Prognostic role of the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in renal cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 25854964
- PMCID: PMC4390726
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-006404
Prognostic role of the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in renal cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: Increasing evidence suggests that cancer-associated inflammation is associated with poor prognosis in patients with cancer. The role of the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) as a predictor in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) remains controversial. We conducted the meta-analysis to determine the association between NLR and clinical outcome of patients with RCC.
Methods and materials: Studies were identified from PubMed and EMBASE databases in March 2014. Meta-analysis was performed to generate combined HRs with 95% CIs for overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free/progress-free survival (RFS/PFS).
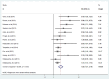
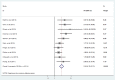
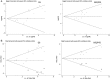
Results: 15 cohorts containing 3357 patients were included. Our analysis results indicated that elevated NLR predicted poorer OS (HR=1.82, 95% CI 1.51 to 2.19) and RFS/PFS (HR=2.18, 95% CI 1.75 to 2.71) in patients with RCC. These findings were robust when stratified by study region, sample size, therapeutic intervention, types of RCC and study quality. However, it differed significantly by assessment of the cut-off value defining 'elevated NLR' in RFS/PFS (p=0.004). The heterogeneity in our meta-analysis was mild to moderate.
Conclusions: Elevated NLR indicates a poorer prognosis for patients with RCC. NLR should be monitored in patients with RCC for rational risk stratification and treatment individualisation.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Figures

References
-
- MacDonald N. Cancer cachexia and targeting chronic inflammation: a unified approach to cancer treatment and palliative/supportive care. J Support Oncol 2007;5:157–62; discussion 164–156, 183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
