TDP-43 as a possible biomarker for frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a systematic review of existing antibodies
- PMID: 25853864
- PMCID: PMC4380254
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-015-0195-1
TDP-43 as a possible biomarker for frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a systematic review of existing antibodies
Abstract
Frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) is one of the leading causes of dementia after Alzheimer's disease. A high-ranking candidate to become a diagnostic marker for a major pathological subtype of FTLD is the transactive response DNA binding protein of 43 kDa (TDP-43). The main objective is to elucidate which antibodies are specific for pathological TDP-43, with special interest in its modified isoforms. Indeed, TDP-43 has been shown to be hyperphosphorylated and truncated in disease. A secondary objective is to review existing immunoassays that quantify TDP-43 in biofluids. A systematic review of literature was performed by searching PubMed and Web of Science using predefined keywords. Of considered research papers the methods section was reviewed to select publications that enabled us to answer our learning objective. After quality assessment, antibody characteristics and related outcomes were extracted. We identified a series of well-characterized antibodies based on a scoring system that assessed the ability of each antibody to detect TDP-43 pathology. A selection of 29 unique antibodies was made comprising 10 high-ranking antibodies which were reported multiple times to detect TDP-43 pathology in both immunostaining and immunoblotting experiments and 19 additional antibodies which detected TDP-43 pathology but were only scored once. This systematic review provides an overview of antibodies that are reported to detect pathological TDP-43. These antibodies can be used in future studies of TDP-43 proteinopathies. Additionally, selected antibodies hold the potential to be used in the development of novel immunoassays for the quantification of TDP-43 in biofluids, as a possible biomarker for FTLD-TDP.
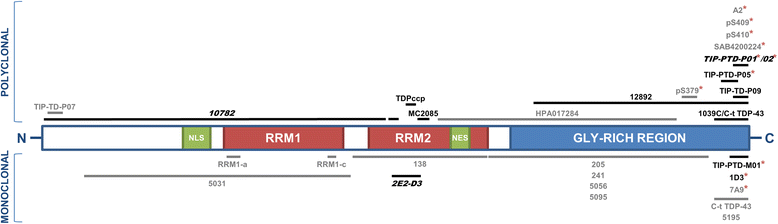
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regional cerebral blood flow single photon emission computed tomography for detection of Frontotemporal dementia in people with suspected dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jun 23;2015(6):CD010896. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010896.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26102272 Free PMC article.
-
Methylome analysis of FTLD patients with TDP-43 pathology identifies epigenetic signatures specific to pathological subtypes.Mol Neurodegener. 2025 Jul 6;20(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s13024-025-00869-2. Mol Neurodegener. 2025. PMID: 40619440 Free PMC article.
-
Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy (LATE): consensus working group report.Brain. 2019 Jun 1;142(6):1503-1527. doi: 10.1093/brain/awz099. Brain. 2019. PMID: 31039256 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
LATE-NC Stage 3: a diagnostic rubric to differentiate severe LATE-NC from FTLD-TDP.Acta Neuropathol. 2025 Apr 28;149(1):38. doi: 10.1007/s00401-025-02876-5. Acta Neuropathol. 2025. PMID: 40293530 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Metal content and kinetic properties of yeast RNA lariat debranching enzyme Dbr1.RNA. 2022 Jul;28(7):927-936. doi: 10.1261/rna.079159.122. Epub 2022 Apr 22. RNA. 2022. PMID: 35459748 Free PMC article.
-
Latest advances in cerebrospinal fluid and blood biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2019 Dec 18;12:1756286419888819. doi: 10.1177/1756286419888819. eCollection 2019. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2019. PMID: 31897088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TDP-43 Epigenetic Facets and Their Neurodegenerative Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 7;24(18):13807. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813807. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implications of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Age-Altered Proteostasis.Aging Dis. 2020 May 9;11(3):692-704. doi: 10.14336/AD.2019.0814. eCollection 2020 May. Aging Dis. 2020. PMID: 32489713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma TDP-43 levels are associated with neuroimaging measures of brain structure in limbic regions.Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2023 May 31;15(2):e12437. doi: 10.1002/dad2.12437. eCollection 2023 Apr-Jun. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2023. PMID: 37266411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Dementia: a public health priority. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2012.
-
- Cairns NJ, Bigio EH, Mackenzie IRA, Neumann M, Lee VM-Y, Hatanpaa KJ, et al. Neuropathologic diagnostic and nosologic criteria for frontotemporal lobar degeneration: consensus of the Consortium for Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;114:5–22. doi: 10.1007/s00401-007-0237-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

