Antioxidant and anticholinesterase investigations of Rumex hastatus D. Don: potential effectiveness in oxidative stress and neurological disorders
- PMID: 25857346
- PMCID: PMC4381421
- DOI: 10.1186/s40659-015-0010-2
Antioxidant and anticholinesterase investigations of Rumex hastatus D. Don: potential effectiveness in oxidative stress and neurological disorders
Abstract
Background: Rumex species are traditionally used for the treatment of neurological disorders including headache, migraine, depression, paralysis etc. Several species have been scientifically validated for antioxidant and anticholinestrase potentials. This study aims to investigate Rumex hastatus D. Don crude methanolic extract, subsequent fractions, saponins and flavonoids for acetylcholinestrase, butyrylcholinestrase inhibition and diverse antioxidant activities to validate its folkloric uses in neurological disorders. Rumex hastatus crude methanolic extract (Rh. Cr), subsequent fractions; n-hexane (Rh. Hex), chloroform (Rh. Chf), ethyl acetate (Rh. EtAc), aqueous fraction (Rh. Aq), crude saponins (Rh. Sp) and flavonoids (Rh. Fl) were investigated against acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) at various concentrations (125, 250, 500, 1000 μg/mL) using Ellman's spectrophotometric analysis. Antioxidant potentials of Rh. Sp and Rh. Fl were evaluated using DPPH, H2O2 and ABTS free radical scavenging assays at 62.5, 125, 250, 500, 1000 μg/mL.
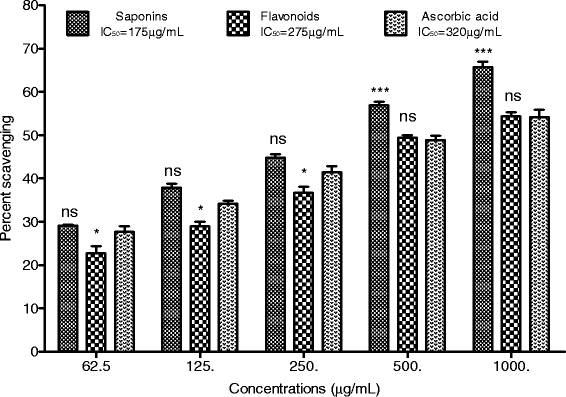
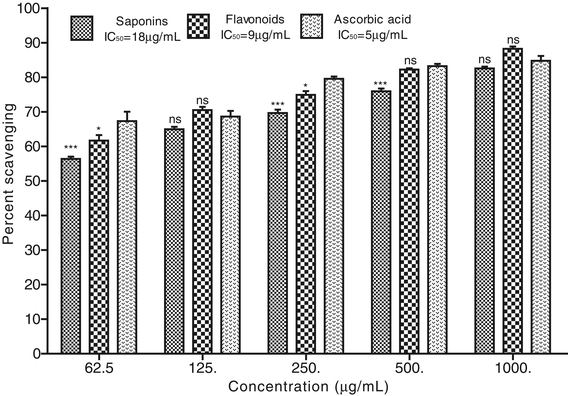
Results: All the test samples showed concentration dependent cholinesterase inhibition and radicals scavenging activity. The AChE inhibition potential of Rh. Sp and Rh. Fl were most prominent i.e., 81.67 ± 0.88 and 91.62 ± 1.67 at highest concentration with IC50 135 and 20 μg/mL respectively. All the subsequent fractions exhibited moderate to high AChE inhibition i.e., Rh. Cr, Rh. Hex, Rh. Chf, Rh. EtAc and Rh. Aq showed IC50 218, 1420, 75, 115 and 1210 μg/mL respectively. Similarly, against BChE various plant extracts i.e., Rh. Sp, Rh. Fl, Rh. Cr, Rh. Hex, Rh. Chf, Rh. EtAc and Rh. Aq resulted IC50 165, 175, 265, 890, 92, 115 and 220 μg/mL respectively. In DPPH free radical scavenging assay, Rh. Sp and Rh. Fl showed comparable results with the positive control i.e., 63.34 ± 0.98 and 76.93 ± 1.13% scavenging at 1 mg/mL concentration (IC50 312 and 104 μg/mL) respectively. The percent ABTS radical scavenging potential exhibited by Rh. Sp and Rh. Fl (1000 μg/mL) were 82.58 ± 0.52 and 88.25 ± 0.67 with IC50 18 and 9 μg/mL respectively. Similarly in H2O2 scavenging assay, the Rh. Sp and Rh. Fl exhibited IC50 175 and 275 μg/mL respectively.
Conclusion: The strong anticholinesterase and antioxidant activities of Rh. Sp, Rh. Fl and various fractions of R. hastatus support the purported ethnomedicinal uses and recommend R. hastatus as a possible remedy for the treatment of AD and neurodegenerative disorders.
Figures
References
-
- WHO, Salud OMdl . The World Health Report 2001: Mental Health: New Understanding. New Hope: World Health Organization Geneva; 2001.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

