Interplay between chemotaxis and contact inhibition of locomotion determines exploratory cell migration
- PMID: 25851023
- PMCID: PMC4391292
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms7619
Interplay between chemotaxis and contact inhibition of locomotion determines exploratory cell migration
Abstract
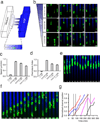
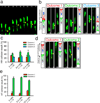
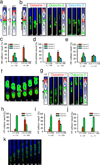
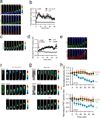
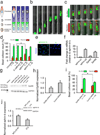
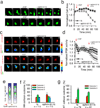
Directed cell migration in native environments is influenced by multiple migratory cues. These cues may include simultaneously occurring attractive soluble growth factor gradients and repulsive effects arising from cell-cell contact, termed contact inhibition of locomotion (CIL). How single cells reconcile potentially conflicting cues remains poorly understood. Here we show that a dynamic crosstalk between epidermal growth factor (EGF)-mediated chemotaxis and CIL guides metastatic breast cancer cell motility, whereby cells become progressively insensitive to CIL in a chemotactic input-dependent manner. This balance is determined via integration of protrusion-enhancing signalling from EGF gradients and protrusion-suppressing signalling induced by CIL, mediated in part through EphB. Our results further suggest that EphB and EGF signalling inputs control protrusion formation by converging onto regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K). We propose that this intricate interplay may enhance the spread of loose cell ensembles in pathophysiological conditions such as cancer, and possibly other physiological settings.
Figures

References
-
- Schmitt AM, et al. Wnt-Ryk signalling mediates medial-lateral retinotectal topographic mapping. Nature. 2006;439:31–37. - PubMed
-
- Condeelis J, Singer RH, Segall JE. THE GREAT ESCAPE: When Cancer Cells Hijack the Genes for chemotaxis and Motility. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology. 2005;21:695–718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

