Closed-loop, ultraprecise, automated craniotomies
- PMID: 25855700
- PMCID: PMC4480624
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.01055.2014
Closed-loop, ultraprecise, automated craniotomies
Abstract
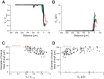
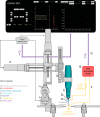
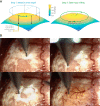
A large array of neuroscientific techniques, including in vivo electrophysiology, two-photon imaging, optogenetics, lesions, and microdialysis, require access to the brain through the skull. Ideally, the necessary craniotomies could be performed in a repeatable and automated fashion, without damaging the underlying brain tissue. Here we report that when drilling through the skull a stereotypical increase in conductance can be observed when the drill bit passes through the skull base. We present an architecture for a robotic device that can perform this algorithm, along with two implementations--one based on homebuilt hardware and one based on commercially available hardware--that can automatically detect such changes and create large numbers of precise craniotomies, even in a single skull. We also show that this technique can be adapted to automatically drill cranial windows several millimeters in diameter. Such robots will not only be useful for helping neuroscientists perform both small and large craniotomies more reliably but can also be used to create precisely aligned arrays of craniotomies with stereotaxic registration to standard brain atlases that would be difficult to drill by hand.
Keywords: automation; cranial windows; craniotomy; robotics.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Brunoni AR, Nitsche MA, Bolognini N, Bikson M, Wagner T, Merabet L, Edwards DJ, Valero-Cabre A, Rotenberg A, Pascual-Leone A, Ferrucci R, Priori A, Boggio PS, Fregni F. Clinical research with transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS): challenges and future directions. Brain Stimul 5: 175–195, 2012. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chaieb L, Antal A, Paulus W. Transcranial alternating current stimulation in the low kHz range increases motor cortex excitability. Restor Neurol Neurosci 29: 167–175, 2011. - PubMed
-
- Cunha-Cruz V, Follmann A, Popovic A, Bast P, Wu T, Heger S, Engelhardt M, Schmieder K, Radermacher K. Robot- and computer-assisted craniotomy (CRANIO): from active systems to synergistic man-machine interaction. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 224: 441–452, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Holtmaat A, Bonhoeffer T, Chow DK, Chuckowree J, De Paola V, Hofer SB, Hübener M, Keck T, Knott G, Lee WC, Mostany R, Mrsic-Flogel TD, Nedivi E, Portera-Cailliau C, Svoboda K, Trachtenberg JT, Wilbrecht L. Long-term, high-resolution imaging in the mouse neocortex through a chronic cranial window. Nat Protoc 4: 1128–1144, 2009. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

