Shear wave elastography of placenta: in vivo quantitation of placental elasticity in preeclampsia
- PMID: 25858523
- PMCID: PMC4463268
- DOI: 10.5152/dir.2014.14338
Shear wave elastography of placenta: in vivo quantitation of placental elasticity in preeclampsia
Abstract
Purpose: We aimed to evaluate the utility of shear wave elastography (SWE) for assessing the placenta in preeclampsia disease.
Methods: A total of 50 pregnant women in the second or third trimester (23 preeclampsia patients and 27 healthy control subjects) were enrolled in the study. Obstetrical grayscale and Doppler ultrasonography, SWE findings of placenta, and prenatal/postnatal clinical data were analyzed and the best SWE cutoff value which represents the diagnosis of preeclampsia was determined. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and diagnostic accuracy of preeclampsia were calculated based on SWE measurements.
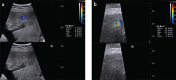
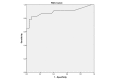
Results: Mean stiffness values were much higher in preeclamptic placentas in all regions and layers than in normal controls. The most significant difference was observed in the central placental area facing the fetus where the umbilical cord inserts, with a median of 21 kPa (range, 3-71 kPa) for preeclampsia and 4 kPa (range, 1.5-14 kPa) for the control group (P < 0.01). The SWE data showed a moderate correlation with the uterine artery resistivity and pulsatility indices. The cutoff value maximizing the accuracy of diagnosis was 7.35 kPa (area under curve, 0.895; 95% confidence interval, 0.791-0.998); sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and accuracy were 90%, 86%, 82%, 92%, and 88%, respectively.
Conclusion: Stiffness of the placenta is significantly higher in patients with preeclampsia. SWE appears to be an assistive diagnostic technique for placenta evaluation in preeclampsia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterizing placental stiffness using ultrasound shear-wave elastography in healthy and preeclamptic pregnancies.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2020 Nov;302(5):1103-1112. doi: 10.1007/s00404-020-05697-x. Epub 2020 Jul 16. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2020. PMID: 32676857 Free PMC article.
-
The role of shear wave elastography in the assessment of placentas in healthy pregnancy women during third-trimester: A preliminary study.J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2022 Feb;51(2):102292. doi: 10.1016/j.jogoh.2021.102292. Epub 2021 Dec 18. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2022. PMID: 34933147
-
Role of Shear Wave Elastography of Placenta in Prediction of Preeclampsia in High-Risk Pregnancy.Ultrasound Q. 2024 Jun 1;40(2):119-125. doi: 10.1097/RUQ.0000000000000662. Ultrasound Q. 2024. PMID: 38193810
-
Review of shear wave elastography in placental function evaluations.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2023 Dec;36(1):2203792. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2023.2203792. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2023. PMID: 37121902 Review.
-
Usage of shear wave elastography for diagnosis of changes of oculomotor muscles in endocrine orbitopathy.Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2019 Spring;75(1):14-24. doi: 10.31348/2019/1/2. Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2019. PMID: 31382752 Review. English.
Cited by
-
Mechanobiological regulation of placental trophoblast fusion and function through extracellular matrix rigidity.Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 3;10(1):5837. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62659-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32246004 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of uterine involution using B-mode ultrasonography, color Doppler and elastography (acoustic radiation force impulse) for assessing postpartum in Santa Inês ewes.Anim Reprod. 2023 Jun 30;20(2):e20220110. doi: 10.1590/1984-3143-AR2022-0110. eCollection 2023. Anim Reprod. 2023. PMID: 37416868 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning Trophoblast Motility in a Gelatin Hydrogel via Soluble Cues from the Maternal-Fetal Interface.Tissue Eng Part A. 2021 Aug;27(15-16):1064-1073. doi: 10.1089/ten.tea.2020.0097. Epub 2020 Nov 20. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021. PMID: 33216701 Free PMC article.
-
A straightforward cell culture insert model to incorporate biochemical and biophysical stromal properties into transplacental transport studies.Placenta. 2025 Jun 13;166:54-61. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2024.09.001. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Placenta. 2025. PMID: 39266436
-
A gelatin hydrogel to study endometrial angiogenesis and trophoblast invasion.Interface Focus. 2019 Oct 6;9(5):20190016. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2019.0016. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Interface Focus. 2019. PMID: 31485309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xiong X, Buekens P, Pridjian G, Fraser WD. Pregnancy-induced hypertension and perinatal mortality. J Reprod Med. 2007;52:402–406. - PubMed
-
- Brown MC, Best KE, Pearce MS, Waugh J, Robson SC, Bell R. Cardiovascular disease risk in women with pre-eclampsia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Epidemiol. 2013;28:1–19. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10654-013-9762-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kuklina EV, Ayala C, Callaghan WM. Hypertensive disorders and severe obstetric morbidity in the United States. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;113:1299–1306. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181a45b25. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gupta LM, Gaston L, Chauhan SP. Detection of fetal growth restriction with preterm severe preeclampsia: experience at two tertiary centers. Am J Perinatol. 2008;25:247–249. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1075034. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cosgrove DO, Berg WA, Dore CJ, et al. Shear wave elastography for breast masses is highly reproducible. Eur Radiol. 2012;22:1023–1032. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2340-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

