A Sativex(®) -like combination of phytocannabinoids as a disease-modifying therapy in a viral model of multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 25857324
- PMCID: PMC4507161
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13159
A Sativex(®) -like combination of phytocannabinoids as a disease-modifying therapy in a viral model of multiple sclerosis
Abstract
Background and purpose: Sativex(®) is an oromucosal spray, containing equivalent amounts of Δ(9) -tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ(9) -THC) and cannabidiol (CBD)-botanical drug substance (BDS), which has been approved for the treatment of spasticity and pain associated to multiple sclerosis (MS). In this study, we investigated whether Sativex may also serve as a disease-modifying agent in the Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus-induced demyelinating disease model of MS.
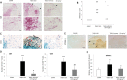
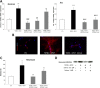
Experimental approach: A Sativex-like combination of phytocannabinoids and each phytocannabinoid alone were administered to mice once they had established MS-like symptoms. Motor activity and the putative targets of these cannabinoids were assessed to evaluate therapeutic efficacy. The accumulation of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPGs) and astrogliosis were assessed in the spinal cord and the effect of Sativex on CSPGs production was evaluated in astrocyte cultures.
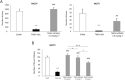
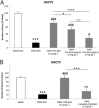
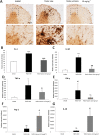
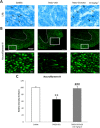
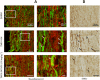
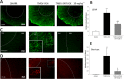
Key results: Sativex improved motor activity - reduced CNS infiltrates, microglial activity, axonal damage - and restored myelin morphology. Similarly, we found weaker vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 staining and IL-1β gene expression but an up-regulation of arginase-1. The astrogliosis and accumulation of CSPGs in the spinal cord in vehicle-infected animals were decreased by Sativex, as was the synthesis and release of CSPGs by astrocytes in culture. We found that CBD-BDS alone alleviated motor deterioration to a similar extent as Sativex, acting through PPARγ receptors whereas Δ(9) -THC-BDS produced weaker effects, acting through CB2 and primarily CB1 receptors.
Conclusions and implications: The data support the therapeutic potential of Sativex to slow MS progression and its relevance in CNS repair.
© 2015 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The disease-modifying effects of a Sativex-like combination of phytocannabinoids in mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis are preferentially due to Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol acting through CB1 receptors.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2015 Nov;4(6):505-11. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2015.08.001. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2015. PMID: 26590655
-
Sativex-like combination of phytocannabinoids is neuroprotective in malonate-lesioned rats, an inflammatory model of Huntington's disease: role of CB1 and CB2 receptors.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2012 May 16;3(5):400-6. doi: 10.1021/cn200114w. Epub 2012 Feb 9. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22860209 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a Sativex-Like Combination of Phytocannabinoids on Disease Progression in R6/2 Mice, an Experimental Model of Huntington's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Mar 23;18(4):684. doi: 10.3390/ijms18040684. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28333097 Free PMC article.
-
Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol/Cannabidiol Oromucosal Spray (Sativex®): A Review in Multiple Sclerosis-Related Spasticity.Drugs. 2017 Apr;77(5):563-574. doi: 10.1007/s40265-017-0720-6. Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28293911 Review.
-
THC and CBD oromucosal spray (Sativex®) in the management of spasticity associated with multiple sclerosis.Expert Rev Neurother. 2011 May;11(5):627-37. doi: 10.1586/ern.11.47. Epub 2011 Apr 1. Expert Rev Neurother. 2011. PMID: 21456949 Review.
Cited by
-
The Treatment of Cognitive, Behavioural and Motor Impairments from Brain Injury and Neurodegenerative Diseases through Cannabinoid System Modulation-Evidence from In Vivo Studies.J Clin Med. 2020 Jul 27;9(8):2395. doi: 10.3390/jcm9082395. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32726998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Botanically-Derived Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol and Cannabidiol, and Their 1:1 Combination, Modulate Toll-like Receptor 3 and 4 Signalling in Immune Cells from People with Multiple Sclerosis.Molecules. 2022 Mar 8;27(6):1763. doi: 10.3390/molecules27061763. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35335126 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoids as Multitarget Drugs for the Treatment of Autoimmunity in Glaucoma.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2025 Mar 26;8(4):932-950. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00583. eCollection 2025 Apr 11. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2025. PMID: 40242585 Review.
-
The Therapeutic Potential and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Neuroprotective Effects of Sativex® - A Cannabis-derived Spray.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(15):1427-1448. doi: 10.2174/0113895575285934240123110158. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38318827 Review.
-
Current status of neuroprotective and neuroregenerative strategies in multiple sclerosis: A systematic review.Mult Scler. 2022 Jan;28(1):29-48. doi: 10.1177/13524585211008760. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Mult Scler. 2022. PMID: 33870797 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

