The evolution of WRKY transcription factors
- PMID: 25849216
- PMCID: PMC4350883
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-015-0456-y
The evolution of WRKY transcription factors
Abstract
Background: The availability of increasing numbers of sequenced genomes has necessitated a re-evaluation of the evolution of the WRKY transcription factor family. Modern day plants descended from a charophyte green alga that colonized the land between 430 and 470 million years ago. The first charophyte genome sequence from Klebsormidium flaccidum filled a gap in the available genome sequences in the plant kingdom between unicellular green algae that typically have 1-3 WRKY genes and mosses that contain 30-40. WRKY genes have been previously found in non-plant species but their occurrence has been difficult to explain.
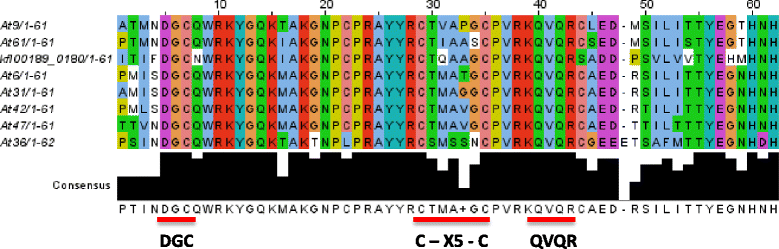
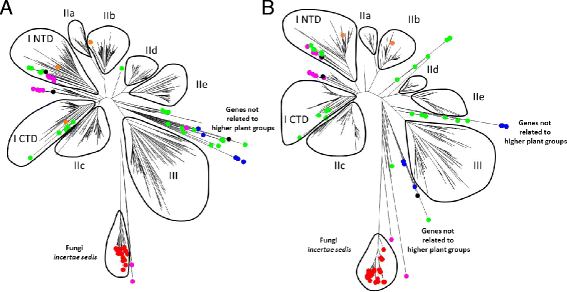
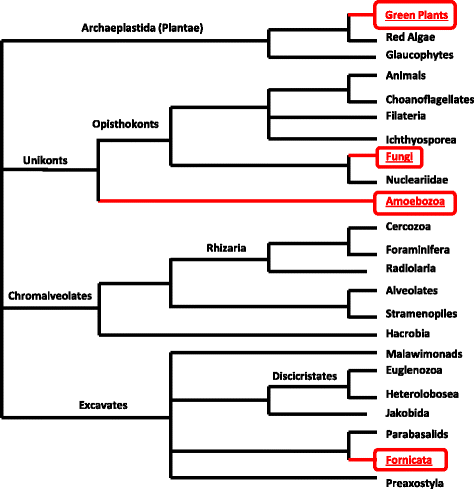
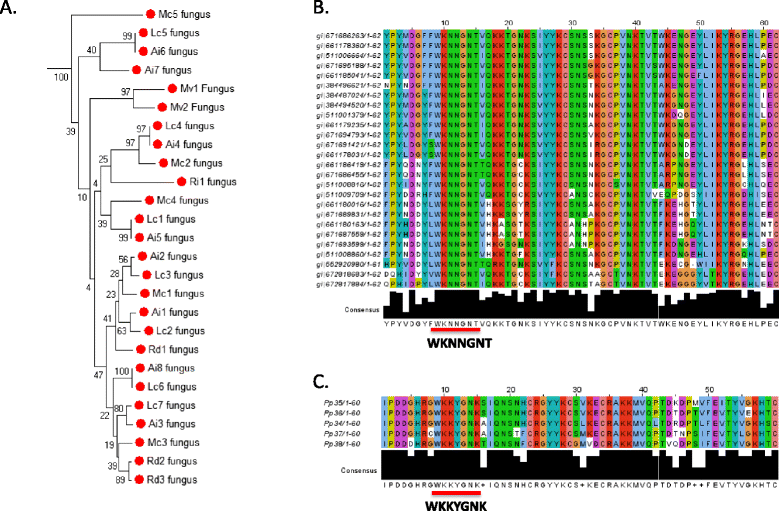
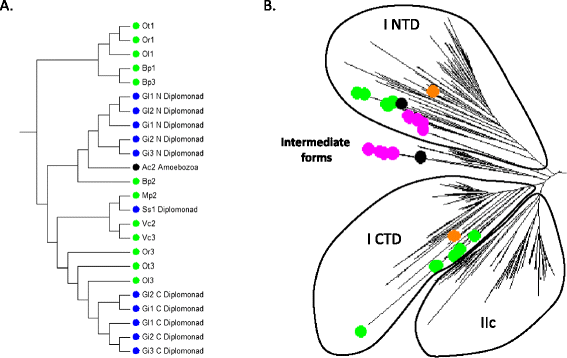
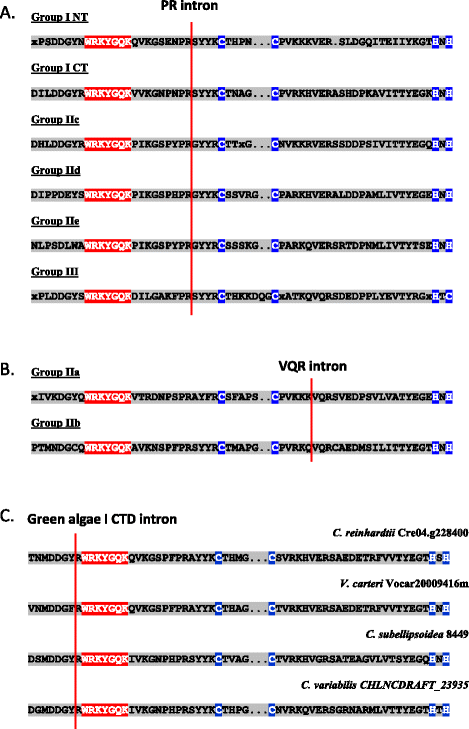
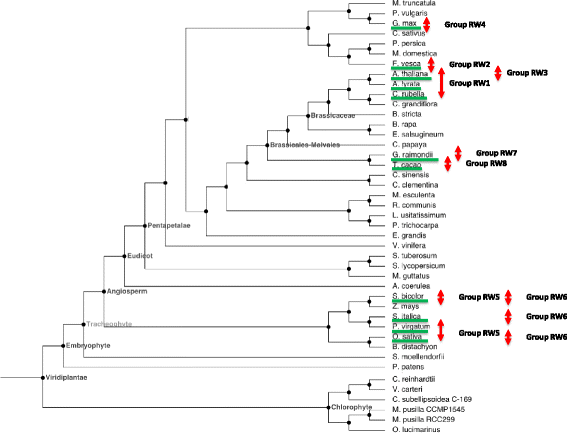
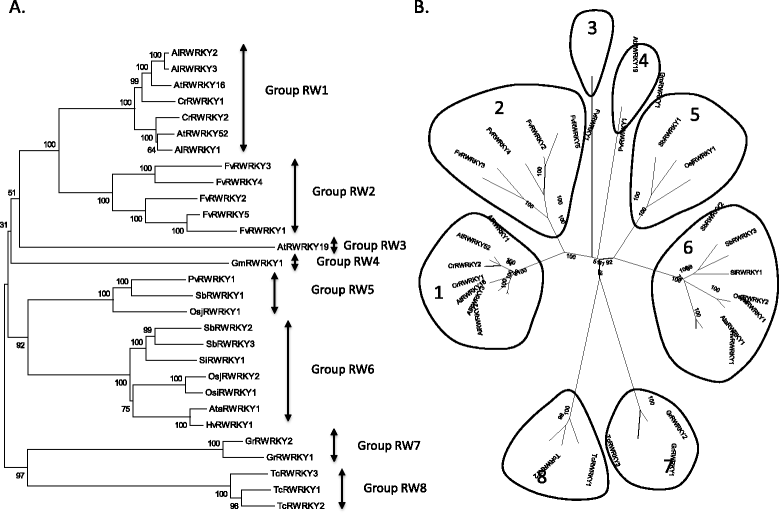
