Unscheduled-return-visits after an emergency department (ED) attendance and clinical link between both visits in patients aged 75 years and over: a prospective observational study
- PMID: 25853822
- PMCID: PMC4390330
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123803
Unscheduled-return-visits after an emergency department (ED) attendance and clinical link between both visits in patients aged 75 years and over: a prospective observational study
Abstract
Background: Predictors of unscheduled return visits (URV), best time-frame to evaluate URV rate and clinical relationship between both visits have not yet been determined for the elderly following an ED visit.
Methods: We conducted a prospective-observational study including 11,521 patients aged ≥75-years and discharged from ED (5,368 patients (53.5%)) or hospitalized after ED visit (6,153 patients). Logistic Regression and time-to-failure analyses including Cox proportional model were performed.
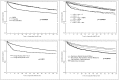
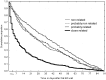
Results: Mean time to URV was 17 days; 72-hour, 30-day and 90-day URV rates were 1.8%, 6.1% and 10% respectively. Multivariate analysis indicates that care-pathway and final disposition decisions were significantly associated with a 30-day URV. Thus, we evaluated predictors of 30-day URV rates among non-admitted and hospitalized patient groups. By using the Cox model we found that, for non-admitted patients, triage acuity and diagnostic category and, for hospitalized patients, that visit time (day, night) and diagnostic categories were significant predictors (p<0.001). For URV, we found that 25% were due to closely related-clinical conditions. Time lapses between both visits constituted the strongest predictor of closely related-clinical conditions.
Conclusion: Our study shows that a decision of non-admission in emergency departments is linked with an accrued risk of URV, and that some diagnostic categories are also related for non-admitted and hospitalized subjects alike. Our study also demonstrates that the best time frame to evaluate the URV rate after an ED visit is 30 days, because this is the time period during which most URVs and cases with close clinical relationships between two visits are concentrated. Our results suggest that URV can be used as an indicator or quality.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictors of Admission in Adult Unscheduled Return Visits to the Emergency Department.West J Emerg Med. 2018 Nov;19(6):912-918. doi: 10.5811/westjem.2018.8.38225. Epub 2018 Sep 10. West J Emerg Med. 2018. PMID: 30429921 Free PMC article.
-
Unscheduled return visits (URV) in adults to the emergency department (ED): a rapid evidence assessment policy review.Emerg Med J. 2015 Apr;32(4):324-9. doi: 10.1136/emermed-2013-202719. Epub 2013 Oct 28. Emerg Med J. 2015. PMID: 24165201 Review.
-
Unscheduled return visits with and without admission post emergency department discharge.J Emerg Med. 2012 Dec;43(6):1110-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2012.01.062. Epub 2012 Jun 5. J Emerg Med. 2012. PMID: 22674038
-
The recidivism characteristics of an emergency department observation unit.Ann Emerg Med. 2010 Jul;56(1):34-41. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2010.02.012. Epub 2010 Mar 29. Ann Emerg Med. 2010. PMID: 20303200
-
Upstreamist leaders: how risk factors for unscheduled return visits (URV) to the emergency department can inform integrated healthcare.Leadersh Health Serv (Bradf Engl). 2022 Dec 29;ahead-of-print(ahead-of-print). doi: 10.1108/LHS-06-2022-0069. Leadersh Health Serv (Bradf Engl). 2022. PMID: 36573622 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between access to primary care and unplanned emergency department return visits among patients 75 years and older.Can Fam Physician. 2022 Aug;68(8):599-606. doi: 10.46747/cfp.6808599. Can Fam Physician. 2022. PMID: 35961725 Free PMC article.
-
Revisits and frailty in older patients in the emergency department - a prospective observational multicenter study.BMC Emerg Med. 2024 Oct 29;24(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s12873-024-01123-6. BMC Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 39468432 Free PMC article.
-
Safety assessment of a redirection program using an electronic application for low-acuity patients visiting an emergency department.BMC Emerg Med. 2022 Apr 29;22(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12873-022-00626-4. BMC Emerg Med. 2022. PMID: 35488215 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of mortality and cardiopulmonary arrest in critical patients presenting to the emergency department using machine learning and natural language processing.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 2;15(4):e0230876. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230876. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32240233 Free PMC article.
-
Burden and patient characteristics associated with repeat consultation for unscheduled care within 30 days in primary care: a retrospective case control study with implications for aging and public health.Front Public Health. 2023 Jul 25;11:1079755. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1079755. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37559737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Percentage of population age 65 or over. Available: http://www.data360.org/dsg.aspx?Data_Set_Group_Id=466. Accessed March 1, 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

