Average genome size estimation improves comparative metagenomics and sheds light on the functional ecology of the human microbiome
- PMID: 25853934
- PMCID: PMC4389708
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-015-0611-7
Average genome size estimation improves comparative metagenomics and sheds light on the functional ecology of the human microbiome
Abstract
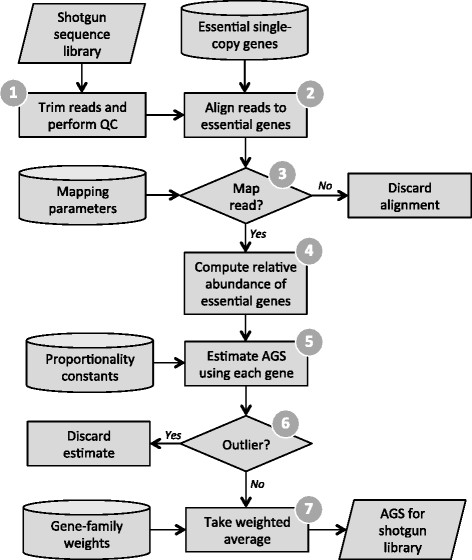
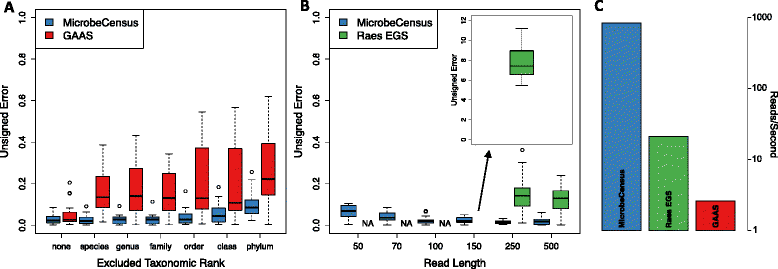
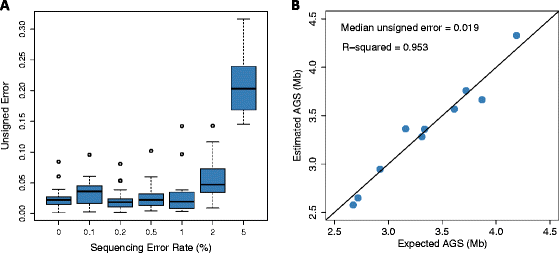
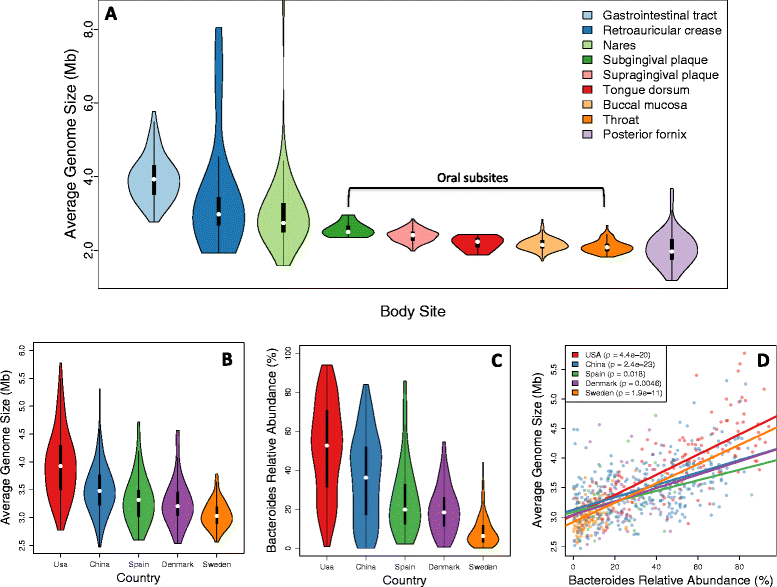
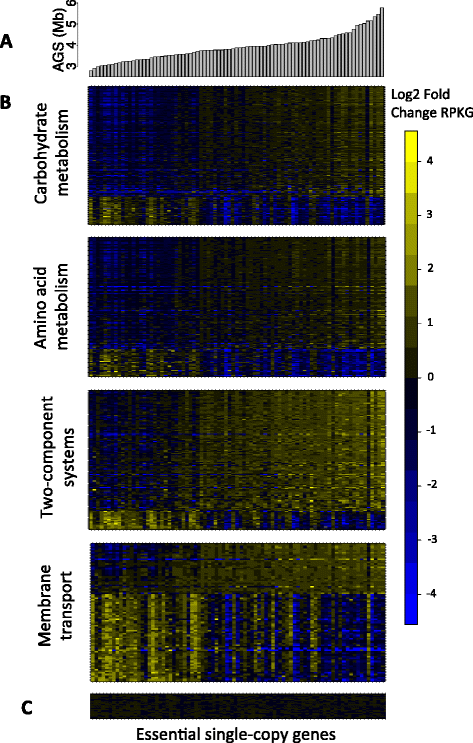
Average genome size is an important, yet often overlooked, property of microbial communities. We developed MicrobeCensus to rapidly and accurately estimate average genome size from shotgun metagenomic data and applied our tool to 1,352 human microbiome samples. We found that average genome size differs significantly within and between body sites and tracks with major functional and taxonomic differences. In the gut, average genome size is positively correlated with the abundance of Bacteroides and genes related to carbohydrate metabolism. Importantly, we found that average genome size variation can bias comparative analyses, and that normalization improves detection of differentially abundant genes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Metagenomic binning and association of plasmids with bacterial host genomes using DNA methylation.Nat Biotechnol. 2018 Jan;36(1):61-69. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4037. Epub 2017 Dec 11. Nat Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29227468 Free PMC article.
-
Use of whole genome shotgun metagenomics: a practical guide for the microbiome-minded physician scientist.Semin Reprod Med. 2014 Jan;32(1):5-13. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1361817. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Semin Reprod Med. 2014. PMID: 24390915 Review.
-
Functional Metagenomics of the Bronchial Microbiome in COPD.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 3;10(12):e0144448. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144448. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26632844 Free PMC article.
-
Automated and Accurate Estimation of Gene Family Abundance from Shotgun Metagenomes.PLoS Comput Biol. 2015 Nov 13;11(11):e1004573. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004573. eCollection 2015 Nov. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015. PMID: 26565399 Free PMC article.
-
Application of metagenomics in the human gut microbiome.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan 21;21(3):803-14. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.803. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25624713 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The coral Oculina patagonica holobiont and its response to confinement, temperature, and Vibrio infections.Microbiome. 2024 Oct 29;12(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s40168-024-01921-x. Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 39472959 Free PMC article.
-
Extremely halophilic brine community manipulation shows higher robustness of microbiomes inhabiting human-driven solar saltern than naturally driven lake.mSystems. 2024 Jul 23;9(7):e0053824. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00538-24. Epub 2024 Jun 27. mSystems. 2024. PMID: 38934645 Free PMC article.
-
Fast and accurate average genome size and 16S rRNA gene average copy number computation in metagenomic data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Sep 5;20(1):453. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-3031-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31488068 Free PMC article.
-
A most wanted list of conserved microbial protein families with no known domains.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 17;13(10):e0205749. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205749. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30332487 Free PMC article.
-
Resistome expansion in disease-associated human gut microbiomes.Microbiome. 2023 Jul 29;11(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01610-1. Microbiome. 2023. PMID: 37507809 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

