Organisational interventions for improving wellbeing and reducing work-related stress in teachers
- PMID: 25851427
- PMCID: PMC10993096
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010306.pub2
Organisational interventions for improving wellbeing and reducing work-related stress in teachers
Abstract
Background: The teaching profession is an occupation with a high prevalence of work-related stress. This may lead to sustained physical and mental health problems in teachers. It can also negatively affect the health, wellbeing and educational attainment of children, and impose a financial burden on the public budget in terms of teacher turnover and sickness absence. Most evaluated interventions for the wellbeing of teachers are directed at the individual level, and so do not tackle the causes of stress in the workplace. Organisational-level interventions are a potential avenue in this regard.
Objectives: To evaluate the effectiveness of organisational interventions for improving wellbeing and reducing work-related stress in teachers.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO, ASSIA, AEI, BEI, BiblioMap, DARE, DER, ERIC, IBSS, SSCI, Sociological Abstracts, a number of specialist occupational health databases, and a number of trial registers and grey literature sources from the inception of each database until January 2015.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs), cluster-RCTs, and controlled before-and-after studies of organisational-level interventions for the wellbeing of teachers.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodological procedures expected by Cochrane.
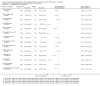
Main results: Four studies met the inclusion criteria. They were three cluster-randomised controlled trials and one with a stepped-wedge design.Changing task characteristicsOne study with 961 teachers in eight schools compared a task-based organisational change intervention along with stress management training to no intervention. It found a small reduction at 12 months in 10 out of 14 of the subscales in the Occupational Stress Inventory, with a mean difference (MD) varying from -3.84 to 0.13, and a small increase in the Work Ability Index (MD 2.27; 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.64 to 2.90; 708 participants, low-quality evidence).Changing organisational characteristicsTwo studies compared teacher training combined with school-wide coaching support to no intervention. One study with 59 teachers in 43 schools found no significant effects on job-related anxiety (MD -0.25 95% CI -0.61 to 0.11, very low-quality evidence) or depression (MD -0.26 95% CI -0.57 to 0.05, very low-quality evidence) after 24 months. The other study with 77 teachers in 18 schools found no significant effects on the Maslach Burnout Inventory subscales (e.g. emotional exhaustion subscale: MD -0.05 95% CI -0.52 to 0.42, low-quality evidence) or the Teacher Perceived Emotional Ability subscales (e.g. regulating emotions subscale: MD 0.11 95% CI -0.11 to 0.33, low-quality evidence) after six months.Multi-component interventionOne study with 1102 teachers in 34 schools compared a multi-component intervention containing performance bonus, job promotion opportunities and mentoring support to a matched-comparison group consisting of 300 schools. It found moderately higher teacher retention rates (MD 11.50 95% CI 3.25 to 19.75 at 36 months follow-up, very low-quality evidence). However, the authors reported results only from one cohort out of four (eight schools), demonstrating a high risk of reporting bias.
Authors' conclusions: We found low-quality evidence that organisational interventions lead to improvements in teacher wellbeing and retention rates. We need further evaluation of the effects of organisational interventions for teacher wellbeing. These studies should follow a complex-interventions framework, use a cluster-randomised design and have large sample sizes.
Conflict of interest statement
Ali Naghieh: He is directly involved in the ongoing study Naghieh 2014.
Paul Montgomery: He is directly involved in the ongoing study Naghieh 2014.
Christopher Bonell: None known.
Marc Thompson: He is directly involved in the ongoing study Naghieh 2014.
J. Lawrence Aber: None known.
Figures
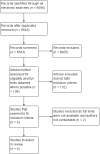

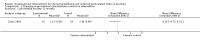
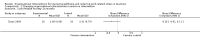

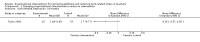



Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010306
References
References to studies included in this review
Brown 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Brown JL, Jones SM, Aber JL. The longitudinal impact of a universal school‐based social‐emotional and literacy intervention on classroom climate and teacher processes and practices. Society for Research on Educational Effectiveness (SREE) Conference. 2010.
-
- Brown JL, Jones SM, LaRusso MD, Aber JL. Improving Classroom Quality: Teacher Influences and Experimental Impacts of the 4Rs Program. Journal of Educational Psychology 2010;102(1):153‐167.
-
- Brown JL, Jones SM, Torrente C, Aber JL. The Longitudinal Impact of a Universal School‐Based Social‐Emotional and Literacy Intervention on Teachers’ Affective Experiences and Classroom Practices. American Educational Research Association. New Orleans, Louisiana. 2011.
Glazerman 2012 {published data only}
-
- Glazerman S, Seifullah A. An evaluation of the Chicago Teacher Advancement Program (Chicago TAP) after four years, final report. www.mathematica‐mpr.com/publications/pdfs/education/tap_year4_impacts.pdf. (accessed 14th March 2015).
