Mind and body therapy for fibromyalgia
- PMID: 25856658
- PMCID: PMC8409283
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001980.pub3
Mind and body therapy for fibromyalgia
Abstract
Background: Mind-body interventions are based on the holistic principle that mind, body and behaviour are all interconnected. Mind-body interventions incorporate strategies that are thought to improve psychological and physical well-being, aim to allow patients to take an active role in their treatment, and promote people's ability to cope. Mind-body interventions are widely used by people with fibromyalgia to help manage their symptoms and improve well-being. Examples of mind-body therapies include psychological therapies, biofeedback, mindfulness, movement therapies and relaxation strategies.
Objectives: To review the benefits and harms of mind-body therapies in comparison to standard care and attention placebo control groups for adults with fibromyalgia, post-intervention and at three and six month follow-up.
Search methods: Electronic searches of the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE (Ovid), EMBASE (Ovid), PsycINFO (Ovid), AMED (EBSCO) and CINAHL (Ovid) were conducted up to 30 October 2013. Searches of reference lists were conducted and authors in the field were contacted to identify additional relevant articles.
Selection criteria: All relevant randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of mind-body interventions for adults with fibromyalgia were included.
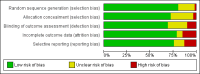
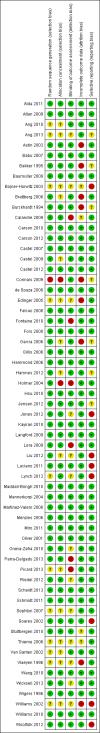
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently selected studies, extracted the data and assessed trials for low, unclear or high risk of bias. Any discrepancy was resolved through discussion and consensus. Continuous outcomes were analysed using mean difference (MD) where the same outcome measure and scoring method was used and standardised mean difference (SMD) where different outcome measures were used. For binary data standard estimation of the risk ratio (RR) and its 95% confidence interval (CI) was used.
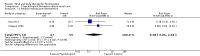
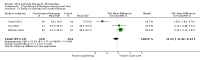
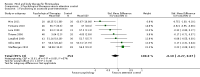
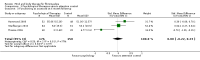
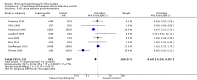
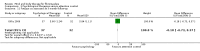
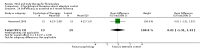
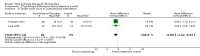
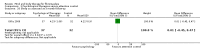
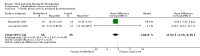
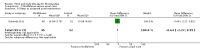
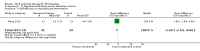
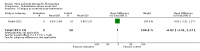
Main results: Seventy-four papers describing 61 trials were identified, with 4234 predominantly female participants. The nature of fibromyalgia varied from mild to severe across the study populations. Twenty-six studies were classified as having a low risk of bias for all domains assessed. The findings of mind-body therapies compared with usual care were prioritised.There is low quality evidence that in comparison to usual care controls psychological therapies have favourable effects on physical functioning (SMD -0.4, 95% CI -0.6 to -0.3, -7.5% absolute change, 2 point shift on a 0 to 100 scale), pain (SMD -0.3, 95% CI -0.5 to -0.2, -3.5% absolute change, 2 point shift on a 0 to 100 scale) and mood (SMD -0.5, 95% CI -0.6 to -0.3, -4.8% absolute change, 3 point shift on a 20 to 80 scale). There is very low quality evidence of more withdrawals in the psychological therapy group in comparison to usual care controls (RR 1.38, 95% CI 1.12 to 1.69, 6% absolute risk difference). There is lack of evidence of a difference between the number of adverse events in the psychological therapy and control groups (RR 0.38, 95% CI 0.06 to 2.50, 4% absolute risk difference).There was very low quality evidence that biofeedback in comparison to usual care controls had an effect on physical functioning (SMD -0.1, 95% CI -0.4 to 0.3, -1.2% absolute change, 1 point shift on a 0 to 100 scale), pain (SMD -2.6, 95% CI -91.3 to 86.1, -2.6% absolute change) and mood (SMD 0.1, 95% CI -0.3 to 0.5, 1.9% absolute change, less than 1 point shift on a 0 to 90 scale) post-intervention. In view of the quality of evidence we cannot be certain that biofeedback has a little or no effect on these outcomes. There was very low quality evidence that biofeedback led to more withdrawals from the study (RR 4.08, 95% CI 1.43 to 11.62, 20% absolute risk difference). No adverse events were reported.There was no advantage observed for mindfulness in comparison to usual care for physical functioning (SMD -0.3, 95% CI -0.6 to 0.1, -4.8% absolute change, 4 point shift on a scale 0 to 100), pain (SMD -0.1, CI -0.4 to 0.3, -1.3% absolute change, less than 1 point shift on a 0 to 10 scale), mood (SMD -0.2, 95% CI -0.5 to 0.0, -3.7% absolute change, 2 point shift on a 20 to 80 scale) or withdrawals (RR 1.07, 95% CI 0.67 to 1.72, 2% absolute risk difference) between the two groups post-intervention. However, the quality of the evidence was very low for pain and moderate for mood and number of withdrawals. No studies reported any adverse events.Very low quality evidence revealed that movement therapies in comparison to usual care controls improved pain (MD -2.3, CI -4.2 to -0.4, -23% absolute change) and mood (MD -9.8, 95% CI -18.5 to -1.2, -16.4% absolute change) post-intervention. There was no advantage for physical functioning (SMD -0.2, 95% CI -0.5 to 0.2, -3.4% absolute change, 2 point shift on a 0 to 100 scale), participant withdrawals (RR 1.95, 95% CI 1.13 to 3.38, 11% absolute difference) or adverse events (RR 4.62, 95% CI 0.23 to 93.92, 4% absolute risk difference) between the two groups, however rare adverse events may include worsening of pain.Low quality evidence revealed that relaxation based therapies in comparison to usual care controls showed an advantage for physical functioning (MD -8.3, 95% CI -10.1 to -6.5, -10.4% absolute change) and pain (SMD -1.0, 95% CI -1.6 to -0.5, -3.5% absolute change, 2 point shift on a 0 to 78 scale) but not for mood (SMD -4.4, CI -14.5 to 5.6, -7.4% absolute change) post-intervention. There was no difference between the groups for number of withdrawals (RR 4.40, 95% CI 0.59 to 33.07, 31% absolute risk difference) and no adverse events were reported.
Authors' conclusions: Psychological interventions therapies may be effective in improving physical functioning, pain and low mood for adults with fibromyalgia in comparison to usual care controls but the quality of the evidence is low. Further research on the outcomes of therapies is needed to determine if positive effects identified post-intervention are sustained. The effectiveness of biofeedback, mindfulness, movement therapies and relaxation based therapies remains unclear as the quality of the evidence was very low or low. The small number of trials and inconsistency in the use of outcome measures across the trials restricted the analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Alice Theadom is a psychologist who specialises in conducting research of psychological interventions in health care.
Figures



































































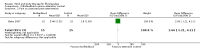
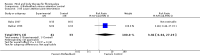




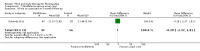


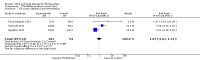









































Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001980.pub2
References
References to studies included in this review
Alda 2011 {published data only}
Altan 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Altan L, Korkmaz N, Bingol U, Gunay B. Effect of pilates training on people with fibromyalgia syndrome: a pilot study. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2009;90:1983‐8. - PubMed
Ang 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ang DC, Hakr R, Mazzuca S, France CR, Steiner J, Stump T. Cognitive‐behavioral therapy attenuates nociceptive responding in patients with fibromyalgia: a pilot study. Arthritis Care and Research 2010;62(5):618‐23. - PubMed
Ang 2013 {published data only}
Astin 2003 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Astin JA, Berman BM, Bausell B, Lee WL, Hochberg M, Forys KL. The efficacy of mindfulness meditation plus Gigong movement therapy in the treatment of fibromylagia: a randomized clinical trial. The Journal of Rheumatology 2003;30(10):2257‐62. - PubMed
Babu 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Babu A, Mathew E, Danda D, Prakash H. Management of patients with fibromyalgia using biofeedback: a randomized control trial. Indian Journal of Medical Sciences 2007;61(8):455‐61. - PubMed
Bakker 1995 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bakker C, Linden S, Santen‐Hoeufft M, Bolwijn P, Hidding A. Problem elicitation to assess patient priorities in ankylosing spondylitis and fibromyalgia. The Journal of Rheumatology 1995;22(7):1304‐10. - PubMed
Baumuller 2009 {published data only}
-
- Baumuller EU. Electromyogram‐biofeedback in patients with fibromylagia: a randomized controlled trial. Dissertation 2009. - PubMed
Bojner‐Horwitz 2003 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Bojner‐Horwitz E, Theorell T, Anderberg UM. Dance/movement therapy and changes in stress‐related hormones: a study of fibromyalgia patients with video‐interpretation. The Arts in Psychotherapy 2003;30:255‐64.
