Thiobenzothiazole-modified Hydrocortisones Display Anti-inflammatory Activity with Reduced Impact on Islet β-Cell Function
- PMID: 25851902
- PMCID: PMC4505588
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.632190
Thiobenzothiazole-modified Hydrocortisones Display Anti-inflammatory Activity with Reduced Impact on Islet β-Cell Function
Abstract
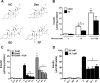
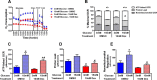
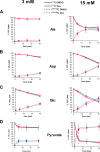
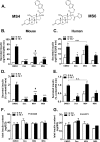
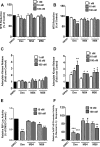
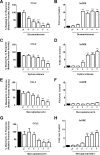
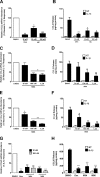
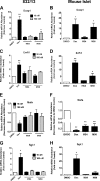
Glucocorticoids signal through the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and are administered clinically for a variety of situations, including inflammatory disorders, specific cancers, rheumatoid arthritis, and organ/tissue transplantation. However, glucocorticoid therapy is also associated with additional complications, including steroid-induced diabetes. We hypothesized that modification of the steroid backbone is one strategy to enhance the therapeutic potential of GR activation. Toward this goal, two commercially unavailable, thiobenzothiazole-containing derivatives of hydrocortisone (termed MS4 and MS6) were examined using 832/13 rat insulinoma cells as well as rodent and human islets. We found that MS4 had transrepression properties but lacked transactivation ability, whereas MS6 retained both transactivation and transrepression activities. In addition, MS4 and MS6 both displayed anti-inflammatory activity. Furthermore, MS4 displayed reduced impact on islet β-cell function in both rodent and human islets. Similar to dexamethasone, MS6 promoted adipocyte development in vitro, whereas MS4 did not. Moreover, neither MS4 nor MS6 activated the Pck1 (Pepck) gene in primary rat hepatocytes. We conclude that modification of the functional groups attached to the D-ring of the hydrocortisone steroid molecule produces compounds with altered structure-function GR agonist activity with decreased impact on insulin secretion and reduced adipogenic potential but with preservation of anti-inflammatory activity.
Keywords: adipogenesis; chemokine; glucocorticoid; inflammation; insulin secretion.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Schäcke H., Döcke W. D., Asadullah K. (2002) Mechanisms involved in the side effects of glucocorticoids. Pharmacol. Ther. 96, 23–43 - PubMed
-
- van Raalte D. H., Diamant M. (2014) Steroid diabetes: from mechanism to treatment? Neth. J. Med. 72, 62–72 - PubMed
-
- Blondeau B., Sahly I., Massouridès E., Singh-Estivalet A., Valtat B., Dorchene D., Jaisser F., Bréant B., Tronche F. (2012) Novel transgenic mice for inducible gene overexpression in pancreatic cells define glucocorticoid receptor-mediated regulations of beta cells. PLoS One 7, e30210. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 DK072476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1P30-DK072476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R44 GM099207/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK089572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK103860/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R44-GM099207/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK103860/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103528/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20-GM103528/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK097829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 8 P20-GM103528/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

