Assay reproducibility in clinical studies of plasma miRNA
- PMID: 25853871
- PMCID: PMC4390277
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121948
Assay reproducibility in clinical studies of plasma miRNA
Abstract
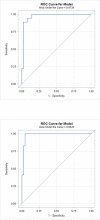
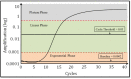
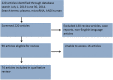
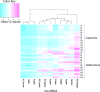
There are increasing reports of plasma miRNAs as biomarkers of human disease but few standards in methodologic reporting, leading to inconsistent data. We systematically reviewed plasma miRNA studies published between July 2013-June 2014 to assess methodology. Six parameters were investigated: time to plasma extraction, methods of RNA extraction, type of miRNA, quantification, cycle threshold (Ct) setting, and methods of statistical analysis. We compared these data with a proposed standard methodologic technique. Beginning with initial screening for 380 miRNAs using microfluidic array technology and validation in an additional cohort of patients, we compared 11 miRNAs that exhibited differential expression between 16 patients with benign colorectal neoplasms (advanced adenomas) and 16 patients without any neoplasm (controls). Plasma was isolated immediately, 12, 24, 48, or 72 h following phlebotomy. miRNA was extracted using two different techniques (Trizol LS with pre-amplification or modified miRNeasy). We performed Taqman-based RT-PCR assays for the 11 miRNAs with subsequent analyses using a variable Ct setting or a fixed Ct set at 0.01, 0.03, 0.05, or 0.5. Assays were performed in duplicate by two different operators. RNU6 was the internal reference. Systematic review yielded 74 manuscripts meeting inclusion criteria. One manuscript (1.4%) documented all 6 methodological parameters, while < 5% of studies listed Ct setting. In our proposed standard technique, plasma extraction ≤12 h provided consistent ΔCt. miRNeasy extraction yielded higher miRNA concentrations and fewer non-expressed miRNAs compared to Trizol LS (1/704 miRNAs [0.14%] vs 109/704 miRNAs [15%], not expressed, respectively). A fixed Ct bar setting of 0.03 yielded the most reproducible data, provided that <10% miRNA were non-expressed. There was no significant intra-operator variability. There was significant inter-operator variation using Trizol LS extraction, while this was negligible using modified miRNeasy. For standardized reporting, we recommend plasma extraction ≤ 12 h, using modified miRNeasy extraction and utilizing a 0.03 Ct.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Housekeeping genes for studies of plasma microRNA: A need for more precise standardization.Surgery. 2015 Nov;158(5):1345-51. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2015.04.025. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Surgery. 2015. PMID: 26094174
-
Optimized microRNA purification from TRIzol-treated plasma.BMC Genomics. 2015 Feb 18;16(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1299-5. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25765146 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing cellular and circulating miRNA recovery: the impact of the RNA isolation method and the quantity of input material.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 20;6:19529. doi: 10.1038/srep19529. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26787294 Free PMC article.
-
Methodological challenges in utilizing miRNAs as circulating biomarkers.J Cell Mol Med. 2014 Mar;18(3):371-90. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12236. Epub 2014 Feb 18. J Cell Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24533657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study Design and qPCR Data Analysis Guidelines for Reliable Circulating miRNA Biomarker Experiments: A Review.Clin Chem. 2018 Sep;64(9):1308-1318. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2017.285288. Epub 2018 Jun 14. Clin Chem. 2018. PMID: 29903876 Review.
Cited by
-
Synovial-Fluid miRNA Signature for Diagnosis of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis.Cells. 2019 Nov 26;8(12):1521. doi: 10.3390/cells8121521. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31779271 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Suitable Internal Control miRNAs in Bovine Milk Small Extracellular Vesicles for Normalization in Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Feb 2;13(2):185. doi: 10.3390/membranes13020185. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36837688 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating MicroRNA Biomarkers for Lung Cancer Detection in East Asian Populations.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Mar 23;11(3):415. doi: 10.3390/cancers11030415. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30909610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Statistical Issues and Group Classification in Plasma MicroRNA Studies With Data Application.Evol Bioinform Online. 2020 Apr 14;16:1176934320913338. doi: 10.1177/1176934320913338. eCollection 2020. Evol Bioinform Online. 2020. PMID: 32313420 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison and optimisation of microRNA extraction from the plasma of healthy pregnant women.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Apr;23(4):1. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.11897. Epub 2021 Feb 12. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33576446 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

