Different prognostic values of plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA and maximal standardized uptake value of 18F-FDG PET/CT for nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients with recurrence
- PMID: 25853677
- PMCID: PMC4390333
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122756
Different prognostic values of plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA and maximal standardized uptake value of 18F-FDG PET/CT for nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients with recurrence
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate and compare the prognostic value of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA and maximal standard uptake values (SUVmax ) of 18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography (18F-FDG-PET) in subgroups of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients with locoregional or distant recurrence.
Patients and methods: A total of 194 patients with recurrent NPC (locoregional recurrence: 107, distant recurrence: 87) were enrolled. Patients took evidence of recurrence performed with 18F-FDG-PET and an EBV DNA test before salvage treatment. Clinical parameters, the status of EBV DNA and the value of SUVmax were used for survival analysis using the Kaplan-Meier method and the Cox proportional hazards regression model.
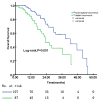
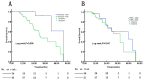
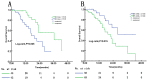
Results: In the subgroup of patients with locoregional recurrence, patients with SUVmax<8.65 had significantly better overall survival (OS) (P=0.005) compared with the patients with SUVmax ≥8.65. However, both elevated EBV DNA load (≥21,100 copies/ml) and distant SUVmax (≥13.55) were significantly associated with worse OS compared with the patients with EBV DNA <21,100 copies/ml or distant SUVmax <13.55 for the subgroup with distant recurrence (P=0.015 and P=0.006, respectively). The predictive ability of EBV DNA was superior to that of SUVmax (P=0.062). Multivariate analysis showed that SUVmax was only an independent prognostic factor for OS in patients with locoregional recurrence (P=0.042), whereas EBV DNA independently predicted OS for the patients with distant recurrence (P=0.007). For those patients with undetectable EBV DNA, SUVmax<8.65 was still an independent favorable prognostic factor (P=0.038).
Conclusions: SUVmax is a useful biomarker for predicting OS in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients with locoregional recurrence or with undetectable EBV DNA. Both distant SUVmax and EBV DNA appear to be independent predictors of OS in patients with distant recurrence; however, the predictive ability of EBV DNA was superior to that of SUVmax.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combining plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA and nodal maximal standard uptake values of 18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography improved prognostic stratification to predict distant metastasis for locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 10;6(35):38296-307. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5699. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26512922 Free PMC article.
-
Maximal standard uptake values of 18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography compared with Epstein-Barr virus DNA as prognostic indicators in de novo metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients.BMC Cancer. 2019 Sep 11;19(1):908. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6106-2. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31511059 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective study of tailoring whole-body dual-modality [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography with plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA for detecting distant metastasis in endemic nasopharyngeal carcinoma at initial staging.J Clin Oncol. 2013 Aug 10;31(23):2861-9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.46.0816. Epub 2013 Jul 15. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23857969
-
Prognostic value of Epstein-Barr virus DNA level for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a meta-analysis of 8128 cases.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Jan;277(1):9-18. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05699-9. Epub 2019 Oct 28. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 31659449 Review.
-
Prognostic role of plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA load for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Clin Invest Med. 2017 Feb 19;40(1):E1-E12. doi: 10.25011/cim.v40i1.28049. Clin Invest Med. 2017. PMID: 28218577 Review.
Cited by
-
Maintenance therapy improves the survival outcomes of patients with metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma responding to first-line chemotherapy: a multicentre, randomized controlled clinical study.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Jul;149(8):4327-4338. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04341-2. Epub 2022 Sep 8. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36075994 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical outcomes of residual or recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with endoscopic nasopharyngectomy plus chemoradiotherapy or with chemoradiotherapy alone: a retrospective study.PeerJ. 2017 Oct 9;5:e3912. doi: 10.7717/peerj.3912. eCollection 2017. PeerJ. 2017. PMID: 29038762 Free PMC article.
-
Significant value of 18F-FDG-PET/CT in diagnosing small cervical lymph node metastases in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy.Chin J Cancer. 2017 Dec 19;36(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s40880-017-0265-9. Chin J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29258597 Free PMC article.
-
Initial evaluation of (4S)-4-(3-[18F]fluoropropyl)-L-glutamate (FSPG) PET/CT imaging in patients with head and neck cancer, colorectal cancer, or non-Hodgkin lymphoma.EJNMMI Res. 2020 Aug 28;10(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s13550-020-00678-2. EJNMMI Res. 2020. PMID: 32857284 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of oral maintenance chemotherapy and predictive value of circulating EBV DNA in metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2020 Apr;9(8):2732-2741. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2926. Epub 2020 Feb 23. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32090498 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yu MC, Yuan JM. Epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Seminars in cancer biology. 2002;12(6):421–9. - PubMed
-
- Wei WI, Sham JS. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 2005;365(9476):2041–54. - PubMed
-
- Al-Sarraf M, LeBlanc M, Giri PG, Fu KK, Cooper J, Vuong T, et al. Chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy in patients with advanced nasopharyngeal cancer: phase III randomized Intergroup study 0099. Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 1998;16(4):1310–7. . - PubMed
-
- Wee J, Tan EH, Tai BC, Wong HB, Leong SS, Tan T, et al. Randomized trial of radiotherapy versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy followed by adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with American Joint Committee on Cancer/International Union against cancer stage III and IV nasopharyngeal cancer of the endemic variety. Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2005;23(27):6730–8. - PubMed
-
- Kam MK, Teo PM, Chau RM, Cheung KY, Choi PH, Kwan WH, et al. Treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma with intensity-modulated radiotherapy: the Hong Kong experience. International journal of radiation oncology, biology, physics. 2004;60(5):1440–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

