Crotoxin from Crotalus durissus terrificus is able to down-modulate the acute intestinal inflammation in mice
- PMID: 25853847
- PMCID: PMC4390225
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121427
Crotoxin from Crotalus durissus terrificus is able to down-modulate the acute intestinal inflammation in mice
Abstract
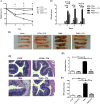
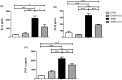
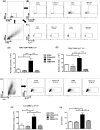
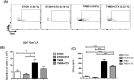
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) is the result of dysregulation of mucosal innate and adaptive immune responses. Factors such as genetic, microbial and environmental are involved in the development of these disorders. Accordingly, animal models that mimic human diseases are tools for the understanding the immunological processes of the IBD as well as to evaluate new therapeutic strategies. Crotoxin (CTX) is the main component of Crotalus durissus terrificus snake venom and has an immunomodulatory effect. Thus, we aimed to evaluate the modulatory effect of CTX in a murine model of colitis induced by 2,4,6- trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS). The CTX was administered intraperitoneally 18 hours after the TNBS intrarectal instillation in BALB/c mice. The CTX administration resulted in decreased weight loss, disease activity index (DAI), macroscopic tissue damage, histopathological score and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity analyzed after 4 days of acute TNBS colitis. Furthermore, the levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 were lower in colon tissue homogenates of TNBS-mice that received the CTX when compared with untreated TNBS mice. The analysis of distinct cell populations obtained from the intestinal lamina propria showed that CTX reduced the number of group 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3) and Th17 population; CTX decreased IL-17 secretion but did not alter the frequency of CD4+Tbet+ T cells induced by TNBS instillation in mice. In contrast, increased CD4+FoxP3+ cell population as well as secretion of TGF-β, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and lipoxin A4 (LXA4) was observed in TNBS-colitis mice treated with CTX compared with untreated TNBS-colitis mice. In conclusion, the CTX is able to modulate the intestinal acute inflammatory response induced by TNBS, resulting in the improvement of clinical status of the mice. This effect of CTX is complex and involves the suppression of the pro-inflammatory environment elicited by intrarectal instillation of TNBS due to the induction of a local anti-inflammatory profile in mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Geboes K. From inflammation to lesion. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 1994;57: 273–284. - PubMed
-
- Sartor RB Current concepts of the etiology and pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1995;24: 475–507. - PubMed
-
- Kraus TA, Mayer L. Oral tolerance and inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2005;21: 692–696. - PubMed
-
- Sartor RB. Pathogenesis and immune mechanisms of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997;92: 5S–11S. - PubMed
-
- Brandtzaeg P. Inflammatory bowel disease: clinics and pathology. Do inflammatory bowel disease and periodontal disease have similar immunopathogeneses? Acta OdontolScand, 2001;59: 235–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

