The diagnostic accuracy of dopamine transporter SPECT imaging to detect nigrostriatal cell loss in patients with Parkinson's disease or clinically uncertain parkinsonism: a systematic review
- PMID: 25853018
- PMCID: PMC4385258
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-015-0087-1
The diagnostic accuracy of dopamine transporter SPECT imaging to detect nigrostriatal cell loss in patients with Parkinson's disease or clinically uncertain parkinsonism: a systematic review
Abstract
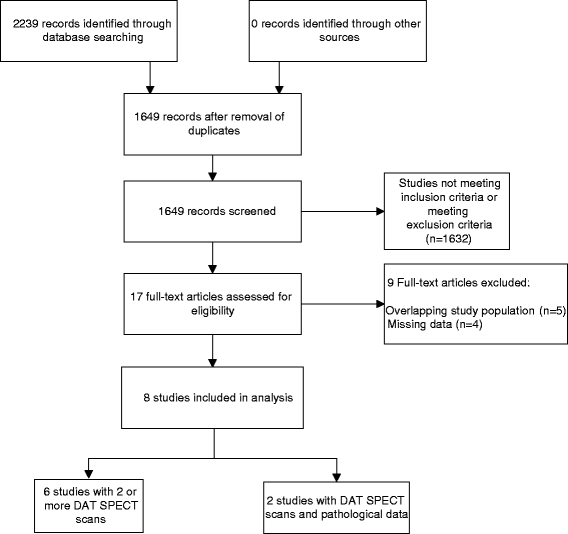
In specialized movement disorder centers, Parkinson's disease (PD) is wrongly diagnosed in 6 to 25% of cases. To improve the accuracy of the clinical diagnosis, it is necessary to have a reliable and practical reference standard. Dopamine transporter single-photon emission computed tomography (DAT SPECT) imaging might have the potential (high diagnostic accuracy and practical to use) to act as reference standard in detecting nigrostriatal cell loss in patients with (early stage) parkinsonism. We performed a systematic review to evaluate if DAT SPECT imaging can be used as such. Relevant studies were searched in the MEDLINE and EMBASE databases. Studies were selected when they met the following criteria: (1) all patients were adults with a clinical diagnosis of PD or clinically uncertain parkinsonism and (2) the study reported original data. In addition, studies needed to fulfill one of the two following criteria: (1) patients underwent at least one DAT SPECT and had a neuropathological confirmed diagnosis and (2) patients underwent at least two DAT SPECT scans, performed at least 2 years apart. The search identified 1,649 articles. Eight studies fulfilled our selection criteria and were included in this review. There was only one study including patients with diagnostic uncertainty. Sensitivity and specificity of DAT SPECT imaging to detect nigrostriatal cell loss were 98%. The other studies included patients with a diagnosis of PD in whom there was no uncertainty. In these studies, sensitivity was 100%. Our systematic review indicates that DAT SPECT imaging seems to be accurate to detect nigrostriatal cell loss in patients with parkinsonism.
Keywords: Clinical diagnosis; Diagnostic accuracy; Dopamine transporter; Nigrostriatal cell loss; Parkinsonism; Parkinson’s disease; Single-photon emission computed tomography.
Similar articles
-
Dopamine transporter imaging as a diagnostic tool for parkinsonism and related disorders in clinical practice.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2015 Feb;21(2):87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.11.007. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2015. PMID: 25487733 Review.
-
Nuclear Imaging in the Diagnosis of Clinically Uncertain Parkinsonian Syndromes.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019 Nov 1;116(44):747-754. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2019.0747. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019. PMID: 31774054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopamine transporter density measured by [123I]beta-CIT single-photon emission computed tomography is normal in dopa-responsive dystonia.Ann Neurol. 1998 Jun;43(6):792-800. doi: 10.1002/ana.410430614. Ann Neurol. 1998. PMID: 9629849
-
Dopamine transporter single photon emission computed tomography (DaT-SPECT) use in the diagnosis and clinical management of parkinsonism: an 8-year retrospective study.J Neurol. 2023 May;270(5):2550-2558. doi: 10.1007/s00415-023-11563-y. Epub 2023 Feb 16. J Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36795149 Free PMC article.
-
SPECT Molecular Imaging in Familial Parkinson's Disease.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2018;142:225-260. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2018.09.004. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 30409254 Review.
Cited by
-
Computed-tomography-guided anatomic standardization for quantitative assessment of dopamine transporter SPECT.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017 Mar;44(3):366-372. doi: 10.1007/s00259-016-3496-0. Epub 2016 Aug 20. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017. PMID: 27544223
-
The predictive value of SS-16 in clinically diagnosed Parkinson's disease patients: comparison with (99m)Tc-TRODAT-1 SPECT scans.Transl Neurodegener. 2016 Aug 20;5:15. doi: 10.1186/s40035-016-0062-4. eCollection 2016. Transl Neurodegener. 2016. PMID: 27547386 Free PMC article.
-
Inclusion of quasi-vertex views in a brain-dedicated multi-pinhole SPECT system for improved imaging performance.Phys Med Biol. 2021 Jan 27;66(3):035007. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/abc22e. Phys Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33065564 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of Axial and Angular Sampling in Multi-Detector Pinhole-SPECT Brain Imaging.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2020 Dec;39(12):4209-4224. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2020.3015079. Epub 2020 Nov 30. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32763850 Free PMC article.
-
Data-driven, voxel-based analysis of brain PET images: Application of PCA and LASSO methods to visualize and quantify patterns of neurodegeneration.PLoS One. 2018 Nov 5;13(11):e0206607. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206607. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30395576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Rijk MC, Tzourio C, Breteler MM, Dartigues JF, Amaducci L, Lopez-Pouza S, et al. Prevalence of parkinsonism and Parkinson’s disease in Europe: the EUROPARKINSON Collaborative Study. European Community Concerted Action on the Epidemiology of Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997;62:10–5. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.62.1.10. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous