Angiotensin AT2 receptor agonist prevents salt-sensitive hypertension in obese Zucker rats
- PMID: 25855512
- PMCID: PMC4469886
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00002.2015
Angiotensin AT2 receptor agonist prevents salt-sensitive hypertension in obese Zucker rats
Abstract
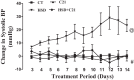
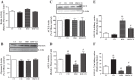
High-sodium intake is a risk factor for the pathogenesis of hypertension, especially in obesity. The present study is designed to investigate whether angiotensin type 2 receptor (AT2R) activation with selective agonist C21 prevents high-sodium diet (HSD)-induced hypertension in obese animals. Male obese rats were treated with AT2R agonist C21 (1 mg·kg(-1)·day(-1), oral) while maintained on either normal-sodium diet (NSD; 0.4%) or HSD (4%) for 2 wk. Radiotelemetric recording showed a time-dependent increase in systolic blood pressure in HSD-fed obese rats, being maximal increase (∼27 mmHg) at day 12 of the HSD regimen. C21 treatment completely prevented the increase in blood pressure of HSD-fed rats. Compared with NSD controls, HSD-fed obese rats had greater natriuresis/diuresis and urinary levels of nitrates, and these parameters were further increased by C21 treatment. Also, C21 treatment improved glomerular filtration rate in HSD-fed rats. HSD-fed rats expressed higher level of cortical ANG II, which was reduced to 50% by C21 treatment. HSD feeding and/or C21 treatment had no effects on cortical renin activity and the expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and chymase, which are ANG II-producing enzymes. However, ANG(1-7) concentration and ACE2 activity in the renal cortex were reduced by HSD feeding, and C21 treatment rescued both the parameters. Also, C21 treatment reduced the cortical expression of AT1R in HSD-fed rats, but had no effect of AT2R expression. We conclude that chronic treatment with the AT2R agonist C21 prevents salt-sensitive hypertension in obese rats, and a reduction in the renal ANG II/AT1R and enhanced ACE2/ANG(1-7) levels may play a potential role in this phenomenon.
Keywords: blood pressure; compound 21; high-sodium diet; obesity.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Angiotensin II Type 2-Receptor Agonist C21 Reduces Proteinuria and Oxidative Stress in Kidney of High-Salt-Fed Obese Zucker Rats.Hypertension. 2016 May;67(5):906-15. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.06881. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Hypertension. 2016. PMID: 27021008 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic AT2 receptor activation increases renal ACE2 activity, attenuates AT1 receptor function and blood pressure in obese Zucker rats.Kidney Int. 2013 Nov;84(5):931-9. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.193. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Kidney Int. 2013. PMID: 23823602 Free PMC article.
-
High Na intake increases renal angiotensin II levels and reduces expression of the ACE2-AT(2)R-MasR axis in obese Zucker rats.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 Aug 1;303(3):F412-9. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00097.2012. Epub 2012 May 16. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22592638 Free PMC article.
-
Update on angiotensin AT2 receptors.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2017 Mar;26(2):91-96. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000304. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2017. PMID: 27906747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AT2 Receptors: Potential Therapeutic Targets for Hypertension.Am J Hypertens. 2017 Apr 1;30(4):339-347. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpw121. Am J Hypertens. 2017. PMID: 27664954 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of angiotensin type 2 receptor in improving lipid metabolism and preventing adiposity.Mol Cell Biochem. 2019 Nov;461(1-2):195-204. doi: 10.1007/s11010-019-03602-y. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31414336 Free PMC article.
-
Dimerization of AT2 and Mas Receptors in Control of Blood Pressure.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2018 May 1;20(5):41. doi: 10.1007/s11906-018-0845-3. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2018. PMID: 29717388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined Angiotensin Receptor Modulation in the Management of Cardio-Metabolic Disorders.Drugs. 2016 Jan;76(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0509-4. Drugs. 2016. PMID: 26631237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor: A Target for Protection Against Hypertension, Metabolic Dysfunction, and Organ Remodeling.Hypertension. 2021 Jun;77(6):1845-1856. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.11941. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Hypertension. 2021. PMID: 33840201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin-II type 2 receptor-mediated renoprotection is independent of receptor Mas in obese Zucker rats fed high-sodium diet.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 29;15:1409313. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1409313. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39135807 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abadir PM, Carey RM, Siragy HM. Angiotensin AT2 receptors directly stimulate renal nitric oxide in bradykinin B2-receptor-null mice. Hypertension 42: 600–604, 2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