Tyson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Tyson O, Roberts CM, Kane R. Can implementation of a resilience program for primary school children enhance the mental health of teachers?. Australian Journal of Guidance and Counselling 2009;19(2):116‐30.
Wu 2006 {published data only}
-
- Wu S, Li J, Wang M, Wang Z, Li H. Short communication: Intervention on occupational stress among teachers in the middle schools in China. Stress and Health 2006;22(5):329‐36.
References to studies excluded from this review
Allegrante 1990 {published data only}
-
- Allegrante JP, Michela JL. Impact of a school‐based workplace health promotion program on morale of inner‐city teachers. Journal of School Health 1990;60(1):25‐8. - PubMed
Bishop 1983 {published data only}
-
- Bishop JE. Effects of "Ounce" Classroom Management Training on the Self‐Esteem, Self‐Actualization and Burnout of Elementary School Teachers. Washington State University, 1983.
Blair 1986 {published data only}
-
- Blair SN, Smith M, Collingwood TR, Reynolds R, Prentice MC, Sterling CL. Health promotion for educators: impact on absenteeism. Preventive Medicine 1986;15(2):166‐75. - PubMed
Cecil 1990 {published data only}
-
- Cecil MA, Forman SG. Effects of stress inoculation training and co‐worker support groups on teachers' stress. Journal of School Psychology 1990;28(2):105‐18.
Charters 1978 {published data only}
-
- Charters WW Jr. The effects of the team organization of elementary schools on teacher influence and work attitudes: a replication. Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. Toronto, Canada, 1978:41.
Coad 1976 {published data only}
-
- Coad RA. The effects of an organization development program on satisfaction, group process, climate, leadership, and student achievement. Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. San Francisco, California, 1978:25.
Cullen 1999 {published data only}
-
- Cullen KW, Baranowski T, Baranowski J, Hebert D, Moor C, Hearn MD, et al. Influence of school organizational characteristics on the outcomes of a school health promotion program. Journal of School Health 1999;69(9):376‐80. - PubMed
Goodman 2010 {published data only}
-
- Goodman S, Turner L. Teacher incentive pay and educational outcomes: evidence from the NYC Bonus Program. PEPG Conference "Merit Pay: Will It Work? Is It Politically Viable?". Harvard Kennedy School, Cambridge, MA, 2010:37.
Larsson 1990 {published data only}
-
- Larsson G, Setterlind S, Starrin B. Routinization of stress control programmes in organizations: A study of Swedish teachers. Health Promotion International 1990;5(4):269‐78.
Sharp 1982 {published data only}
-
- Sharp JJ. Effects of Stress Management Training and Classroom Management Training on Teacher Affect and Classroom Behavior. University of South Carolina, 1982.
Sharp 1985 {published data only}
-
- Sharp JJ. A comparison of two approaches to anxiety management for teachers. Behavior Therapy 1985;16(4):370‐383.
Snyder 1986 {published data only}
-
- Snyder NV. The Effects of a Discipline Management In‐service Program on Teacher Stress. University of Florida, 1986.
References to ongoing studies
Naghieh 2014 {unpublished data only}
-
- Naghieh A, Montgomery P, Thompson M, et al. Aligning staff wellbeing with organisational development: A pilot trial of the Change Laboratory in UK secondary schools. Unpublished.
Additional references
Aelterman 2007
-
- Aelterman A, Engels N, Petegem K, Verhaeghe JP. The well‐being of teachers in Flanders: the importance of a supportive school culture. Educational Studies 2007;33(3):285‐97.
Al‐Mohannadi 2007
-
- Al‐Mohannadi A, Capel S. Stress in physical education teachers in Qatar. Social Psychology of Education 2007;10:55‐75.
Bamford 2003
-
- Bamford DR, Forrester PL. Managing planned and emergent change within an operations management environment. International Journal of Operations & Production Management 2003;23:546‐64.
Belkic 2004
-
- Belkic KL, Landsbergis PA, Schnall PL, Baker D. Is job strain a major source of cardiovascular disease risk?. Scandinavian Journal of Work, Environment & Health 2004;30(2):85‐128. - PubMed
Benach 2007
-
- Benach J, Muntaner C, Santana V, World Health Organization. Employment Conditions and Health Inequalities: Final Report to the WHO Commission on Social Determinants of Health (CSDH), 2007. www.who.int/social_determinants/resources/articles/emconet_who_report.pdf. WHO, (accessed 14th March 2015).
Benmansour 1998
-
- Benmansour N. Job satisfaction, stress and coping strategies among Moroccan high school teachers. Mediterranean Journal of Educational Studies 1998;3(1):13‐33.
Bhui 2012
Black 2008
-
- Black C. Dame Carol Blacks Review of the Health of the Working Age Population ‐ Working for a Healthier Tomorrow. www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/209782... (accessed 14th March 2015).
