Potent effects of dioscin against liver fibrosis
- PMID: 25853178
- PMCID: PMC4389718
- DOI: 10.1038/srep09713
Potent effects of dioscin against liver fibrosis
Abstract
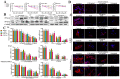
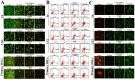
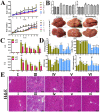
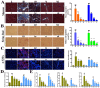
We previously reported the promising effects of dioscin against liver injury, but its effect on liver fibrosis remains unknown. The present work investigated the activities of dioscin against liver fibrosis and the underlying molecular mechanisms. Dioscin effectively inhibited the cell viabilities of HSC-T6, LX-2 and primary rat hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), but not hepatocytes. Furthermore, dioscin markedly increased peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) expression and significantly reduced a-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), collagen α1 (I) (COL1A1) and collagen α1 (III) (COL3A1) levels in vitro. Notably, dioscin inhibited HSCs activation and induced apoptosis in activated HSCs. In vivo, dioscin significantly improved body weight and hydroxylproline, laminin, α-SMA, TGF-β1, COL1A1 and COL3A1 levels, which were confirmed by histopathological assays. Dioscin facilitated matrix degradation, and exhibited hepatoprotective effects through the attenuation of oxidative stress and inflammation, in addition to exerting anti-fibrotic effects through the modulation of the TGF-β1/Smad, Wnt/β-catenin, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and mitochondrial signaling pathways, which triggered the senescence of activated HSCs. In conclusion, dioscin exhibited potent effects against liver fibrosis through the modulation of multiple targets and signaling pathways and should be developed as a novel candidate for the treatment of liver fibrosis in the future.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
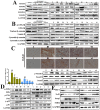
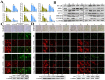
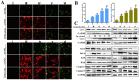
References
-
- Parola M., Marra F. & Pinzani M. Myofibroblast-like cells and liver fibrogenesis: emerging concepts in a rapidly moving scenario. Mol Aspects Med 29, 58–66 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Van Hul N. K. et al. Relation between liver progenitor cell expansion and extracellular matrix deposition in a CDE-induced murine model of chronic liver injury. Hepatology 49, 1625–1635 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