Brattberg 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Brattberg G. Self‐administered EFT (Emotional Freedom Techniques) in individuals with fibromyalgia: a randomized trial. Integrative Medicine 2008;7(4):30‐5.
Burckhardt 1994 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Burckhardt CS, Mannerkorpi K, Hedenberg L, Bjelle A. A randomized, controlled clinical trial of education and physical training for women with fibromyalgia. The Journal of Rheumatology 1994;21(4):714‐20. - PubMed
Calandre 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Calandre EP, Rodriquez‐Claro ML, Rico‐Villademoros F, Vilchez JS, Hidalgo J, Delgado‐Rodriquez A. Effects of pool‐based exercise in fibromyalgia symptomatology and sleep quality: a prospective ransomized comparison between stretching and Tai Chi. Clincial and Experimental Rheumatology 2009;27:S21‐8. - PubMed
Carson 2010 {published and unpublished data}
Carson 2012 {published and unpublished data}
Castel 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Castel A, Perez M, Sala J, Padrol A, Rull M. Effect of hypnotic suggestion on fibromyalgic pain: comparison between hypnosis and relaxation. European Journal of Pain 2007;11(4):463‐8. - PubMed
Castel 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Castel A, Salvat M, Sala J, Rull M. Cognitive‐behavioural group treatment with hypnosis: a randomized pilot trial in fibromyalgia. Contemporary Hypnosis 2009;26(1):48‐59.
Castel 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Castel A, Cascon R, Padrol A, Sala J, Rull M. Multicomponent cognitive‐behavioral group therapy with hypnosis for the treatment of fibromyalgia: long‐term outcome. The Journal of Pain 2012;13(3):255‐65. - PubMed
Connais 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Effectiveness of EFT on fibromyalgia. Thesis.
de Souza 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Souza JB, Bourgault P, Charest J, Marchand S. Interactional school of fibromyalgia: learning to cope with pain ‐ a randomized controlled study. Revista Brasileira de Reumatologia 2008;48(4):218‐25.
Edinger 2005 {published data only}
-
- Edinger JD, Wohlgemuth WK, Krystal AD, Rice JR. Behavioral insomnia therapy for fibromyalgia patients. Archives of Internal Medicine 165;28:2527‐35. - PubMed
Falcao 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Falcao DM, Sales L, Leite JR, Feldman D, Valim V, Natour J. Cognitive behavioral therapy for the treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 2008;16(3):133‐40.
Fontaine 2010 {published and unpublished data}
Fors 2000 {published data only}
-
- Fors EA, Gotestam KG. Patient education, guided imagery and pain related talk in fibromyalgia coping. European Journal of Psychiatry 2000;14(4):233‐40.
Garcia 2006 {published data only}
-
- Garcia J, Simon MA, Duran M, Canceller J, Aneiros FJ. Differential efficacy of a cognitive‐behavioral intervention versus pharmacological treatment in the management of fibromyalgic syndrome. Psychology, Health and Medicine 2006;11(4):498‐506. - PubMed
Gillis 2006 {published and unpublished data}
Hammond 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hammond A, Freeman K. Community patient education and exercise for people with fibromyalgia: a parallel group randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2006;20:835‐46. - PubMed
Hamnes 2012 {published data only}
Holmer 2004 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Holmer ML, Gevirtz R, Spira JL, Greenberg MA. The effects of yoga on symptoms and psychosocial adjustment in fibromyalgia syndrome patients. Conference abstracts from papers presented at the 35th annual meeting. 2004; Vol. 29:302.
Hsu 2010 {published and unpublished data}
Jensen 2012 {published data only}
-
- Jensen KB, Kosek E, Wicksell R, Kemani M, Olsson G, Merle JV, et al. Cognitive behavioral therapy increases pain‐evoked activation of the prefrontal cortex in patients with fibromyalgia. Pain 2012;153:1495‐503. - PubMed
Jones 2012 {published and unpublished data}
Kayiran 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kayiran S, Dursun E, Dursun N, Ermutlu N, Karamursel S. Neurofeedback intervention in fibromyalgia syndrome; a randomized, controlled, rater blind clinical trial. Applied Psychophysiology Biofeedback 2010;35:293‐302. - PubMed
Langford 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Langford MM. The efficacy of a combined cognitive‐behavioural and interpersonal therapy approach to the treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Dissertation.
Lera 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Lera S, Gelman SM, Lopez M, Abenoza M, Zorrilla JG, Castro‐Fornieles J, et al. Multi‐disciplinary treatment of fibromyalgia: does cognitive behavior therapy increase the response to treatment?. Journal of Psychosomatic Research 2009;67:433‐41. - PubMed
Liu 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Liu W, Zahner L, Cornell M, Le T, Ratner J, Wang Y, et al. Benefit of Qigong exercise in patients with fibromyalgia: a pilot study. International Journal of Neuroscience 2012;122:657‐64. - PubMed
Luciano 2011 {published data only}
-
- Luciano JV, Martinez N, Penarrubia‐Maria MT, Fernandez‐Vergel R, Garcia‐Campayo J, Verduras C, Blanco, et al and the FibroQoL Study Group. Effectiveness of a psychoeducational treatment program implemented in a general practice for fibromyalgia patients. Clinical Journal of Pain 2011;27(5):383‐90. - PubMed
Lynch 2012 {published and unpublished data}
Maddali‐Bongh 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Maddali‐Bongi S, Felice C, Rosso A, Galluccio F, Landi G, Tai G, et al. The efficacy of the Resseguier method in the treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome: a randomised controlled trial. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2010;28:S46‐S50. - PubMed
Mannerkorpi 2004 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Mannerkorpi K, Arndorw M. Efficacy and feasibility of a combination of body awareness therapy and qigong in patients with fibromyalgia: a pilot study. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2004;36(6):279‐81. - PubMed
Martinez‐Valero 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Martinez‐Valero C, Castel A, Capafons A, Sala J, Espejo B, Cardena E. Hypnotic treatment synergizes the psychological treatement of fibromyalgia: a pilot study. American Journal of Clinical Hypnosis 2008;50(4):311‐21. - PubMed
Menzies 2006 {published and unpublished data}
Miro 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Miro E, Lupianez J, Martinez MP, Snachez AI, Diaz‐Piedra C, Guzman MA, et al. Cognitive‐behavioral therapy for insomnia improves attention function in fibromyalgia syndrome: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Journal of Health Psychology 2011;16(5):770‐82. - PubMed
Oliver 2001 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Oliver K, Cronan TA, Walen HR, Tomita M. Effects of social support and education on health care costs for patients with fibromyalgia. The Journal of Rheumatology 2001;28(12):2711‐9. - PubMed
Oneva‐Zafra 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Oneva‐Zaffra MD, Castro‐Sanchez AM, Mataran‐Penarrocha GA, Moreno‐Lorenzo C. Effect of music as nursing intervention for people diagnosed with fibromyalgia. Pain Management 2010;14(2):e39‐46. - PubMed
Parra‐Delgado 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Parra‐Delgado M, Latorre‐Postigo JM. Effectiveness of mindfulness‐based cognitive therapy in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomised trial. Cognitive Therapy Research 2013;37:1015‐26.
Picard 2013 {published data only}
-
- Picard P, Jusseaume C, Boutet M, Duale C, Mulliez A, Aublet‐Cuvellier B. Hypnosis for management of fibromyalgia. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis 2013;61(1):111‐23. - PubMed
Riedel 2012 {published data only}
-
- Riedel SL, Bluefield WV. Effects of guided imagery in persons with fibromyalgia. Electronic thesis 2012.
Scheidt 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Scheidt CE, Waller E, Endorf K, Schmidt S, Konig R, Zeeck A, et al. Is brief psychodynamic psychotherapy in primary fibromyalgia syndrome with concurrent depression an effective treatment? A randomized controlled trial. General Hospital Psychiatry 2013;35:160‐7. - PubMed
Schmidt 2011 {published data only}
-
- Schmidt S, Grossman P, Schwarzer B, Jena S, Naumann J, Walach H. Treating fibromyalgia with mindfulness‐based stress reduction: results from a 3‐armed randomized controlled trial. Pain 2010;152(2):361‐9. - PubMed
Sephton 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Sephton SE, Salmon P, Weissbecker I, Ulmer C, Floyd A, Hoover K, et al. Mindfulness meditation alleviates depressive symptoms in women with fibromyalgia: results of a randomized clinical trial. Arthritis Care and Research 2007;15:77‐85. - PubMed
-
- Weissbecker I, Salmon P, Studts JL, Floyd AR, Dedert EA, Sephton SE. Mindfulness‐based stress reduction and sense of coherence among women with fibromyalgia.. Jourrnal of Clinical Psychology in Medical Settings 2002;9(4):297‐305.
Soares 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Soares JJF, Grossi G. A randomized, controlled comparison of educational and behavioural interventions for women with fibromyalgia. Scandinavian Journal of Occupational Therapy 2002;9(1):35‐45.
Stuifbergen 2010 {published and unpublished data}
Thieme 2006 {published data only}
Van Santen 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Santen M, Bolwijn P, Verstappen F, Bakker C, Hidding A, Houben H, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing fitness and biofeedback training versus basic treatment in patients with fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29(3):575‐81. - PubMed
Vlaeyen 1996 {published data only}
-
- Vlaeyen JWS, Teeken‐Gruben NJG, Goosens MEKB, Rutten van Molken MPMH, Pelt RAGB, Eek H, et al. Cognitive ‐educational treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomized clinical trial. 1. Clinical Effects. The Journal of Rheumatology 1996;23(7):1237‐45. - PubMed
Wang 2010 {published and unpublished data}
Wicksell 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Wicksell RK, Kemani M, Jensen K, Kosek E, Kadetoff D, Sorjonen K, et al. Acceptance and commitment therapy for fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. European Journal of Pain 2012;17:599‐611. - PubMed
Wigers 1996 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Wigers SH, Stiles TC, Vogel PA. Effects of aerobic exercise versus stress management treatment in fibromyalgia. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 1996;25(2):77‐86. - PubMed
Williams 2002 {published data only}
-
- Williams DA, Cary MA, Groner KH, Chaplin W, Glazier LJ, Rodriquez AM, et al. Improving physical functional status in patients with fibromyalgia: a brief cognitive behavioral intervention. The Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29(6):1280‐6. - PubMed
Williams 2010 {published and unpublished data}
References to studies excluded from this review
Alvarez‐Nemegyei 2006 {published data only}
-
- Alvarez‐Nemegyei J, Negreros‐Castillo A, Nuno‐Gutierrez BL, Alvarez‐Berzunza J, Alcocer‐Martinez LM. Efficacy of Eriksonian hypnosis in women with fibromyalgia syndrome [Eficacia de la hipnosis ericksoniana en el sindrome de fibromialgia en mujeres]. Revista Medica del Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social 2006;45(4):395‐401. - PubMed
Ang 2013b {published data only}
Arcos‐Carmona 2011 {published data only}
-
- Arcos‐Carmona. Effects of aerobic exercise program and relaxation techniques on anxiety, quality of sleep, depression, and quality of life in patients with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Medicina Clinica 2011;137(9):398‐401. - PubMed
Bieber 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bieber C, Müller KG, Blumenstiel K, Schuller‐Roma B, Richter A, Hochlehnert A, et al. Shared decision making (SDM) with chronic pain patients. The patient as a partner in the medical decision making process. Bundesgesundheitsblatt, Gesundheitsforschung, Gesundheitsschutz 2004;47(10):985‐91. - PubMed
Bieber 2008 {published data only}
-
- Bieber C, Müller KG, Blumenstiel K, Hochlehnert A, Wilke S, Hartmann M, et al. A shared decision‐making communication training program for physicians treating fibromyalgia patients: effects of a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Psychosomatic Research 2008;64(1):13‐20. - PubMed
Bosch‐Romero 2002 {published data only}
Casanueva‐Fernandez 2012 {published data only}
-
- Casanueva‐Fernandez B, Llorca J, Blanch i Rubio J, Rodero‐Fernandez B, Gonzalez‐Gay MA. Efficacy of a multidisciplinary treatment program in patients with severe fibromyalgia. Rheumatology International 2012;32:2497‐502. - PubMed
Castel 2013 {published data only}
-
- Castel A, Fontova R, Montull S, Perinan R, Poveda MJ, Miralles I, et al. Efficacy of a multi‐disciplinary fibromyalgia treatment adapted for women with low educational levels: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Care and Research 2013;65(3):421‐31. - PubMed
Cedraschi 2004 {published data only}
Gowans 1999 {published data only}
-
- Gowans SE, deHueck A, Voss S, Richardson M. A randomized, controlled trial of exercise and education for individuals with fibromyalgia. Arthritis Care & Research 1999;12(2):120‐8. - PubMed
Hochlehnert 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hochlehnert A, Richter A, Bludau HB, Bieber C, Blumenstiel K, Mueller K, et al. A computer‐based information‐tool for chronic pain patients. Computerized information to support the process of shared decision‐making. Patient Education and Counseling 2006;61(1):92‐8. - PubMed
Hunt 2000 {published data only}
-
- Hunt J, Bogg J. An evaluation of the impact of a fibromyalgia self‐management programme on patient morbidity and coping. Advances in Physiotherapy 2000;2(4):168‐75.
King 2002a {published data only}
-
- King SJ, Wessel J, Bhambhani Y, Sholter D, Maksymowych W. The effects of exercise and education, individually or combined, in women with fibromyalgia. The Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29(12):2620‐7. - PubMed
King 2002b {published data only}
-
- King SJ, Wessel J, Bhambhani Y, Sholter D, Maksymowych W. Predictors of success of intervention programs for persons with fibromyalgia. The Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29(5):1034‐40. - PubMed
Kravitz 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kravitz HM, Esty ML, Katz RS, Fawcett J. Treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome using low‐intensity neurofeedback with the Flexyx Neurotherapy System: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Journal of Neurotherapy 2006;10(2‐3):41‐58.
Lemstra 2005 {published data only}
-
- Lemstra M, Olszynski WP, Lemstra M. The effectiveness of multidisciplinary rehabilitation in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Journal of Pain 2005;21(2):166‐74. - PubMed
Mannerkorpi 2000 {published data only}
-
- Mannerkorpi K, Nyberg B, Ahlmén M, Ekdahl C. Pool exercise combined with an education program for patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. A prospective, randomized study. Journal of Rheumatology 2000;27(10):2473‐81. - PubMed
McBeth 2012 {published data only}
-
- McBeth J, Prescott G, Scotland G, Lovell K, Keeley P, Hannaford P, et al. Cognitive behaviour therapy, exercise or both for treating chronic widespread pain. Archives of Internal Medicine 2012;172(1):48‐57. - PubMed
McVeigh 2006 {published data only}
-
- McVeigh JG, Hurley DA, Basford JR, Sim J, Baxter GD, Finch MB. Effectiveness of a combined pool‐based exercise and education programme compared to usual medical care in fibromyalgia syndrome: a randomised, controlled trial. Physical Therapy Reviews 2006;11(3):217.
Nelson 2010 {published data only}
-
- Nelson DV, Bennett RM, Barkhuizen A, Sexton GJ, Jones KD, Esty ML, et al. Neurotherapy of fibromyalgia?. Pain Medicine 2010;11(6):912‐9. - PubMed
Van Eijk‐Hustings 2013 {published data only}
-
- Eijk‐Hustings Y, Kroese M, Tan F, Boonen A, Bessems‐Beks M, Landewe R. Challenges in demonstrating the effectiveness of multidisciplinary treatment on quality of life, participation and health care utilisation in patients with fibromyalgia: a randomised controlled trial. Clinical Rheumatology 2013;32:199‐209. - PubMed
van Koulil 2010 {published data only}
-
- Koulil S, Lankveld W, Kraaimaat FW, Helmond T, Vedder A, Hoorn H, et al. Tailored cognitive‐behavioral therapy and exercise training for high‐risk patients with fibromyalgia. Arthritis Care & Research 2010;62(10):1377‐85. - PubMed
Zhang 2009 {published data only}
-
- Zhang. Influence of psychological intervention on therapeutic effects of massage therapy for fibromyalgia syndrome. Journal of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2009; Vol. 26, issue 1:20‐3.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Thorsell 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Thorsell J, Finnes A, Dahl JA, Lundgren T, Gybrant M, Gordh T, et al. A comparative study of 2 manual‐based self‐help interventions, acceptance and commitment therapy and applied relaxation for persons with chronic pain. Clinical Journal of Pain 2011;27(8):716‐23. - PubMed
Toussaint 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Toussaint LT, Whipple MO, Abboud LL, Vincent A, Wahner‐Roedler DL. A mind‐body technique for symptoms related to fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue. Explore 2012;8(2):92‐8. - PubMed
Wang 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Wang C. Cost‐effectiveness of tai chi mind‐body exercise for the treatment of fibromyalgia. Explore Meeting. 2013.
References to ongoing studies
Garcia‐Campayo 2009 {published data only}
Miles 2010 {published data only}
-
- Miles. Effects of gentle yoga versus CBT on fibromyalgia symptoms. APA Convention Presentation. 2010:Topic 36.5.
Additional references
Altman 1996
Altman 2000
-
- Altman DG. Statistics in medical journals: some recent trends. Statistics in Medicine 2000;19(23):3275‐89. - PubMed
Anderson 1995
-
- Anderson KO, Dowds BN, Pelletz RE, Edwards WT, Peeters‐Asdourian C. Development and initial validation of a scale to measure self‐efficacy beliefs in patients with chronic pain. Pain 1995;63(1):77‐84. - PubMed
Arnold 2011
Bennett 2007
Bennett 2009
Berger 2007
Bergman 2005
-
- Bergman S. Psychosocial aspects of chronic widespread pain and fibromyalgia. Disability and Rehabilitation 2005;27(12):675‐83. - PubMed
Bernardy 2011
Bernardy 2013
Branco 2010
Burckhardt 1991
-
- Burckhardt CS, Clark SR, Bennett RM. The fibromyalgia impact questionnaire: development and validation. The Journal of Rheumatology 1991;18:728‐33. - PubMed
Busch 2007
Busch 2013
Buysse 1989
-
- Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Research 1989;28(2):193‐213. - PubMed
Ceko 2011
Chan 2012
-
- Chan CL, Wang CW, Ho RT, Ng SM, Ziea ET, Wong VT. Qigong exercise for the treatment of fibromyalgia: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 2012;18(7):641‐6. - PubMed
Choy 2009
-
- Choy EH, Mease PJ. Key symptom domains to be assessed in fibromyalgia (outcome measures in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials). Rheumatology Diseases Clinics of North America 2009;35(2):329‐37. - PubMed
Clauw 2011
Dworkin 2003
-
- Dworkin RH, Corbin AE, Young JP, Sharma U, LaMoreaux L, Bockbrader H, et al. Pregabalin for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. Neurology 2003;60:1274‐83. - PubMed
Farrar 2001
-
- Farrar JT, Young JP, LaMoreaux L, Werth JL, Poole M. Clinical importance of changes in chronic pain intensity measured on an 11 point numerical pain rating scale. Pain 2001;94:149‐58. - PubMed
Fewtrell 2008
-
- Fewtrell MS, Kennedy K, Singhal A, Martin RM, Ness A, Hadders‐Algra M, et al. How much loss to follow‐up isacceptable in long‐term randomised trials and prospective. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2008;93(6):458‐61. - PubMed
Glombiewski 2013
Hadhazy 2000
-
- Hadhazy VA, Ezzo J, Creamer P, Berman BM. Mind‐body therapies for the treatment of fibromyalgia. A systematic review. Journal of Rheumatology 2000;27(12):2911‐8. - PubMed
Hauser 2010
Hauser 2013
Hays 1993
-
- Hays RD, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36‐item short‐form health survey 1.0. Health Economics 1993;2(3):217‐27. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (Editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org 2011.
Lau 2006
Lauche 2013
-
- Lauche R, Cramer H, Dobos G, Langhorst J, Schmidt S. A systematic review and meta‐analysis of mindfulness‐based stress reduction for the fibromyalgia syndrome. Journal of Psychosomatic Research 2013;75(6):500‐10. - PubMed
MacFarlane 2002
-
- Macfarlane TV, Blinkhorn A, Worthington HV, Davies RM, Macfarlane GJ. Sex hormonal factors and chronic widespread pain: a population study among women. Rheumatology 2002;41(4):454‐7. - PubMed
Mease 2005
-
- Mease P. Fibromyalgia syndrome: review of clinical presentation, pathogenesis, outcome measures and treatment. The Journal of Rhematology 2005;32(75):6‐21. - PubMed
Moore 2009
Moore 2011
NCCAM 2005
-
- National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine. Mind‐Body Medicine: an o. National Institutes of Health, US Department of Health and Human Services 2005.
NCCAM 2012
-
- National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine. Mind–body Medicine: an overview. http://nccam.nih.gov/health/backgrounds/mindbody.htm 2012.
Nicassio 2002
-
- Nicassio PM, Moxham EG, Schuman EC, Gevirtz RN. The contribution of pain, reported sleep quality, and depressive symptoms to fatigue in fibromyalgia. Pain 2002;100:271‐9. - PubMed
Puhan 2006
Sicras‐Mainar 2009
Smets 1995
-
- Smets EM, Garssen B, Bonke B, Haes JC. The multidimensional fatigue inventory (MFI) psychometric qualities of an instrument to assess fatigue. Journal of Psychosomatic Research 1995;39(3):315‐25. - PubMed
Theadom 2008
-
- Theadom A, Cropley M. Dysfunctional beliefs, stress and sleep disturbance in fibromyalgia. Sleep Medicine 2008;9(4):376‐81. - PubMed
Vitetta 2005
-
- Vitetta L, Anton B, Cortizo F, Sali A. Mind–body medicine: stress and its impact on overall health and longevity. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2005;1057:492‐505. - PubMed
Wahbeh 2008
Wells 2010
White 1999
-
- White KP, Speechley M, Harth M, Ostbye T. The London fibromyalgia epidemiology study: the prevalence of fibromyalgia syndrome in London, Ontario. The Journal of Rheumatology 1999;26(7):1570‐6. - PubMed
Williams 2012
Wolfe 1990
-
- Wolfe F, Smythe A, Yunus M. The College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of fibromyalgia. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1990;33:160‐72. - PubMed
Wolfe 1995
-
- Wolfe F, Ross K, Anderson J, Russell IJ, Herbert L. The prevalence and characteristics of fibromyalgia in the general population. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1995;38:19‐28. - PubMed
Wolfe 2010
-
- Wolfe F, Clauw DJ, Fitzcharles MA, Goldenberg DL, Katz RS, Mease PJ, et al. The American College of Rheumatology preliminary diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia and measurement of symptom severity. Arthritis Care & Research 2010;62(5):600‐10. - PubMed
Wolfe 2011
-
- Wolfe F, Clauw DJ, Fitzcharles MA, Goldenberg DL, Hauser W, Katz RS, et al. Fibromyalgia criteria and severity scales for clinical and epidemiological studies: a modification of the ACR Preliminary Diagnostic Criteria for Fibromyalgia. The Journal of Rheumatology. 2011;38(6):1113‐22. - PubMed
Wolfe 2011b
-
- Wolfe F. How to use the new American College of Rheumatology fibromyalgia diagnostic criteria. Arthritis Care & Research 2011;63(7):1073‐4. - PubMed
Yunus 2001
-
- Yunus MB. The role of gender in fibromyalgia syndrome. Current Rheumatology Reports 2001;3(2):128‐34. - PubMed
Zigmond 1983
-
- Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1983;67(6):361‐70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

