The alteration of gray matter volume and cognitive control in adolescents with internet gaming disorder
- PMID: 25852507
- PMCID: PMC4367166
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00064
The alteration of gray matter volume and cognitive control in adolescents with internet gaming disorder
Abstract
Objective: Internet gaming disorder (IGD) has been investigated by many behavioral and neuroimaging studies, for it has became one of the main behavior disorders among adolescents. However, few studies focused on the relationship between alteration of gray matter volume (GMV) and cognitive control feature in IGD adolescents.
Methods: Twenty-eight participants with IAD and twenty-eight healthy age and gender matched controls participated in the study. Brain morphology of adolescents with IGD and healthy controls was investigated using an optimized voxel-based morphometry (VBM) technique. Cognitive control performances were measured by Stroop task, and correlation analysis was performed between brain structural change and behavioral performance in IGD group.
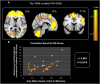
Results: The results showed that GMV of the bilateral anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), precuneus, supplementary motor area (SMA), superior parietal cortex, left dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), left insula, and bilateral cerebellum decreased in the IGD participants compared with healthy controls. Moreover, GMV of the ACC was negatively correlated with the incongruent response errors of Stroop task in IGD group.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that the alteration of GMV is associated with the performance change of cognitive control in adolescents with IGD, which indicating substantial brain image effects induced by IGD.
Keywords: anterior cingulate cortex; cognitive control; color-word stroop; gray matter; internet addiction disorder.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gray matter differences in the anterior cingulate and orbitofrontal cortex of young adults with Internet gaming disorder: Surface-based morphometry.J Behav Addict. 2018 Mar 1;7(1):21-30. doi: 10.1556/2006.7.2018.20. Epub 2018 Mar 13. J Behav Addict. 2018. PMID: 29529887 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal Granger causal connectivity based on altered gray matter volume and associated neurotransmitters of adolescents with internet gaming disorder revealed by a multimodal neuroimaging study.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2024 Dec;70:101472. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2024.101472. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39486388 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal prefrontal cortex resting state functional connectivity and severity of internet gaming disorder.Brain Imaging Behav. 2016 Sep;10(3):719-29. doi: 10.1007/s11682-015-9439-8. Brain Imaging Behav. 2016. PMID: 26311395
-
Meta-analysis of structural and functional brain alterations in internet gaming disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Oct 25;13:1029344. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1029344. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 37033880 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Functional Brain Abnormalities in Internet Gaming Disorder and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Comparative Meta-Analysis.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Jul 1;12:679437. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.679437. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34276447 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Discriminating Pathological and Non-pathological Internet Gamers Using Sparse Neuroanatomical Features.Front Psychiatry. 2018 Jun 29;9:291. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00291. eCollection 2018. Front Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30008681 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Differences in Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD): From Psychological Features to Neuroanatomical Networks.J Clin Med. 2022 Feb 16;11(4):1018. doi: 10.3390/jcm11041018. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35207293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroscience of Internet Pornography Addiction: A Review and Update.Behav Sci (Basel). 2015 Sep 18;5(3):388-433. doi: 10.3390/bs5030388. Behav Sci (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26393658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Classifying problematic gaming using a latent profile approach based on personality traits in Chinese young adolescent.BMC Psychiatry. 2025 Feb 6;25(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s12888-025-06561-5. BMC Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39915799 Free PMC article.
-
Altered amygdala-related structural covariance and resting-state functional connectivity in end-stage renal disease patients.Metab Brain Dis. 2018 Oct;33(5):1471-1481. doi: 10.1007/s11011-018-0254-y. Epub 2018 Jun 4. Metab Brain Dis. 2018. PMID: 29869149
References
-
- Andersson J., Jenkinson M., Smith S. (2007). Non-Linear Registration, Aka Spatial Normalisation. FMRIB Analysis Group Technical Reports: TR07JA02; Available online at: www.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/analysis/techrep
-
- Block J. J. (2007). Prevalence underestimated in problematic internet use study. CNS Spectr. 12, 14–15. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources