Decreased STAT4 indicates poor prognosis and enhanced cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 25852285
- PMCID: PMC4385547
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i13.3983
Decreased STAT4 indicates poor prognosis and enhanced cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the role of signal transduction and activation of transcription 4 (STAT4) in the development and progression of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
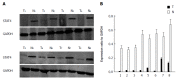
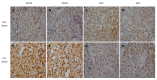
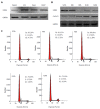
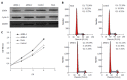
Methods: Recent genetic investigations have identified that a genetic variant of STAT4 is associated with hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related HCC. The level of STAT4 in 90 HCC patients was examined via Western blot and immunohistochemical analyses. The correlation between STAT4 expression and the clinicopathological characteristics of the patients was analyzed. The level of STAT4 expression in the HCC liver tissues was significantly lower than that in the non-HCC liver tissues and correlated with tumor size, histological grade of HCC and serum hepatitis B surface antigen level in HCC patients. The data were statistically analyzed using SPSS. Furthermore, siRNA oligos targeting STAT4 were employed to investigate the influence of STAT4 RNA interference on HCC cell physiology. Based on Cell Counting Kit-8 and flow cytometric assays, we found that depletion of STAT4 expression significantly enhanced the proliferation of L02 cells.
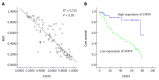
Results: STAT4 protein expression was significantly lower in HCC tissues than in normal liver tissues. Immunohistochemistry followed by statistical analysis revealed that the expression of STAT4 negatively correlated with Ki67 expression (r = 0.851; P < 0.05) and positively correlated with maximal tumor size (P < 0.05), HBV (P = 0.012) and histological grade (P < 0.05). Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed significant differences in the survival curves between HCC patients expressing low and high levels of STAT4 and Ki67 (P < 0.05). Based on a multivariate Cox proportional hazard model, STAT4 expression was an independent prognostic indicator for HCC patients who underwent curative resection. In vitro, following the release of L02 cell lines from serum starvation, the expression of STAT4 was downregulated, and transfection of L02 cells with siRNA targeting STAT4 inhibited cell proliferation.
Conclusion: Our data indicate that STAT4 may inhibit HCC development by modulating HCC cell proliferation.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Prognosis; Proliferation; Signal transduction and activation of transcription 4.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Makuuchi M, Imamura H, Sugawara Y, Takayama T. Progress in surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology. 2002;62 Suppl 1:74–81. - PubMed
-
- Wang XM, Yang LY, Guo L, Fan C, Wu F. p53-induced RING-H2 protein, a novel marker for poor survival in hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatic resection. Cancer. 2009;115:4554–4563. - PubMed
-
- Hung JH, Lu YS, Wang YC, Ma YH, Wang DS, Kulp SK, Muthusamy N, Byrd JC, Cheng AL, Chen CS. FTY720 induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through activation of protein kinase C delta signaling. Cancer Res. 2008;68:1204–1212. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

