TYK2 protein-coding variants protect against rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmunity, with no evidence of major pleiotropic effects on non-autoimmune complex traits
- PMID: 25849893
- PMCID: PMC4388675
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122271
TYK2 protein-coding variants protect against rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmunity, with no evidence of major pleiotropic effects on non-autoimmune complex traits
Abstract
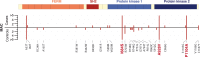
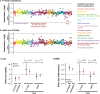
Despite the success of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) in detecting a large number of loci for complex phenotypes such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) susceptibility, the lack of information on the causal genes leaves important challenges to interpret GWAS results in the context of the disease biology. Here, we genetically fine-map the RA risk locus at 19p13 to define causal variants, and explore the pleiotropic effects of these same variants in other complex traits. First, we combined Immunochip dense genotyping (n = 23,092 case/control samples), Exomechip genotyping (n = 18,409 case/control samples) and targeted exon-sequencing (n = 2,236 case/controls samples) to demonstrate that three protein-coding variants in TYK2 (tyrosine kinase 2) independently protect against RA: P1104A (rs34536443, OR = 0.66, P = 2.3 x 10(-21)), A928V (rs35018800, OR = 0.53, P = 1.2 x 10(-9)), and I684S (rs12720356, OR = 0.86, P = 4.6 x 10(-7)). Second, we show that the same three TYK2 variants protect against systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE, Pomnibus = 6 x 10(-18)), and provide suggestive evidence that two of the TYK2 variants (P1104A and A928V) may also protect against inflammatory bowel disease (IBD; P(omnibus) = 0.005). Finally, in a phenome-wide association study (PheWAS) assessing >500 phenotypes using electronic medical records (EMR) in >29,000 subjects, we found no convincing evidence for association of P1104A and A928V with complex phenotypes other than autoimmune diseases such as RA, SLE and IBD. Together, our results demonstrate the role of TYK2 in the pathogenesis of RA, SLE and IBD, and provide supporting evidence for TYK2 as a promising drug target for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of rare coding variants in TYK2 protective for rheumatoid arthritis in the Japanese population and their effects on cytokine signalling.Ann Rheum Dis. 2019 Aug;78(8):1062-1069. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215062. Epub 2019 May 22. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019. PMID: 31118190
-
Influence of TYK2 in systemic sclerosis susceptibility: a new locus in the IL-12 pathway.Ann Rheum Dis. 2016 Aug;75(8):1521-6. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208154. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016. PMID: 26338038 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms in IRF5 and TYK2 Genes Are Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis in a Chinese Han Population.Med Sci Monit. 2021 Feb 15;27:e928455. doi: 10.12659/MSM.928455. Med Sci Monit. 2021. PMID: 33583939 Free PMC article.
-
Mendelian randomization and clinical trial evidence supports TYK2 inhibition as a therapeutic target for autoimmune diseases.EBioMedicine. 2023 Mar;89:104488. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104488. Epub 2023 Feb 24. EBioMedicine. 2023. PMID: 36842216 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic susceptibility to autoimmune disorders: clues from gene association and gene expression studies.Curr Mol Med. 2008 Sep;8(6):551-61. doi: 10.2174/156652408785747906. Curr Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18781962 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic variants regulating the immune response improve the prediction of COVID-19 severity provided by clinical variables.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 5;14(1):20728. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71476-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39237611 Free PMC article.
-
Increased incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in multiple sclerosis: A nationwide cohort study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jun;95(26):e3999. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003999. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27368008 Free PMC article.
-
Two common disease-associated TYK2 variants impact exon splicing and TYK2 dosage.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 21;15(1):e0225289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225289. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31961910 Free PMC article.
-
The role of IL-18 in addition to Th17 cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis development and treatment in women.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 28;11(1):15391. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-94841-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34321563 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Big (Clinical) Data and Genomics on Precision Medicine and Drug Development.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Mar;103(3):409-418. doi: 10.1002/cpt.951. Epub 2018 Feb 5. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29171014 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01-AR057108/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AR060257/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR059648/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM010685/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR070253/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM092691/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR059648/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR063759/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067677/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR056768/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01-GM092691/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR057108/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR063759/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR056768/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR049880/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

