Neuromechanical principles underlying movement modularity and their implications for rehabilitation
- PMID: 25856485
- PMCID: PMC4392340
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.02.042
Neuromechanical principles underlying movement modularity and their implications for rehabilitation
Abstract
Neuromechanical principles define the properties and problems that shape neural solutions for movement. Although the theoretical and experimental evidence is debated, we present arguments for consistent structures in motor patterns, i.e., motor modules, that are neuromechanical solutions for movement particular to an individual and shaped by evolutionary, developmental, and learning processes. As a consequence, motor modules may be useful in assessing sensorimotor deficits specific to an individual and define targets for the rational development of novel rehabilitation therapies that enhance neural plasticity and sculpt motor recovery. We propose that motor module organization is disrupted and may be improved by therapy in spinal cord injury, stroke, and Parkinson's disease. Recent studies provide insights into the yet-unknown underlying neural mechanisms of motor modules, motor impairment, and motor learning and may lead to better understanding of the causal nature of modularity and its underlying neural substrates.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

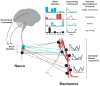
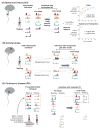
References
-
- Adkins DL, Boychuk J, Remple MS, Kleim JA. Motor training induces experience-specific patterns of plasticity across motor cortex and spinal cord. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2006;101:1776–1782. - PubMed
-
- Alberts JL, Linder SM, Penko AL, Lowe MJ, Phillips M. It is not about the bike, it is about the pedaling: forced exercise and Parkinson’s disease. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2011;39:177–186. - PubMed
-
- Allen JL, McKay JL, Ting LH. Rehabilitation improves generalization of muscle synergies across balance and walking in individuals with Parkinson’s disease. World Congress of Biomechanics; Boston, MA. 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HD46922/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000455/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R21HD075612/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- NIH KL2TR000455/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD075612/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD046922/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HD079584/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD055931/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- IK2 RX000870/RX/RRD VA/United States
- T32 NS007480/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS007480-14/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS087249/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD081274/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

