The serine threonine kinase RIP3: lost and found
- PMID: 25858093
- PMCID: PMC4578615
- DOI: 10.5483/bmbrep.2015.48.6.068
The serine threonine kinase RIP3: lost and found
Abstract
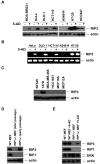
Receptor-interacting protein kinase-3 (RIP3, or RIPK3) is an essential protein in the "programmed", or "regulated" necrosis cell death pathway that is activated in response to death receptor ligands and other types of cellular stress. Programmed necrotic cell death is distinguished from its apoptotic counterpart in that it is not characterized by the activation of caspases; unlike apoptosis, programmed necrosis results in plasma membrane rupture, thus spilling the contents of the cell and triggering the activation of the immune system and inflammation. Here we discuss findings, including our own recent data, which show that RIP3 protein expression is absent in many cancer cell lines. The recent data suggests that the lack of RIP3 expression in a majority of these deficient cell lines is due to methylation-dependent silencing, which limits the responses of these cells to pro-necrotic stimuli. Importantly, RIP3 expression may be restored in many cancer cells through the use of hypomethylating agents, such as decitabine. The potential implications of loss of RIP3 expression in cancer are explored, along with possible consequences for chemotherapeutic response.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Roles of RIPK3 in necroptosis, cell signaling, and disease.Exp Mol Med. 2022 Oct;54(10):1695-1704. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00868-z. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Exp Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36224345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methylation-dependent loss of RIP3 expression in cancer represses programmed necrosis in response to chemotherapeutics.Cell Res. 2015 Jun;25(6):707-25. doi: 10.1038/cr.2015.56. Epub 2015 May 8. Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 25952668 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha.Cell. 2009 Jun 12;137(6):1100-11. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.021. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19524512
-
Distinctive roles of receptor-interacting protein kinases 1 and 3 in caspase-independent cell death of L929.Cell Biochem Funct. 2014 Jan;32(1):62-9. doi: 10.1002/cbf.2972. Epub 2013 Apr 15. Cell Biochem Funct. 2014. PMID: 23584955
-
Programmed cell death with a necrotic-like phenotype.Biomol Concepts. 2013 Jun;4(3):259-75. doi: 10.1515/bmc-2012-0056. Biomol Concepts. 2013. PMID: 25436579 Review.
Cited by
-
RIPK3 in necroptosis and cancer.Mol Cells. 2025 May;48(5):100199. doi: 10.1016/j.mocell.2025.100199. Epub 2025 Feb 24. Mol Cells. 2025. PMID: 40010643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subversion of Programed Cell Death by Poxviruses.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2023;442:105-131. doi: 10.1007/82_2020_229. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2023. PMID: 33507400 Free PMC article.
-
EBV(LMP1)-induced metabolic reprogramming inhibits necroptosis through the hypermethylation of the RIP3 promoter.Theranostics. 2019 Apr 13;9(9):2424-2438. doi: 10.7150/thno.30941. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31131045 Free PMC article.
-
A Bak-dependent mitochondrial amplification step contributes to Smac mimetic/glucocorticoid-induced necroptosis.Cell Death Differ. 2017 Jan;24(1):83-97. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.102. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Cell Death Differ. 2017. PMID: 27834956 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of RIPK3 in necroptosis, cell signaling, and disease.Exp Mol Med. 2022 Oct;54(10):1695-1704. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00868-z. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Exp Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36224345 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

