Unveiling the potential of novel yeast protein extracts in white wines clarification and stabilization
- PMID: 25853122
- PMCID: PMC4364169
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2015.00020
Unveiling the potential of novel yeast protein extracts in white wines clarification and stabilization
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Unveiling the potential of novel yeast protein extracts in white wines clarification and stabilization.Front Chem. 2015 May 8;3:31. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2015.00031. eCollection 2015. Front Chem. 2015. PMID: 26005671 Free PMC article.
Abstract
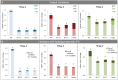
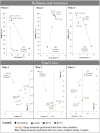
Fining agents derived from animal and mineral sources are widely used to clarify and stabilize white wines. Nevertheless, health and environmental problems are being raised, concerning the allergenic and environmental impact of some of those fining products. In this study, our aim is to validate the potential of yeast protein extracts, obtained from an alternative and safe source, naturally present in wine: oenological yeasts. Three untreated white wines were used in this work in order to evaluate the impact of these novel yeast protein extracts (YPE) in terms of the wine clarification and stabilization improvement. Two separated fining trials were thus conducted at laboratory scale and the yeast alternatives were compared with reference fining agents, obtained from mineral, animal and vegetable origins. Our results indicate that YPE were capable to promote (i) brilliance/color improvement, (ii) turbidity reduction (76-89% comparing with the untreated wines), and (iii) production of compact and homogeneous lees (44% smaller volume than obtained with bentonite). Additionally, after submitting wines to natural and forced oxidations, YPE treatments revealed (iv) different forms of colloidal stabilization, by presenting comparable or superior effects when particularly compared to casein. Altogether, this study reveals that YPE represent a promising alternative for white wine fining, since they are resultant from a natural and more sustainable origin, at present not regarded as potential allergenic according to Regulation (EC) No. 1169/2011.
Keywords: browning potential; clarification; fining agents; oxidation; protein content; white wine; yeast protein extracts.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Wine Fining with Plant Proteins.Molecules. 2019 Jun 11;24(11):2186. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112186. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31212597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of Potential Yeast Protein Extracts for Red Wine Clarification and Stabilization.Front Microbiol. 2019 Oct 9;10:2310. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02310. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31649649 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of wine manufacturing practice on the occurrence of fining agents with allergenic potential.Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2014;31(11):1805-17. doi: 10.1080/19440049.2014.963700. Epub 2014 Oct 9. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2014. PMID: 25208236
-
Study of the potential use of mesoporous nanomaterials as fining agent to prevent protein haze in white wines and its impact in major volatile aroma compounds and polyols.Food Chem. 2018 Feb 1;240:751-758. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.07.163. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 28946339
-
Determination of trace levels of organic fining agents in wines: Latest and relevant findings.Front Chem. 2022 Aug 5;10:944021. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.944021. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35991603 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Wine Fining with Plant Proteins.Molecules. 2019 Jun 11;24(11):2186. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112186. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31212597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Plant-Based Byproducts as Green Fining Agents for Precision Winemaking.Molecules. 2022 Mar 3;27(5):1671. doi: 10.3390/molecules27051671. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35268772 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Potential Yeast Protein Extracts for Red Wine Clarification and Stabilization.Front Microbiol. 2019 Oct 9;10:2310. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02310. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31649649 Free PMC article.
-
Upcycling Rocha do Oeste Pear Pomace as a Sustainable Food Ingredient: Composition, Rheological Behavior and Microstructure Alone and Combined with Yeast Protein Extract.Molecules. 2022 Dec 25;28(1):179. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010179. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615374 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achaerandio I., Pachova V., Guell C., Lopez F. (2001). Protein adsorption by bentonite in a white wine model solution: effect of protein molecular weight and ethanol concentration. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 52, 122–126.
-
- Armada L., Falque E. (2007). Repercussion of the clarification treatment agents before the alcoholic fermentation on volatile composition of white wines. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 225, 553–558 10.1007/s00217-006-0453-3 - DOI
-
- Benucci I., Esti M., Liburdi K. (2014). Effect of free and immobilised stem bromelain on protein haze in white wine. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 20, 347–352 10.1111/ajgw.12093 - DOI
-
- Blade W. H., Boulton R. (1988). Adsorption of protein by bentonite in a model wine solution. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 39, 193–199.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

