Physiological responses of Kosteletzkya virginica to coastal wetland soil
- PMID: 25853144
- PMCID: PMC4379433
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/354581
Physiological responses of Kosteletzkya virginica to coastal wetland soil
Abstract
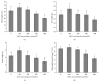
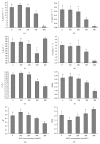
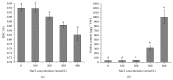
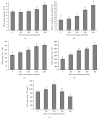
Effects of salinity on growth and physiological indices of Kosteletzkya virginica seedlings were studied. Plant height, fresh weight (FW), dry weight (DW), and net photosynthetic rate (Pn) increased at 100 mM NaCl and slightly declined at 200 mM, but higher salinity induced a significant reduction. Chlorophyll content, stomatal conductance (Gs), intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci), and transpiration rate (E) were not affected under moderate salinities, while markedly decreased at severe salinities except for the increased Ci at 400 mM NaCl. Furthermore, no significant differences of Fv/Fm and ΦPSII were found at lower than 200 mM NaCl, whereas higher salinity caused the declines of Fv/Fm, ΦPSII, and qP similar to Pn, accompanied with higher NPQ. Besides, salt stress reduced the leaf RWC, but caused the accumulation of proline to alleviate osmotic pressure. The increased activities of antioxidant enzymes maintained the normal levels of MDA and relative membrane permeability. To sum up, Kosteletzkya virginica seedlings have good salt tolerance and this may be partly attributed to its osmotic regulation and antioxidant capacity which help to maintain water balance and normal ROS level to ensure the efficient photosynthesis. These results provided important implications for Kosteletzkya virginica acting as a promising multiuse species for reclaiming coastal soil.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antioxidant enzyme activities and hormonal status in response to Cd stress in the wetland halophyte Kosteletzkya virginica under saline conditions.Physiol Plant. 2013 Mar;147(3):352-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2012.01667.x. Epub 2012 Jul 30. Physiol Plant. 2013. PMID: 22697433
-
Effects of concentrations of sodium chloride on photosynthesis, antioxidative enzymes, growth and fiber yield of hybrid ramie.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014 Mar;76:86-93. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.12.021. Epub 2014 Jan 13. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24486583
-
Effects of di-n-butyl phthalate and di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate on the growth, photosynthesis, and chlorophyll fluorescence of wheat seedlings.Chemosphere. 2016 May;151:76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.02.061. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Chemosphere. 2016. PMID: 26928333
-
Wheat cultivars selected for high Fv /Fm under heat stress maintain high photosynthesis, total chlorophyll, stomatal conductance, transpiration and dry matter.Physiol Plant. 2015 Feb;153(2):284-98. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12245. Epub 2014 Aug 8. Physiol Plant. 2015. PMID: 24962705
-
Kosteletzkya pentacarpos: A Potential Halophyte Candidate for Phytoremediation in the Meta(loid)s Polluted Saline Soils.Plants (Basel). 2021 Nov 18;10(11):2495. doi: 10.3390/plants10112495. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34834857 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
KvLEA, a New Isolated Late Embryogenesis Abundant Protein Gene from Kosteletzkya virginica Responding to Multiabiotic Stresses.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:9823697. doi: 10.1155/2016/9823697. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27123459 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Analyses of Transcriptome and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Characteristics Reveal the Mechanism Underlying Saline-Alkali Stress Tolerance in Kosteletzkya pentacarpos.Front Plant Sci. 2022 May 6;13:865572. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.865572. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35599866 Free PMC article.
-
The Tonoplast Intrinsic Protein Gene KvTIP3 is Responsive to Different Abiotic Stresses in Kosteletzkya virginica.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jan 2;2020:2895795. doi: 10.1155/2020/2895795. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31998785 Free PMC article.
-
Proline accumulation and metabolism-related genes expression profiles in Kosteletzkya virginica seedlings under salt stress.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Sep 29;6:792. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00792. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26483809 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of KvCHX Enhances Salt Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana Seedlings.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Dec 1;45(12):9692-9708. doi: 10.3390/cimb45120605. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 38132451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang J. S. Development and prospect of the research on salt-affected soils in China. Acta Pedologica Sinica. 2008;45(5):837–845. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2008.05.010. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

