A de novo FOXP1 variant in a patient with autism, intellectual disability and severe speech and language impairment
- PMID: 25853299
- PMCID: PMC4795189
- DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2015.66
A de novo FOXP1 variant in a patient with autism, intellectual disability and severe speech and language impairment
Abstract
FOXP1 (forkhead box protein P1) is a transcription factor involved in the development of several tissues, including the brain. An emerging phenotype of patients with protein-disrupting FOXP1 variants includes global developmental delay, intellectual disability and mild to severe speech/language deficits. We report on a female child with a history of severe hypotonia, autism spectrum disorder and mild intellectual disability with severe speech/language impairment. Clinical exome sequencing identified a heterozygous de novo FOXP1 variant c.1267_1268delGT (p.V423Hfs*37). Functional analyses using cellular models show that the variant disrupts multiple aspects of FOXP1 activity, including subcellular localization and transcriptional repression properties. Our findings highlight the importance of performing functional characterization to help uncover the biological significance of variants identified by genomics approaches, thereby providing insight into pathways underlying complex neurodevelopmental disorders. Moreover, our data support the hypothesis that de novo variants represent significant causal factors in severe sporadic disorders and extend the phenotype seen in individuals with FOXP1 haploinsufficiency.
Figures

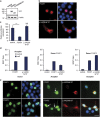
References
-
- Shu W, Yang H, Zhang L, Lu MM, Morrisey EE: Characterization of a new subfamily of winged-helix/forkhead (Fox) genes that are expressed in the lung and act as transcriptional repressors. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 27488–27497. - PubMed
-
- Shu W, Lu MM, Zhang Y, Tucker PW, Zhou D, Morrisey EE: Foxp2 and Foxp1 cooperatively regulate lung and esophagus development. Development 2007; 134: 1991–2000. - PubMed
-
- Wang B, Weidenfeld J, Lu MM et al: Foxp1 regulates cardiac outflow tract, endocardial cushion morphogenesis and myocyte proliferation and maturation. Development 2004; 131: 4477–4487. - PubMed
-
- Dasen JS, De Camilli A, Wang B, Tucker PW, Jessell TM: Hox repertoires for motor neuron diversity and connectivity gated by a single accessory factor, FoxP1. Cell 2008; 134: 304–316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

