Learning from instructional explanations: effects of prompts based on the active-constructive-interactive framework
- PMID: 25853629
- PMCID: PMC4390325
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124115
Learning from instructional explanations: effects of prompts based on the active-constructive-interactive framework
Abstract
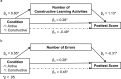
Although instructional explanations are commonly provided when learners are introduced to new content, they often fail because they are not integrated into effective learning activities. The recently introduced active-constructive-interactive framework posits an effectiveness hierarchy in which interactive learning activities are at the top; these are then followed by constructive and active learning activities, respectively. Against this background, we combined instructional explanations with different types of prompts that were designed to elicit these learning activities and tested the central predictions of the active-constructive-interactive framework. In Experiment 1, N = 83 students were randomly assigned to one of four combinations of instructional explanations and prompts. To test the active < constructive learning hypothesis, the learners received either (1) complete explanations and engaging prompts designed to elicit active activities or (2) explanations that were reduced by inferences and inference prompts designed to engage learners in constructing the withheld information. Furthermore, in order to explore how interactive learning activities can be elicited, we gave the learners who had difficulties in constructing the prompted inferences adapted remedial explanations with either (3) unspecific engaging prompts or (4) revision prompts. In support of the active < constructive learning hypothesis, we found that the learners who received reduced explanations and inference prompts outperformed the learners who received complete explanations and engaging prompts. Moreover, revision prompts were more effective in eliciting interactive learning activities than engaging prompts. In Experiment 2, N = 40 students were randomly assigned to either (1) a reduced explanations and inference prompts or (2) a reduced explanations and inference prompts plus adapted remedial explanations and revision prompts condition. In support of the constructive < interactive learning hypothesis, the learners who received adapted remedial explanations and revision prompts as add-ons to reduced explanations and inference prompts acquired more conceptual knowledge.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Active-constructive-interactive: a conceptual framework for differentiating learning activities.Top Cogn Sci. 2009 Jan;1(1):73-105. doi: 10.1111/j.1756-8765.2008.01005.x. Top Cogn Sci. 2009. PMID: 25164801
-
Example-based learning: comparing the effects of additionally providing three different integrative learning activities on physiotherapy intervention knowledge.BMC Med Educ. 2015 Mar 7;15:37. doi: 10.1186/s12909-015-0308-3. BMC Med Educ. 2015. PMID: 25889066 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Health professions learners' evaluation of e-learning scenario-based case study design: Reinvigorating flipped classroom modalities.J Dent Educ. 2023 Dec;87(12):1754-1765. doi: 10.1002/jdd.13379. Epub 2023 Sep 27. J Dent Educ. 2023. PMID: 37753866
-
Authenticity in learning: multimedia design projects in the social studies for students with disabilities.J Learn Disabil. 1996 Sep;29(5):450-60. doi: 10.1177/002221949602900501. J Learn Disabil. 1996. PMID: 8870516 Review.
-
Incorporating the experiential learning theory into the instructional design of online courses.Nurse Educ. 2003 Jan-Feb;28(1):10-4. doi: 10.1097/00006223-200301000-00006. Nurse Educ. 2003. PMID: 12544608 Review.
Cited by
-
Generative preparation tasks in digital collaborative learning: actor and partner effects of constructive preparation activities on deep comprehension.Front Psychol. 2024 Jun 19;15:1335682. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1335682. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38962237 Free PMC article.
-
Is Learning With Elaborative Interrogation Less Desirable When Learners Are Depleted?Front Psychol. 2019 Mar 29;10:707. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00707. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 30984088 Free PMC article.
-
Why the Cells Look Like That - The Influence of Learning With Emotional Design and Elaborative Interrogations.Front Psychol. 2018 Sep 7;9:1653. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01653. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2018. PMID: 30245656 Free PMC article.
-
Can prompts improve self-explaining an online video lecture? Yes, but do not disturb!Int J Educ Technol High Educ. 2023;20(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s41239-023-00383-9. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Int J Educ Technol High Educ. 2023. PMID: 36919042 Free PMC article.
-
Challenging Cognitive Load Theory: The Role of Educational Neuroscience and Artificial Intelligence in Redefining Learning Efficacy.Brain Sci. 2025 Feb 15;15(2):203. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15020203. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40002535 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berthold K, Renkl A. How to foster active processing of explanations in instructional communication. Educ Psychol Rev. 2010;22: 25–40. 10.1007/s10648-010-9124-9 - DOI
-
- Leinhardt G. Instructional explanations: A commonplace for teaching and location for contrast In Richardson V, editor. Handbook of research on teaching. Washington, DC: American Educational Research Association; 2001. pp. 333–357.
-
- Wittwer J, Renkl A. Why instructional explanations often do not work: A framework for understanding the effectiveness of instructional explanations. Educ Psychol. 2008;43: 49–64. 10.1080/00461520701756420 - DOI
-
- Bannert M, Reimann P. Supporting self-regulated hypermedia learning through prompts. Instr Sci. 2012;40: 193–211. 10.1007/s11251-011-9167-4 - DOI
-
- Devolder A, Van Braak J, Tondeur J. Supporting self-regulated learning in computer-based learning environments: Systematic review of effects of scaffolding in the domain of science education. J Comput Assist Lear. 2012;28: 557–573. 10.1111/j.1365-2729.2011.00476.x - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

