Identifying erlotinib-sensitive non-small cell lung carcinoma tumors in mice using [(11)C]erlotinib PET
- PMID: 25853010
- PMCID: PMC4385014
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-014-0080-0
Identifying erlotinib-sensitive non-small cell lung carcinoma tumors in mice using [(11)C]erlotinib PET
Abstract
Background: Non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) represents approximately 80% of lung cancer cases, and over 60% of these tumors express the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Activating mutations in the tyrosine kinase (TK) domain of the EGFR are detected in 10% to 30% of NSCLC patients, and evidence of their presence is a prerequisite for initiation of first-line therapy with selective TK inhibitors (TKIs), such as gefitinib and erlotinib. To date, the selection of candidate patients for first-line treatment with EGFR TKIs requires an invasive tumor biopsy to affirm the mutational status of the receptor. This study was designed to evaluate whether positron emission tomography (PET) of NSCLC tumor-bearing mice using [(11)C]erlotinib could distinguish erlotinib-sensitive from erlotinib-insensitive or erlotinib-resistant tumors.
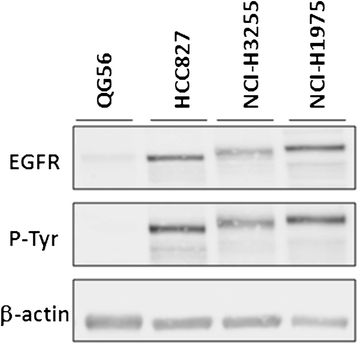
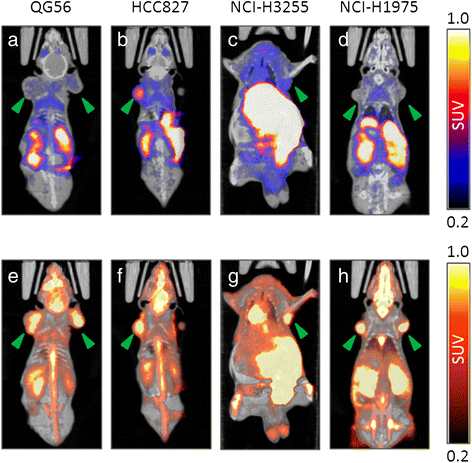
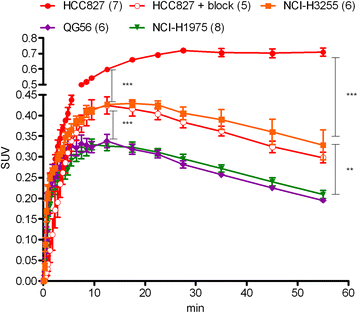
Methods: Four human NSCLC cell lines were employed, expressing either of the following forms of the EGFR: (i) the wild-type receptor (QG56 cells), (ii) a mutant with an exon 19 in-frame deletion (HCC827 cells), (iii) a mutant with the exon 21 L858R point mutation (NCI-H3255 cells), and (iv) a double mutant harboring the L858R and T790M mutations (NCI-H1975 cells). Sensitivity of each cell line to the anti-proliferative effect of erlotinib was determined in vitro. In vivo PET imaging studies following i.v. injection of [(11)C]erlotinib were carried out in nude mice bearing subcutaneous (s.c.) xenografts of the four cell lines.
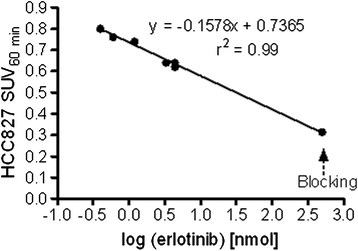
Results: Cells harboring activating mutations in the EGFR TK domain (HCC827 and NCI-H3255) were approximately 1,000- and 100-fold more sensitive to erlotinib treatment in vitro, respectively, compared to the other two cell lines. [(11)C]Erlotinib PET scans could differentiate erlotinib-sensitive tumors from insensitive (QG56) or resistant (NCI-H1975) tumors already at 12 min after injection. Nonetheless, the uptake in HCC827 tumors was significantly higher than that in NCI-H3255, possibly reflecting differences in ATP and erlotinib affinities between the EGFR mutants.
Conclusions: [(11)C]Erlotinib imaging in mice differentiates erlotinib-sensitive NSCLC tumors from erlotinib-insensitive or erlotinib-resistant ones.
Keywords: EGFR; Imaging; NSCLC; PET; TKI; [11C]Erlotinib.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A comparative PET imaging study with the reversible and irreversible EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors [(11)C]erlotinib and [(18)F]afatinib in lung cancer-bearing mice.EJNMMI Res. 2015 Mar 20;5:14. doi: 10.1186/s13550-015-0088-0. eCollection 2015. EJNMMI Res. 2015. PMID: 25853020 Free PMC article.
-
[11C]Erlotinib PET cannot detect acquired erlotinib resistance in NSCLC tumor xenografts in mice.Nucl Med Biol. 2017 Sep;52:7-15. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2017.05.007. Epub 2017 May 25. Nucl Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28575795
-
3'-deoxy-3'-18F-fluorothymidine PET/CT to guide therapy with epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists and Bcl-xL inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer.J Nucl Med. 2012 Mar;53(3):443-50. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.111.096503. Epub 2012 Feb 13. J Nucl Med. 2012. PMID: 22331221
-
[11C]N-(3-Ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-quinazolinamine.2009 May 18 [updated 2009 Jun 18]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2009 May 18 [updated 2009 Jun 18]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641864 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Optimizing the sequencing of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Lung Cancer. 2019 Nov;137:113-122. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.09.017. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31568888 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo PET Imaging of EGFR Expression: An Overview of Radiolabeled EGFR TKIs.Curr Top Med Chem. 2022;22(28):2329-2342. doi: 10.2174/1568026622666220903142416. Curr Top Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36056825
-
Real-time molecular optical micro-imaging of EGFR mutations using a fluorescent erlotinib based tracer.BMC Pulm Med. 2019 Jan 7;19(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12890-018-0760-z. BMC Pulm Med. 2019. PMID: 30612556 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying and correcting for tail vein extravasation in small animal PET scans in cancer research: is there an impact on therapy assessment?EJNMMI Res. 2015 Dec;5(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13550-015-0141-z. Epub 2015 Nov 5. EJNMMI Res. 2015. PMID: 26543028 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical development of G1T38: A novel, potent and selective inhibitor of cyclin dependent kinases 4/6 for use as an oral antineoplastic in patients with CDK4/6 sensitive tumors.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 27;8(26):42343-42358. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16216. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28418845 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of fully-automated radiosyntheses of [11C]erlotinib for preclinical and clinical use starting from in target produced [11C]CO2 or [11C]CH4.EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2018;3(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s41181-018-0044-1. Epub 2018 May 30. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2018. PMID: 29888317 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen P, Cameron R, Wang J, Vallis KA, Reilly RM. Antitumor effects and normal tissue toxicity of 111In-labeled epidermal growth factor administered to athymic mice bearing epidermal growth factor receptor-positive human breast cancer xenografts. J Nucl Med. 2003;44:1469–78. - PubMed
-
- Mamot C, Drummond DC, Greiser U, Hong K, Kirpotin DB, Marks JD, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeted immunoliposomes mediate specific and efficient drug delivery to EGFR- and EGFRvIII-overexpressing tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2003;63:3154–61. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

