994;265 (5181):2088–2090. - PubMed
-
- Gayther SA, Warren W, Mazoyer S, et al. Germline mutations of the BRCA1 gene in breast and ovarian cancer families provide evidence for a genotype-phenotype correlation. Nat Genet. 1995;11(4):428–433. - PubMed
-
- Thompson D, Easton D Breast Cancer Linkage Consortium. Variation in BRCA1 cancer risks by mutation position. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2002;11(4):329–336. - PubMed
-
- Gayther SA, Mangion J, Russell P, et al. Variation of risks of breast and ovarian cancer associated with different germline mutations of the BRCA2 gene. Nat Genet. 1997;15(1):103–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10 CA180868/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA164920/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 11174/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P30 CA168524/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50-CA083638/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA012197/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA083855/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA051008/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 15007/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P50 CA083638/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA074415/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180822/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA140323/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA102776/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 17528/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P50 CA159981/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC4 CA153828/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA101165/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA069398/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA027469/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA112520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA116167/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA116201/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA113916/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA112520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA069631/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037517/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA083855/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16563/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA102776/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA196067/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001425/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

