Interferon α Therapy in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Infection: Quality of Life and Depression
- PMID: 25852845
- PMCID: PMC4378202
- DOI: 10.4081/hr.2015.5632
Interferon α Therapy in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Infection: Quality of Life and Depression
Abstract
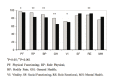
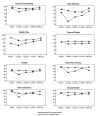
Health-related quality of life was examined in 49 patients with hepatitis C virus with no psychiatric history who received interferon (IFN)-α treatment. Quality of life was assessed at baseline, at 3-time points during IFN-α therapy and at 1-6 month follow-up, using SF-36. Hepatitis C virus patients showed poorer physical functioning and better social and mental functioning than a normal population. Significant decreases from baseline SF-36 scores were observed at an early phase of treatment. Six patients developed major depression during IFN-α treatment. At baseline, they had reported more bodily pain than patients who did not develop depression during treatment. Planned contrasts revealed that worsening in some dimensions of quality of life at 2 months was greater in depressed than in non-depressed patients. Results suggest that depressive symptoms should be accurately monitored during IFN-α therapy even in patients with no psychiatric history, especially if they present with bodily pain.
Keywords: HCV; depression; interferon; quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: the authors declare no potential conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Pockros PJ. Developments in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2002;11:515-28. - PubMed
-
- Strader DB, Wright T, Thomas DL, Seeff LB. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C. Hepatology 2004;39:1147-71. - PubMed
-
- Rowan PJ, Al-Jurdi R, Tavakoli-Tabasi S, et al. Physical and psychosocial contributors to quality of life in veterans with hepatitis C not on antiviral therapy. J Clin Gastroenterol 2005;39:731-6. - PubMed
-
- Spiegel BM, Younossi ZM, Hays RD, et al. Impact of hepatitis C on health related quality of life: a systematic review and quantitative assessment. Hepatology 2005;41:790-800. - PubMed
-
- Taliani G, Rucci P, Biliotti E, et al. Therapy expectations and physical comorbidity affect quality of life in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J Vir Hep 2007;14:875-82. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources