Immune checkpoint blockade: a common denominator approach to cancer therapy
- PMID: 25858804
- PMCID: PMC4400238
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.03.001
Immune checkpoint blockade: a common denominator approach to cancer therapy
Abstract
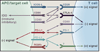
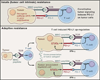
The immune system recognizes and is poised to eliminate cancer but is held in check by inhibitory receptors and ligands. These immune checkpoint pathways, which normally maintain self-tolerance and limit collateral tissue damage during anti-microbial immune responses, can be co-opted by cancer to evade immune destruction. Drugs interrupting immune checkpoints, such as anti-CTLA-4, anti-PD-1, anti-PD-L1, and others in early development, can unleash anti-tumor immunity and mediate durable cancer regressions. The complex biology of immune checkpoint pathways still contains many mysteries, and the full activity spectrum of checkpoint-blocking drugs, used alone or in combination, is currently the subject of intense study.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Baitsch L, Legat A, Barba L, Fuertes Marraco SA, Rivals JP, Baumgaertner P, Christiansen-Jucht C, Bouzourene H, Rimoldi D, et al. Extended co-expression of inhibitory receptors by human CD8 T-cells depending on differentiation, antigen-specificity and anatomical localization. PLoS One. 2012;7:e30852. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barber DL, Wherry EJ, Masopust D, Zhu B, Allison JP, Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ, Ahmed R. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature. 2006;439:682–687. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