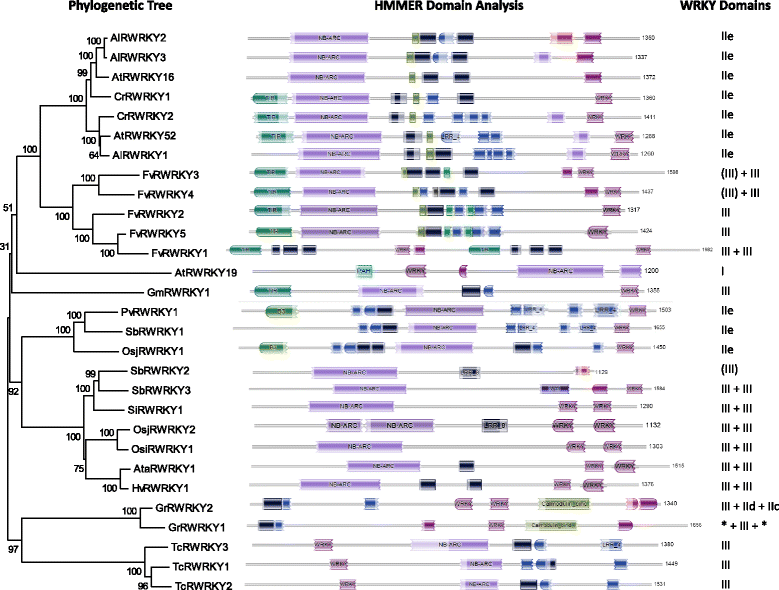
Results: Only two WRKY genes are present in the Klebsormidium flaccidum genome and the presence of a Group IIb gene was unexpected because it had previously been thought that Group IIb WRKY genes first appeared in mosses. We found WRKY transcription factor genes outside of the plant lineage in some diplomonads, social amoebae, fungi incertae sedis, and amoebozoa. This patchy distribution suggests that lateral gene transfer is responsible. These lateral gene transfer events appear to pre-date the formation of the WRKY groups in flowering plants. Flowering plants contain proteins with domains typical for both resistance (R) proteins and WRKY transcription factors. R protein-WRKY genes have evolved numerous times in flowering plants, each type being restricted to specific flowering plant lineages. These chimeric proteins contain not only novel combinations of protein domains but also novel combinations and numbers of WRKY domains. Once formed, R protein WRKY genes may combine different components of signalling pathways that may either create new diversity in signalling or accelerate signalling by short circuiting signalling pathways.
