Borealin dimerization mediates optimal CPC checkpoint function by enhancing localization to centromeres and kinetochores
- PMID: 25854549
- PMCID: PMC4392389
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms7775
Borealin dimerization mediates optimal CPC checkpoint function by enhancing localization to centromeres and kinetochores
Abstract
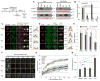
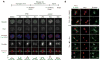
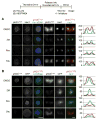
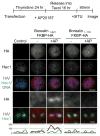
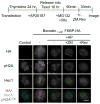
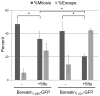
The chromosomal passenger complex (CPC) localizes to centromeres where it activates the mitotic checkpoint in response to inappropriate inter-kinetochore tension. This error correction function is essential for proper chromosome segregation. Here we define several critical features of CPC localization and function. First, the Borealin dimerization domain suppresses dynamic exchange at the centromere to allow optimal CPC function. Second, Borealin dimerization is essential to target a subpopulation of CPC proximal to the kinetochore when the mitotic spindle is disrupted. This subpopulation is also needed for full CPC checkpoint function. The existence of a pool of CPC at the kinetochore suggests that error correction is more complicated than predicted from the Aurora B phosphorylation gradient model. Finally, Haspin kinase plays a key role in maintaining the slowly exchanging centromere Borealin pool, while Aurora B and Mps1 play minimal roles in maintaining CPC localization once cells are in mitosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Forment JV, Kaidi A, Jackson SP. Chromothripsis and cancer: causes and consequences of chromosome shattering. Nature reviews Cancer. 2012;12:663–670. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

