Insulin-like growth factor-1 mRNA isoforms and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor mRNA expression in chronic hepatitis C
- PMID: 25852271
- PMCID: PMC4385533
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i13.3867
Insulin-like growth factor-1 mRNA isoforms and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor mRNA expression in chronic hepatitis C
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the expression of different insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 mRNA isoforms and IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R) mRNA in hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infected livers.
Methods: Thirty-four liver biopsy specimens from chronic hepatitis C (CH-C) patients were obtained before anti-viral therapy. Inflammatory activity (grading) and advancement of fibrosis (staging) were evaluated using a modified point scale of METAVIR. The samples were analyzed using quantitative real-time PCR technique. From fragments of liver biopsies and control liver that were divided and ground in liquid nitrogen, RNA was isolated using RNeasy Fibrous Tissue Mini Kit according to the manufacturer's instruction. Expression levels of IGF-1 mRNA isoforms (IGF-1A, IGF-1B, IGF-1C, P1, and P2) and IGF-1R mRNA were determined through normalization of copy numbers in samples as related to reference genes: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and hydroxymethylbilane synthase. Results on liver expression of the IGF-1 mRNA isoforms and IGF-1R transcript were compared to histological alterations in liver biopsies and with selected clinical data in the patients. Statistical analysis was performed using Statistica PL v. 9 software.
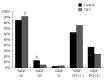
Results: The study showed differences in quantitative expression of IGF-1 mRNA variants in HCV-infected livers, as compared to the control. Higher relative expression of total IGF-1 mRNA and of IGF-1 mRNAs isoforms (P1, A, and C) in HCV-infected livers as compared to the control were detected. Within both groups, expression of the IGF-1A mRNA isoform significantly prevailed over expressions of B and C isoforms. Expression of P1 mRNA was higher than that of P2 only in CH-C. Very high positive correlations were detected between reciprocal expressions of IGF-1 mRNA isoforms P1 and P2 (r = 0.876). Expression of P1 and P2 mRNA correlated with IGF-1A mRNA (r = 0.891; r = 0.821, respectively), with IGF-1B mRNA (r = 0.854; r = 0.813, respectively), and with IGF-1C mRNA (r = 0.839; r = 0.741, respectively). Expression of IGF-1A mRNA significantly correlated with isoform B and C mRNA (r = 0.956; r = 0.869, respectively), and B with C isoforms (r = 0.868) (P < 0.05 in all cases). Lower expression of IGF-1A and B transcripts was noted in the more advanced liver grading (G2) as compared to G1. Multiple negative correlations were detected between expression of various IGF-1 transcripts and clinical data (e.g., alpha fetoprotein, HCV RNA, steatosis, grading, and staging). Expression of IGF-1R mRNA manifested positive correlation with grading and HCV-RNA.
Conclusion: Differences in quantitative expression of IGF-1 mRNA isoforms in HCV-infected livers, as compared to the control, suggest that HCV may induce alteration of IGF-1 splicing profile.
Keywords: Chronic hepatitis C; Insulin-like growth factor-1 mRNA isoforms; Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor; Quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
Figures


References
-
- Kasprzak A, Adamek A. The insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signaling axis and hepatitis C virus-associated carcinogenesis (review) Int J Oncol. 2012;41:1919–1931. - PubMed
-
- Tsai TF, Yauk YK, Chou CK, Ting LP, Chang C, Hu CP, Han SH, Su TS. Evidence of autocrine regulation in human hepatoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988;153:39–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

