Epigenome editing by a CRISPR-Cas9-based acetyltransferase activates genes from promoters and enhancers
- PMID: 25849900
- PMCID: PMC4430400
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.3199
Epigenome editing by a CRISPR-Cas9-based acetyltransferase activates genes from promoters and enhancers
Abstract
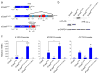
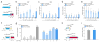
Technologies that enable targeted manipulation of epigenetic marks could be used to precisely control cell phenotype or interrogate the relationship between the epigenome and transcriptional control. Here we describe a programmable, CRISPR-Cas9-based acetyltransferase consisting of the nuclease-null dCas9 protein fused to the catalytic core of the human acetyltransferase p300. The fusion protein catalyzes acetylation of histone H3 lysine 27 at its target sites, leading to robust transcriptional activation of target genes from promoters and both proximal and distal enhancers. Gene activation by the targeted acetyltransferase was highly specific across the genome. In contrast to previous dCas9-based activators, the acetyltransferase activates genes from enhancer regions and with an individual guide RNA. We also show that the core p300 domain can be fused to other programmable DNA-binding proteins. These results support targeted acetylation as a causal mechanism of transactivation and provide a robust tool for manipulating gene regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Comment in
-
Epigenetics: Characterizing enhancers with dCas9.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015 May;16(5):266-7. doi: 10.1038/nrm3983. Epub 2015 Apr 15. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25874740 No abstract available.
References
-
- Snowden AW, Gregory PD, Case CC, Pabo CO. Gene-specific targeting of H3K9 methylation is sufficient for initiating repression in vivo. Curr Biol. 2002;12:2159–2166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