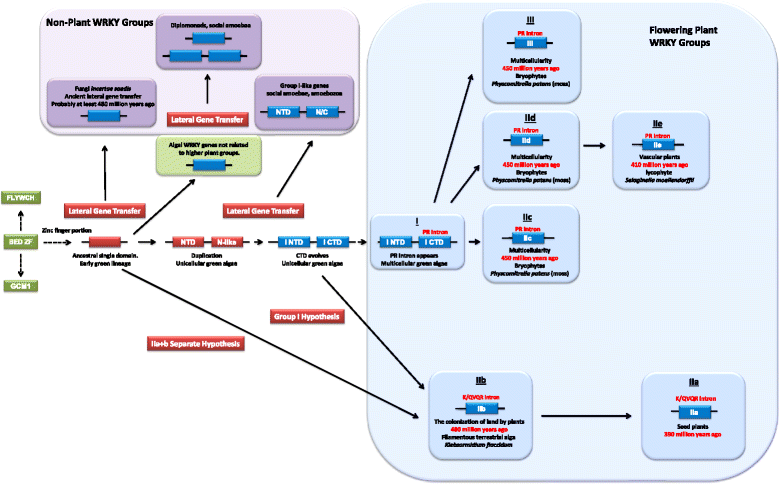
Conclusions: We propose that the evolution of WRKY transcription factors includes early lateral gene transfers to non-plant organisms and the occurrence of algal WRKY genes that have no counterparts in flowering plants. We propose two alternative hypotheses of WRKY gene evolution: The "Group I Hypothesis" sees all WRKY genes evolving from Group I C-terminal WRKY domains. The alternative "IIa + b Separate Hypothesis" sees Groups IIa and IIb evolving directly from a single domain algal gene separate from the Group I-derived lineage.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The WRKY transcription factor superfamily: its origin in eukaryotes and expansion in plants.BMC Evol Biol. 2005 Jan 3;5:1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-5-1. BMC Evol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15629062 Free PMC article.
-
The WRKY family of transcription factors in rice and Arabidopsis and their origins.DNA Res. 2005 Feb 28;12(1):9-26. doi: 10.1093/dnares/12.1.9. DNA Res. 2005. PMID: 16106749
-
[Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the WRKY gene family in peach].Yi Chuan. 2016 Mar;38(3):254-70. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.15-235. Yi Chuan. 2016. PMID: 27001479 Chinese.
-
Evolution in the Cycles of Life.Annu Rev Genet. 2016 Nov 23;50:133-154. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120215-035227. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Annu Rev Genet. 2016. PMID: 27617970 Review.
-
Unlocking nature's secrets: The pivotal role of WRKY transcription factors in plant flowering and fruit development.Plant Sci. 2024 Sep;346:112150. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2024.112150. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38857658 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification, Expression, and Functional Analysis of the Group IId WRKY Subfamily in Upland Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.).Front Plant Sci. 2018 Nov 21;9:1684. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01684. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30519251 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the WRKY Gene Family in Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi under Diverse Abiotic Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 11;23(8):4225. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084225. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457040 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of WRKY transcription factors in Malus spp. and Pyrus spp.Funct Integr Genomics. 2022 Oct;22(5):713-729. doi: 10.1007/s10142-022-00886-0. Epub 2022 Jul 29. Funct Integr Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35906324 Review.
-
A Comprehensive Transcriptome-Wide Identification and Screening of WRKY Gene Family Engaged in Abiotic Stress in Glycyrrhiza glabra.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 15;10(1):373. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-57232-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31941983 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of WRKY Transcription Factors and Their Expression Profile in Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum.Plants (Basel). 2023 May 27;12(11):2131. doi: 10.3390/plants12112131. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37299110 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

