Methylosome Protein 50 and PKCδ/p38δ Protein Signaling Control Keratinocyte Proliferation via Opposing Effects on p21Cip1 Gene Expression
- PMID: 25851901
- PMCID: PMC4505598
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.642868
Methylosome Protein 50 and PKCδ/p38δ Protein Signaling Control Keratinocyte Proliferation via Opposing Effects on p21Cip1 Gene Expression
Retraction in
-
Withdrawal: Methylosome protein 50 and PKCδ/p38δ protein signaling control keratinocyte proliferation via opposing effects on p21Cip1 gene expression.J Biol Chem. 2025 Oct;301(10):110622. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110622. Epub 2025 Sep 13. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40946420 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
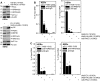
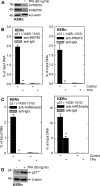
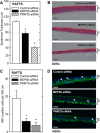
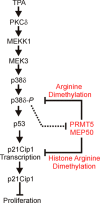
Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) is a key epigenetic regulator that symmetrically dimethylates arginine residues on histones H3 and H4 to silence gene expression. PRMT5 is frequently observed in a complex with the cofactor methylosome protein 50 (MEP50), which is required for PRMT5 activity. PKCδ/p38δ signaling, a key controller of keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation, increases p21(Cip1) expression to suppress keratinocyte proliferation. We now show that MEP50 enhances keratinocyte proliferation and survival via mechanisms that include silencing of p21(Cip1) expression. This is associated with enhanced PRMT5-MEP50 interaction at the p21(Cip1) promoter and enhanced arginine dimethylation of the promoter-associated histones H3 and H4. It is also associated with a MEP50-dependent reduction in the level of p53, a key controller of p21(Cip1) gene expression. We confirm an important biological role for MEP50 and PRMT5 in regulating keratinocyte proliferation using a stratified epidermal equivalent model that mimics in vivo epidermal keratinocyte differentiation. In this model, PRMT5 or MEP50 knockdown results in reduced keratinocyte proliferation. We further show that PKCδ/p38δ signaling suppresses MEP50 expression, leading to reduced H3/H4 arginine dimethylation at the p21(Cip1) promoter, and that this is associated with enhanced p21(Cip1) expression and reduced cell proliferation. These findings describe an opposing action between PKCδ/p38δ MAPK signaling and PRMT5/MEP50 epigenetic silencing mechanisms in regulating cell proliferation.
Keywords: cancer; cell cycle; cyclin; p38 MAPK; protein arginine N-methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5); protein kinase C (PKC).
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
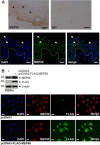
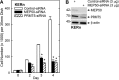
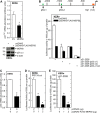
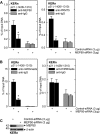
Comment in
-
Findings of Research Misconduct.Fed Regist. 2024 Aug 15;89(158):66420-66422. Fed Regist. 2024. PMID: 39161428 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Efimova T., LaCelle P., Welter J. F., Eckert R. L. (1998) Regulation of human involucrin promoter activity by a protein kinase C, Ras, MEKK1, MEK3, p38/RK, AP1 signal transduction pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 24387–24395 - PubMed
-
- Efimova T., Deucher A., Kuroki T., Ohba M., Eckert R. L. (2002) Novel protein kinase C isoforms regulate human keratinocyte differentiation by activating a p38 δ mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade that targets CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 31753–31760 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