Boje 2011
-
- Boje D, Burnes B, Hassard J (eds). The Routledge Companion to Organizational Change. London: Routledge, 2011.
Bricheno 2009
-
- Bricheno P, Brown S, Lubansky R, Teacher Support Network. Teacher wellbeing: a review of the evidence, 2009.. teachersupport.info/research‐policy/reports/teacher‐wellbeing (accessed 26 November 2012).
Burnes 1996
-
- Burnes B. No such thing as … a "one best way" to manage organizational change. Management Decision 1996;34(10):11‐8.
Chan 1995
-
- Chan DW, Hui EKP. Burnout and coping among Chinese secondary school teachers in Hong Kong. British Journal of Educational Psychology 1995;65(Part 1):15‐25. - PubMed
Chandola 2008
-
- Chandola T, Britton A, Brunner E, Hemingway H, Malik M, Kumari M, et al. Work stress and coronary heart disease: what are the mechanisms?. European Heart Journal 2008;29(5):640‐8. - PubMed
Cho 2000
-
- Cho BK, Rosenfeldt F, Turina MI, Karp RB, Ferguson TB, Bodnar E, et al. Joint statement on redundant (duplicate) publication by the editors of the undersigned cardiothoracic journals. Annals of Thoracic Surgery 2000;69(2):663. - PubMed
Cooper 2008
-
- Cooper C, Dewe P. Well‐being ‐ absenteeism, presenteeism, costs and challenges. Occupational Medicine 2008;58(8):522‐4. - PubMed
Dawson 1994
-
- Dawson P. Organisational Change: A Processual Approach. London: Paul Chapman, 1994.
Dunham 1992
-
- Dunham J. Stress in Teaching. 2nd Edition. London: Routledge, 1992.
Dunlop 2004
-
- Dunlop C, Macdonald E. The Teachers Health and Wellbeing Study Scotland. Healthy Working Lives Group, University of Glasgow. Published by NHS Health Scotland, Edinburgh. Edinburgh: NHS Health Scotland, 2004.
EuroFound 2007
-
- EuroFound. The Fourth Working Conditions Survey, 2007. www.eurofound.europa.eu/surveys/ewcs/2005/ewcs2005individualchapters.htm. (accessed 26 November 2012). Dublin: Office for Official Publications of the European Communities.
Fimian 1988
-
- Fimian MJ. Teacher Stress Inventory Manual. Brandon, VT: Clinical Psychology Publishing Co, 1988.
Goddard 2006
-
- Goddard R, Goddard M. Beginning teacher burnout in Queensland schools: associations with serious intentions to leave. Australian Educational Researcher 2006;33(2):61‐75.
GRADE 2008 [Computer program]
-
- Brozek J, Oxman A, Schünemann H. GRADEpro. Version 3.2 for Windows. The GRADE working group, 2008.
Grieves 2010
-
- Grieves J. Organizational Change: Theory and Practice. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Hemingway 1999
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hoy 1991
-
- Hoy WK, Tarter CJ, Kottkamp RB. Open Schools/Healthy Schools: Measuring organisational climate. Beverly Hills, CA: Sage, 1991.
HSE 2012
-
- HSE. Self‐reported work‐related illness (SWI) and workplace injuries: results from the Labour Force Survey (LFS), 2012. www.hse.gov.uk/statistics/lfs/index.htm#stress (accessed 26 November 2012).
Huberman 1993
-
- Huberman M. The Lives of Teachers. London: Cassell, 1993.
Karasek 1990
-
- Karasek R, Theorell T. Healthy Work: Stress, Productivity and the Reconstruction of Working Life. New York: Basic Books, 1990.
Kivimäki 2002
Kuper 2003
Kyriacou 2011
-
- Kyriacou C. Teacher stress: from prevalence to resilience. In: Langan‐Fox J, Cooper CL editor(s). Handbook of Stress in the Occupations. Cheltenham: Edward Elgar, 2011:161‐73.
Lambert 2006
-
- Lambert G, McCarthy C (eds). Understanding Teacher Stress in an Age of Accountability. Charlotte, NC: Information Age Publishing, 2006.
Lamontagne 2007
-
- Lamontagne AD, Keegel T, Louie AM, Ostry A, Landsbergis PA. A systematic review of the job‐stress intervention evaluation literature, 1990‐2005. International Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine 2007;13(3):268‐80. - PubMed
Lau 2006
Lazuras 2006
-
- Lazuras L. Occupational stress, negative affectivity and physical health in special and general education teachers in Greece. British Journal of Special Education 2006;33(4):204‐9.
Leka 2003
-
- Leka S, Griffiths A, Cox T, World Health Organization. Work Organization and Stress, 2003. www.who.int/occupational_health/publications/en/oehstress.pdf (accessed 26 November 2012).
Maslach 1996
-
- Maslach C, Jackson SE, Leiter MP. Maslach Burnout Inventory‐Educators Survey (MBI‐ES). In: Maslach C, Jackson SE, Leiter MP editor(s). Maslach Burnout Inventory Manual. 3rd Edition. Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press, 1996:27‐32.
Mind 2011
-
- Mind. 'Taking care of business': Populus Poll for Mind of 2,006 Adults in Employment in England and Wales Between 25 and 28 February 2011, and 4–6 March 2011. London: Mind, 2011.
Murphy 1988
-
- Murphy LR. Workplace interventions for stress reduction and prevention. In: Cooper CL, Payne R editor(s). Causes, Coping and Consequences of Stress at Work. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 1988.
Newman 1979
-
- Newman JE, Beehr TA. Personal and organizational strategies for handling job stress: a review of research and opinion. Personnel Psychology 1979;32(1):1‐43.
North 1996
NUT 2011
-
- NUT National Union of Teachers. Teacher Stress, 2011. www.teachers.org.uk/node/12562 (accessed 26th November 20120.
Osipow 1998
-
- Osipow SH. Occupational stress inventory revised edition (Professional Manual). Columbus, OH: Psychological Assessment Resources Inc, 1998.
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre. The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Roberts 2005
-
- Roberts C, Roberts SA. Design and analysis of clinical trials with clustering effects due to treatment. Clinical Trials 2005;2(2):152‐62. - PubMed
Rothi 2010
-
- Rothi D, Leavey G, Loewenthal K. Teachers’ mental health: a study exploring the experiences of teachers with work‐related stress and mental health problems. London: NASUWT 2010.
Schnall 1994
-
- Schnall PL, Landsbergis PA, Baker D. Job strain and cardiovascular disease. Annual Review of Public Health 1994;15:381‐411. - PubMed
Schwab 1986
-
- Schwab RL, Jackson SE, Schuler RS. Educator burnout: sources and consequences. Educational Research Quarterly 1986;10(3):14‐30.
Siegrist 1996
-
- Siegrist J. Adverse health effects of high‐effort/low‐reward conditions. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology 1996;1(1):27‐41. - PubMed
Siegrist 2004
-
- Siegrist J, Marmot M. Health inequalities and the psychosocial environment‐two scientific challenges. Social Science & Medicine 2004;58:1463‐73. - PubMed
Skaalvik 2009
-
- Skaalvik EM, Skaalvik S. Does school context matter? Relations with teacher burnout and job satisfaction. Teaching and Teacher Education 2009;25(3):518‐24.
Smith 2000
-
- Smith A, Johal SS, Wadsworth E, Davey Smith G, Peters T. The Scale of Occupational Stress ‐ a Further Analysis of the Impact of Demographic Factors and Type of Job; Contract Research Report 311/2000. London: HSE, 2000.
Stansfeld 2006
-
- Stansfeld S, Candy B. Psychosocial work environment and mental health ‐ a meta‐analytic review. Scandinavian Journal of Work, Environment & Health 2006;32(6):443‐62. - PubMed
Steptoe 1999
-
- Steptoe A, Cropley M, Joekes K. Job strain, blood pressure and response to uncontrollable stress. Journal of Hypertension 1999;17:193‐200. - PubMed
Steptoe 2000
-
- Steptoe A, Cropley M, Griffith J, Kirschbaum C. Job strain and anger expression predict early morning elevations in salivary cortisol. Psychosomatic Medicine 2000;62(2):286‐92. - PubMed
Sterne 2011
-
- Sterne JAC, Egger M, Moher D. Chapter 10: Addressing reporting biases. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011:Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Travers 1996
-
- Travers CJ, Cooper CL. Teachers Under Pressure: Stress in the Teaching Profession. London: Routledge, 1996.
Tuomi 1998
-
- Tuomi K, Ilmarinen J, Jahkola A, Katajarinne L, Tulkki A. Work Ability Index. 2nd Edition. Helsinki: Finnish Institute of Occupational Health, 1998.
Vandenberghe 1999
-
- Vandenberghe R, Huberman AM. Understanding and Preventing Teacher Burnout: a Sourcebook of International Research and Practice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1999.
Verbeek 2005
Weiss 1967
-
- Weiss DJ, Dawis RV, England GW, Lofquist LH. Manual for the Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota, Industrial Relations Center, 1967.
WHO 2008
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). PRIMA‐EF Guidance on the European Framework for Psychosocial Risk Management. Protecting Worker's Health Series No.9 2008.
Yang 2011
-
- Yang X, Wang L, Ge C, Hu B, Chi T. Factors associated with occupational strain among Chinese teachers: a cross‐sectional study. Public Health 2011;125(2):106‐13. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

