Endocrine-disrupting Chemicals: Review of Toxicological Mechanisms Using Molecular Pathway Analysis
- PMID: 25853100
- PMCID: PMC4384711
- DOI: 10.15430/JCP.2015.20.1.12
Endocrine-disrupting Chemicals: Review of Toxicological Mechanisms Using Molecular Pathway Analysis
Abstract
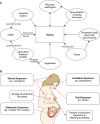
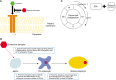
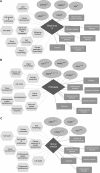
Endocrine disruptors are known to cause harmful effects to human through various exposure routes. These chemicals mainly appear to interfere with the endocrine or hormone systems. As importantly, numerous studies have demonstrated that the accumulation of endocrine disruptors can induce fatal disorders including obesity and cancer. Using diverse biological tools, the potential molecular mechanisms related with these diseases by exposure of endocrine disruptors. Recently, pathway analysis, a bioinformatics tool, is being widely used to predict the potential mechanism or biological network of certain chemicals. In this review, we initially summarize the major molecular mechanisms involved in the induction of the above mentioned diseases by endocrine disruptors. Additionally, we provide the potential markers and signaling mechanisms discovered via pathway analysis under exposure to representative endocrine disruptors, bisphenol, diethylhexylphthalate, and nonylphenol. The review emphasizes the importance of pathway analysis using bioinformatics to finding the specific mechanisms of toxic chemicals, including endocrine disruptors.
Keywords: Endocrine disruptors; Molecular mechanism; Obesogen; Pathway analysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exposure to endocrine disruptors during adulthood: consequences for female fertility.J Endocrinol. 2017 Jun;233(3):R109-R129. doi: 10.1530/JOE-17-0023. Epub 2017 Mar 29. J Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28356401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances on bisphenol-A and endocrine disruptor effects on human prostate cancer.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017 Dec 5;457:35-42. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2017.02.045. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28257827 Review.
-
Endocrine Disruptors and Obesity.Curr Obes Rep. 2017 Mar;6(1):18-27. doi: 10.1007/s13679-017-0240-4. Curr Obes Rep. 2017. PMID: 28205155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review on endocrine disruptors and their possible impacts on human health.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015 Jul;40(1):241-58. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2015.06.009. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26164742 Review.
-
Transgenerational Effects of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals on Male and Female Reproduction.Endocrinology. 2019 Jun 1;160(6):1421-1435. doi: 10.1210/en.2019-00034. Endocrinology. 2019. PMID: 30998239 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mediterranean Diet as a Shield against Male Infertility and Cancer Risk Induced by Environmental Pollutants: A Focus on Flavonoids.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 29;23(3):1568. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031568. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental cadmium exposure and the risk of kidney stones: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 30;12:1555028. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1555028. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40809422 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of wheat species (Triticum aestivum vs T. spelta), farming system (organic vs conventional) and flour type (wholegrain vs white) on composition of wheat flour - Results of a retail survey in the UK and Germany - 3. Pesticide residue content.Food Chem X. 2020 Mar 29;7:100089. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2020.100089. eCollection 2020 Sep 30. Food Chem X. 2020. PMID: 32637911 Free PMC article.
-
An inhibitor of 11-β hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (PF915275) alleviates nonylphenol-induced hyperadrenalism and adiposity in rat and human cells.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018 Jul 18;19(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s40360-018-0235-0. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 30021644 Free PMC article.
-
Risks and benefits related to alimentary exposure to xenoestrogens.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017 Nov 2;57(16):3384-3404. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2015.1126547. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017. PMID: 26744831 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- National Institute of Environmental Health Science. Endocrine disruptors fact sheet. Available from: http://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/materials/endocrine_disruptors_508.pdf. Accessed May, 2010.
-
- Charles JW. Changes in indoor pollutants since the 1950s. Atmos Environ. 2009;43:153–69. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.09.044. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
