The neuronal-specific SGK1.1 (SGK1_v2) kinase as a transcriptional modulator of BAG4, Brox, and PPP1CB genes expression
- PMID: 25849655
- PMCID: PMC4425028
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms16047462
The neuronal-specific SGK1.1 (SGK1_v2) kinase as a transcriptional modulator of BAG4, Brox, and PPP1CB genes expression
Abstract
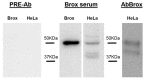
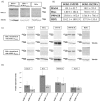
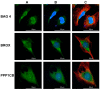
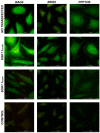
The Serum- and Glucocorticoid-induced Kinase 1, SGK1, exhibits a broad range of cellular functions that include regulation of the number of ion channels in plasma membrane and modulation of signaling pathways of cell survival. This diversity of functions is made possible by various regulatory processes acting upon the SGK1 gene, giving rise to various isoforms: SGK1_v1-5, each with distinct properties and distinct aminotermini that serve to target proteins to different subcellular compartments. Among cellular effects of SGK1 expression is to indirectly modulate gene transcription by phosphorylating transcriptional factors of the FOXO family. Here we examined if SGK1.1 (SGK1_v2; NM_001143676), which associates primarily to the plasma membrane, is also able to regulate gene expression. Using a differential gene expression approach we identified six genes upregulated by SGK1.1 in HeLa cells. Further analysis of transcript and protein levels validated two genes: BCL2-associated athanogene 4 (BAG-4) and Brox. The results indicate that SGK1.1 regulates gene transcription upon a different set of genes some of which participate in cell survival pathways (BAG-4) and others in intracellular vesicular traffic (Brox).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum/glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 (SGK1) is a prominent target gene of the transcriptional response to cytokines in multiple myeloma and supports the growth of myeloma cells.Oncogene. 2011 Jul 14;30(28):3198-206. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.79. Epub 2011 Apr 11. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 21478911
-
Differential regulation of serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 (SGK1) splice variants based on alternative initiation of transcription.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2007;20(6):715-28. doi: 10.1159/000110432. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17982254
-
Activation of SGK1 in Endometrial Epithelial Cells in Response to PI3K/AKT Inhibition Impairs Embryo Implantation.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(5):2077-2087. doi: 10.1159/000447903. Epub 2016 Oct 31. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27825168
-
Regulation and physiological roles of serum- and glucocorticoid-induced protein kinase isoforms.Sci STKE. 2001 Nov 13;2001(108):re17. doi: 10.1126/stke.2001.108.re17. Sci STKE. 2001. PMID: 11707620 Review.
-
Colorectal carcinoma cells--regulation of survival and growth by SGK1.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;42(10):1571-5. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.05.016. Epub 2010 Jun 9. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20541034 Review.
Cited by
-
Melatonin, BAG-1 and cortisol circadian interactions in tumor pathogenesis and patterned immune responses.Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4(5):962-993. doi: 10.37349/etat.2023.00176. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023. PMID: 37970210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum and Glucocorticoid-Inducible Kinase 1 (SGK1) in NSCLC Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Nov 22;13(11):413. doi: 10.3390/ph13110413. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33266470 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kobayashi T., Cohen P. Activation of serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated protein kinase by agonists that activate phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase is mediated by 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) and PDK2. Biochem. J. 1999;339:319–328. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3390319. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baltaev R., Strutz-Seebohm N., Korniychuk G., Myssina S., Lang F., Seebohm G. Regulation of cardiac shal-related potassium channel Kv 4.3 by serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase isoforms in Xenopus oocytes. Pflugers Arch. 2005;450:26–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

