Job exposure matrix for electric shock risks with their uncertainties
- PMID: 25856552
- PMCID: PMC4410222
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph120403889
Job exposure matrix for electric shock risks with their uncertainties
Abstract
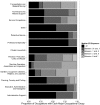
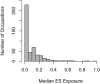
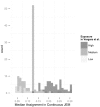
We present an update to an electric shock job exposure matrix (JEM) that assigned ordinal electric shocks exposure for 501 occupational titles based on electric shocks and electrocutions from two available data sources and expert judgment. Using formal expert elicitation and starting with data on electric injury, we arrive at a consensus-based JEM. In our new JEM, we quantify exposures by adding three new dimensions: (1) the elicited median proportion; (2) the elicited 25th percentile; and (3) and the elicited 75th percentile of those experiencing occupational electric shocks in a working lifetime. We construct the relative interquartile range (rIQR) based on uncertainty interval and the median. Finally, we describe overall results, highlight examples demonstrating the impact of cut point selection on exposure assignment, and evaluate potential impacts of such selection on epidemiologic studies of the electric work environment. In conclusion, novel methods allowed for consistent exposure estimates that move from qualitative to quantitative measures in this population-based JEM. Overlapping ranges of median exposure in various categories reflect our limited knowledge about this exposure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Developing a job-exposure matrix with exposure uncertainty from expert elicitation and data modeling.J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2017 Jan;27(1):7-15. doi: 10.1038/jes.2015.37. Epub 2015 May 13. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2017. PMID: 25967069
-
New electric-shock job exposure matrix.Am J Ind Med. 2012 Mar;55(3):232-40. doi: 10.1002/ajim.21027. Epub 2011 Nov 8. Am J Ind Med. 2012. PMID: 22069039
-
Electric shocks at work in Europe: development of a job exposure matrix.Occup Environ Med. 2013 Apr;70(4):261-7. doi: 10.1136/oemed-2012-100732. Epub 2012 Nov 22. Occup Environ Med. 2013. PMID: 23175734
-
Variability and consistency of electric and magnetic field occupational exposure measurements.J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol. 1996 Jul-Sep;6(3):355-74. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol. 1996. PMID: 8889954 Review.
-
Electric shock devices and their effects on the human body.Med Sci Law. 1990 Oct;30(4):285-300. doi: 10.1177/106002809003000403. Med Sci Law. 1990. PMID: 2263172 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a source-exposure matrix for occupational exposure assessment of electromagnetic fields in the INTEROCC study.J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2017 Jul;27(4):398-408. doi: 10.1038/jes.2016.60. Epub 2016 Nov 9. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2017. PMID: 27827378 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a job-exposure matrix with exposure uncertainty from expert elicitation and data modeling.J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2017 Jan;27(1):7-15. doi: 10.1038/jes.2015.37. Epub 2015 May 13. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2017. PMID: 25967069
References
-
- Kheifets L., Bowman J.D., Checkoway H., Feychting M., Harrington M., Kavet R., Marsh G., Mezei G., Renew D.C., Van Wijngaarden E. Future needs of occupational epidemiology of extremely low frequency (ELF) electric and magnetic fields (EMF): Review and recommendations. Occup. Environ. Med. 2008;66:72–80. doi: 10.1136/oem.2007.037994. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Deapen D.M., Henderson B.E. A case-control study of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1986;123:790–799. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical