Cellular size as a means of tracking mTOR activity and cell fate of CD4+ T cells upon antigen recognition
- PMID: 25849206
- PMCID: PMC4388710
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121710
Cellular size as a means of tracking mTOR activity and cell fate of CD4+ T cells upon antigen recognition
Abstract
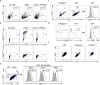
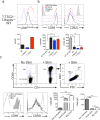
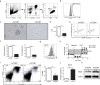
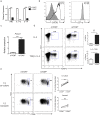
mTOR is a central integrator of metabolic and immunological stimuli, dictating immune cell activation, proliferation and differentiation. In this study, we demonstrate that within a clonal population of activated T cells, there exist both mTORhi and mTORlo cells exhibiting highly divergent metabolic and immunologic functions. By taking advantage of the role of mTOR activation in controlling cellular size, we demonstrate that upon antigen recognition, mTORhi CD4+ T cells are destined to become highly glycolytic effector cells. Conversely, mTORlo T cells preferentially develop into long-lived cells that express high levels of Bcl-2, CD25, and CD62L. Furthermore, mTORlo T cells have a greater propensity to differentiate into suppressive Foxp3+ T regulatory cells, and this paradigm was also observed in human CD4+ T cells. Overall, these studies provide the opportunity to track the development of effector and memory T cells from naïve precursors, as well as facilitate the interrogation of immunologic and metabolic programs that inform these fates.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
IL-7 promotes long-term in vitro survival of unique long-lived memory subset generated from mucosal effector memory CD4+ T cells in chronic colitis mice.Immunol Lett. 2013 Nov-Dec;156(1-2):82-93. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2013.09.001. Epub 2013 Sep 23. Immunol Lett. 2013. PMID: 24070768
-
In-vitro generation and characterisation of murine CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells with indirect allospecificity.Int Immunopharmacol. 2006 Dec 20;6(13-14):1883-8. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2006.07.032. Epub 2006 Sep 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17161341
-
Oscillatory mTOR inhibition and Treg increase in kidney transplantation.Clin Exp Immunol. 2015 Nov;182(2):230-40. doi: 10.1111/cei.12669. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Clin Exp Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26077103 Free PMC article.
-
[The role of regulatory cells CD4+CD25+ in the development of chronic infective diseases].Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 2006;(9-10):24-9. Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 2006. PMID: 17111920 Review. Russian.
-
Proliferative assays for T cell function.Curr Protoc Immunol. 2004 May;Chapter 3:Unit 3.12. doi: 10.1002/0471142735.im0312s60. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2004. PMID: 18432927 Review.
Cited by
-
Asymmetric inheritance of mTORC1 kinase activity during division dictates CD8(+) T cell differentiation.Nat Immunol. 2016 Jun;17(6):704-11. doi: 10.1038/ni.3438. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Nat Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27064374 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-neoplastic sulfonamides alter the metabolic homeostasis and disrupt the suppressor activity of regulatory T cells.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 9;12(1):19112. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23601-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36352020 Free PMC article.
-
SNX27 links DGKζ to the control of transcriptional and metabolic programs in T lymphocytes.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 27;7(1):16361. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16370-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29180720 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive oxygen species are required for driving efficient and sustained aerobic glycolysis during CD4+ T cell activation.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 20;12(4):e0175549. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175549. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28426686 Free PMC article.
-
RORγt limits the amount of the cytokine receptor γc through the prosurvival factor Bcl-xL in developing thymocytes.Sci Signal. 2018 Aug 28;11(545):eaam8939. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aam8939. Sci Signal. 2018. PMID: 30154103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yamagata K, Sanders LK, Kaufmann WE, Yee W, Barnes CA, Nathans D, et al. rheb, a growth factor- and synaptic activity-regulated gene, encodes a novel Ras-related protein. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1994;269(23):16333–9. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

