Brain-derived neurotrophic factor ameliorates learning deficits in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease induced by aβ1-42
- PMID: 25849905
- PMCID: PMC4388634
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122415
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor ameliorates learning deficits in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease induced by aβ1-42
Abstract
An emerging body of data suggests that the early onset of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is associated with decreased brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Because BDNF plays a critical role in the regulation of high-frequency synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation in the hippocampus, the up-regulation of BDNF may rescue cognitive impairments and learning deficits in AD. In the present study, we investigated the effects of hippocampal BDNF in a rat model of AD produced by a ventricle injection of amyloid-β1-42 (Aβ1-42). We found that a ventricle injection of Aβ1-42 caused learning deficits in rats subjected to the Morris water maze and decreased BDNF expression in the hippocampus. Chronic intra-hippocampal BDNF administration rescued learning deficits in the water maze, whereas infusions of NGF and NT-3 did not influence the behavioral performance of rats injected with Aβ1-42. Furthermore, the BDNF-related improvement in learning was ERK-dependent because the inhibition of ERK, but not JNK or p38, blocked the effects of BDNF on cognitive improvement in rats injected with Aβ1-42. Together, our data suggest that the up-regulation of BDNF in the hippocampus via activation of the ERK signaling pathway can ameliorate Aβ1-42-induced learning deficits, thus identifying a novel pathway through which BDNF protects against AD-related cognitive impairments. The results of this research may shed light on a feasible therapeutic approach to control the progression of AD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
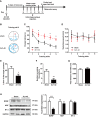
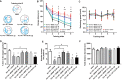
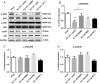
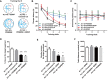
Similar articles
-
Curcumin Improves Amyloid β-Peptide (1-42) Induced Spatial Memory Deficits through BDNF-ERK Signaling Pathway.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 26;10(6):e0131525. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131525. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26114940 Free PMC article.
-
Harpagoside ameliorates the amyloid-β-induced cognitive impairment in rats via up-regulating BDNF expression and MAPK/PI3K pathways.Neuroscience. 2015 Sep 10;303:103-14. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.06.042. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 26135675
-
Davunetide improves spatial learning and memory in Alzheimer's disease-associated rats.Physiol Behav. 2017 May 15;174:67-73. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.02.038. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Physiol Behav. 2017. PMID: 28257938
-
Relevance of abeta1-42 intrahippocampal injection as an animal model of inflamed Alzheimer's disease brain.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2008 Oct;5(5):475-80. doi: 10.2174/156720508785908874. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2008. PMID: 18855589 Review.
-
Amyloid beta soluble forms and plasminogen activation system in Alzheimer's disease: Consequences on extracellular maturation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and therapeutic implications.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019 Mar;25(3):303-313. doi: 10.1111/cns.13082. Epub 2018 Nov 6. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019. PMID: 30403004 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Peptides Derived from Growth Factors to Treat Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 4;22(11):6071. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116071. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34199883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Interaction between Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Stress-Related Glucocorticoids in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 27;25(3):1596. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031596. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photobiomodulation (660 nm) therapy reduces oxidative stress and induces BDNF expression in the hippocampus.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 12;9(1):10114. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46490-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31300736 Free PMC article.
-
Oleuropein Promotes Neural Plasticity and Neuroprotection via PPARα-Dependent and Independent Pathways.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 11;11(8):2250. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082250. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626746 Free PMC article.
-
Calcineurin/P-ERK/Egr-1 Pathway is Involved in Fear Memory Impairment after Isoflurane Exposure in Mice.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 24;7(1):13947. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13975-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29066839 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acosta D, Wortmann M (2009) Alzheimer’s Disease International World Alzheimer Report 2009. Prince, M: 1–92.
-
- Ferri C, Sousa R, Albanese E, Ribeiro W, Honyashiki M (2009) Alzheimer's Disease International World Alzheimer Report 2009. London: Alzheimer’s Disease International.
-
- Selkoe DJ (1999) Translating cell biology into therapeutic advances in Alzheimer's disease. Nature 399: A23–31. - PubMed
-
- Masliah E, Mallory M, Alford M, DeTeresa R, Hansen LA, McKeel DW Jr, et al. (2001) Altered expression of synaptic proteins occurs early during progression of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 56: 127–129. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe DJ (2002) Alzheimer's disease is a synaptic failure. Science 298: 789–791. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

