Interferon-λ3 polymorphisms in pegylated-interferon-α plus ribavirin therapy for genotype-2 chronic hepatitis C
- PMID: 25852275
- PMCID: PMC4385537
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i13.3904
Interferon-λ3 polymorphisms in pegylated-interferon-α plus ribavirin therapy for genotype-2 chronic hepatitis C
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate interferon-λ3 (IFNL3) polymorphisms in response-guided pegylated interferon-α plus ribavirin (Peg-IFNα/RBV) therapy for genotype 2 (G2) chronic hepatitis C.
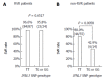
Methods: Between January 2006 and June 2012, a total of 180 patients with chronic infections of G2 hepatitis C virus (HCV) were treated with response-guided Peg-IFNα/RBV therapy. The treatment duration was 24 wk for patients who achieved rapid virologic response (RVR), and 36 or 48 wk for patients who did not. Then, the impact of the IFNL3 single nucleotide polymorphism genotype (TT/non-TT at rs8099917) on treatment outcomes was evaluated in the 180 patients, and between patients infected with either HCV sub-genotype 2a or 2b.
Results: Of the 180 patients evaluated, 111 achieved RVR, while the remaining 69 patients did not. In RVR patients, the sustained virologic response (SVR) rate was 96.4%, and the IFNL3 genotype did not influence the SVR rate (96.6% vs 95.8% in IFNL3 genotype TT vs non-TT). However, in non-RVR patients, the SVR rate decreased to 72.5% (P < 0.0001), and this rate was significantly different between the IFNL3 genotype TT and non-TT groups (80.0% vs 42.9%, P = 0.0146). Multivariate regression analysis in non-RVR patients identified the IFNL3 genotype TT as the only baseline-significant factor associated with SVR (OR = 5.39, 95%CI: 1.29-22.62; P = 0.0189). In analysis according to HCV sub-genotype, no significant difference in the SVR rate was found between HCV sub-genotypes 2a and 2b.
Conclusion: In response-guided Peg-IFNα/RBV combination therapy for chronically HCV G2-infected patients, the impact of the IFNL3 genotype on SVR was limited to non-RVR patients.
Keywords: Hepatitis C virus genotype 2; Interferon-λ3 single nucleotide polymorphism; Pegylated-interferon plus ribavirin response-guided therapy; Rapid virologic response; Sustained virologic response.
Figures


References
-
- Tsubota A, Kumada H, Chayama K, Arase Y, Saitoh S, Koida I, Murashima N, Suzuki Y, Kobayashi M, Takagi K, et al. Relationship between pretreatment viremia level and response to interferon-alpha therapy in chronic hepatitis C differs in viral type 1 and 2 infections. Dig Dis Sci. 1996;41:1925–1932. - PubMed
-
- Tsubota A, Chayama K, Arase Y, Koida I, Saitoh S, Ikeda K, Iwasaki S, Matsumoto T, Kobayashi M, Kumada H. Factors useful in predicting the response to interferon therapy in chronic hepatitis C. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1993;8:535–539. - PubMed
-
- Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Rustgi VK, Shiffman M, Reindollar R, Goodman ZD, Koury K, Ling M, Albrecht JK. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001;358:958–965. - PubMed
-
- Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, Smith C, Marinos G, Gonçales FL, Häussinger D, Diago M, Carosi G, Dhumeaux D, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:975–982. - PubMed
-
- Sato K, Hashizume H, Yamazaki Y, Horiguchi N, Kakizaki S, Takagi H, Mori M. Response-guided peginterferon-alpha-2b plus ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C patients with genotype 2 and high viral loads. Hepatol Res. 2012;42:854–863. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

